Home >
Erectile Dysfunction >
Suspicion of prostate adenocarcinoma
Suspicion of prostate adenocarcinoma
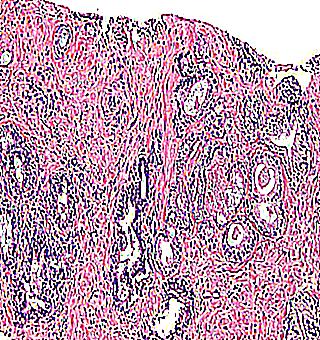
Prostate adenocarcinoma: description, causes, stages, symptoms and treatment
Prostate adenocarcinoma is a serious oncological disease. Previously, it was considered one of the main causes of death among older men. Today, this disease is increasingly being diagnosed at a young age. Is it possible to prevent the development of cancer? How to recognize its manifestations in the early stages?
General information
Prostate adenocarcinoma is a malignant epithelial neoplasm that belongs to oncological diseases. Worldwide, this diagnosis is confirmed annually in 500,000 new patients. Despite the constant improvement of diagnostic and therapeutic methods, mortality from adenocarcinoma is still high. Why? Patients often ignore the initial symptoms of a problem and do not rush to see a doctor for help.
Main causes of disease
Adenocarcinoma develops by tumor invasion into the prostate or migration through the lymphatic ducts. The immediate cause of this disease is known - uncontrolled reproduction of atypical cells. They gradually penetrate into healthy tissues. Atypical elements are formed as a result of genetic mutations. Why this happens, modern medicine can not accurately answer. However, doctors identify a whole group of factors that increase the likelihood of developing the disease:
Other factors common to all forms of oncological diseases also have a certain influence. This is radiation, bad ecology, work in hazardous industries, etc.
How to recognize adenocarcinoma?
The manifestations of this disease cannot be called characteristic. Usually men have symptoms similar to the clinical picture of genitourinary infections. If the tumor is small, it does not make itself felt for a long time. As the neoplasm grows, the patient's condition deteriorates sharply. Here are some manifestations of adenocarcinoma of the prostate:
The initial symptoms of the disease are similar to those recorded in prostate adenoma. Therefore, even at the stage of diagnosis, it is important to differentiate one pathology from another. After the appearance of metastases (stage 4 of the disease), pain discomfort intensifies, swelling of the lower extremities appears. Sometimes paralysis develops against the background of compression of the spine by a tumor.
Types of prostate adenocarcinoma
One of the factors determining the tactics of treatment is the differentiation of adenocarcinoma. This term refers to the degree of maturity of the tumor, the difference between healthy cells and pathological ones. It is used to classify a disease. At the same time, low-, medium- and highly differentiated elements of the neoplasm are distinguished. According to the incidence of incidence, such types of adenocarcinoma are distinguished as:
- small acinar;
- highly differentiated;
- low-differentiated;
- squamous.
Small acinar adenocarcinoma of the prostate is the most common variant of the disease. Its source is the epithelium of the prostate acini. Neoplasms usually develop simultaneously in several places, and then merge together. For treatment, surgical intervention, hormonal blockade of testosterone and radiotherapy are used.
The second most common type of adenocarcinoma is highly differentiated. As a rule, the tumor develops slowly and does not metastasize. Its elements do not differ in structure from normal cells. With timely detection, the prognosis for treatment is favorable.
The rarest and most aggressive form of adenocarcinoma is squamous cell carcinoma. It is characterized by rapid metastasis to the bone. Hormonal therapy and chemotherapy in this form of the disease are often ineffective. Patients are advised to undergo radical prostatectomy.
Poorly differentiated adenocarcinoma of the prostate gland has an average severity. The tumor is characterized by a layered structure, and according to the Gleason scale it corresponds to 8-10 points. The neoplasm quickly grows into neighboring organs.
Disease diagnosis
In European clinics, all men over 45 undergo a mandatory examination to detect prostate diseases. It includes a consultation with a urologist and a blood test for a specific antigen. The latter is considered the most informative test for the early diagnosis of oncology. A high level of prostate-specific antigen in the blood indirectly indicates the presence of a pathological process.
Another indicative method of research is a rectal test. It allows you to assess the state of the body and the degree of its functionality. prostate adenocarcinoma has a positive prognosis only in the initial stages of development. In other cases, expensive and long-term treatment is required.
If this ailment is suspected, it is additionally prescribed:
In many modern clinics, a special rectal sensor is used to assess the condition of the prostate. It allows using a quick-firing needle to take material for research. This device is inserted into the rectum, and the results of the procedure are displayed on the monitor screen.
Stages of disease development
Before starting treatment, it is necessary to determine what type of acinar adenocarcinoma of the prostate gland (what it is is described a little higher), as well as the degree of the pathological process. The development of this disease occurs in the same stages as other forms of prostate cancer. The only difference is the prognosis for a complete cure. For example, squamous forms pass all stages of growth rapidly. Moderately differentiated adenocarcinoma of the prostate is also characterized by a rather high rate of development. However, their discovery at the initial stage of development is considered a real miracle. If you start treatment in a timely manner, you can hope for a favorable outcome.
What are the stages of prostate adenocarcinoma? There are four of them in total:
Basic principles of therapy
You can defeat adenocarcinoma only at the initial stage of the disease. With adequate and complete therapy, it is possible to stop the symptoms and slow down the progression of the pathological process at any stage. The choice of a specific treatment strategy depends on the degree of spread of the tumor. Some options for the location of the neoplasm allow an operation to excise the gland and regional nodes. Today, doctors are trying to use minimally invasive techniques that do not require a long rehabilitation period. Localized adenocarcinoma of the prostate often requires expectant management and constant monitoring. Survival prognosis does not always improve with active therapy.
Conservative and surgical treatment of adenocarcinoma
If the tumor is available for removal, the patient is scheduled for prostatectomy surgery. Currently, it is performed using a laparoscope or a robotic assistant. After a prostatectomy, a long rehabilitation period is required. It includes measures to restore the functions of the pelvic organs, male potency (if this is still relevant).
In the later stages, treatment is supplemented with hormonal drugs and radiation therapy. The latter has several options. The radiation source can be outside or inside (introduction of a capsule with radioactive isotopes of iodine). When prostatectomy is contraindicated, it is replaced by cryotherapy. During this procedure, the tumor is frozen, as a result of which the malignant cells are destroyed.
Acinar adenocarcinoma of the prostate gland of 7 points or higher in elderly patients is usually not amenable to surgical intervention. In this case, dynamic monitoring and palliative measures are prescribed.
What is the outcome of a diagnosis of prostate adenocarcinoma? The prognosis for this disease largely depends on the stage of development of the pathological process, the age of the patient and his general condition. In the early stages, it is assessed as conditionally favorable. Unfortunately, adenocarcinoma at the initial stages of development does not show a bright clinical picture. Therefore, patients do not rush to see a doctor for help. Most of them notice the problem at the 3-4th stage, when metastases are already appearing. In this case, the disease is irreversible.
Conclusion
Oncological diseases in the modern world are increasingly becoming a cause of early death. In the representatives of the stronger sex, adenocarcinoma of the prostate gland is most common. Treatment of this pathology is long and very difficult. Diagnosis of the disease in the later stages usually ends in a quick death. To prevent the development of such an insidious disease, it is necessary to adhere to a healthy lifestyle and regularly undergo preventive examinations. Stay healthy!
Prostate adenocarcinoma: treatment and prognosis
Diseases such as prostatitis and prostate adenoma are known to many men firsthand, because they are very common pathologies. According to statistics, every 2 patients over 60 suffer from prostatitis and benign tumors of the prostate. The latter can become malignant (become malignant), then prostate cancer is diagnosed.
Two types of malignant tumors can form in the prostate region: sarcomas and carcinomas. Adenocarcinoma occurs in 90% of all cases, while more than 50% of men over 70 years of age get sick, but the pathology manifests itself to varying degrees in each patient.
Causes of prostate adenocarcinoma
The exact cause of prostate adenocarcinoma has not yet been established. It is known that this disease is polyetiological, that is, a tumor occurs under the influence of various negative factors.Oncologists identify the following predisposing factors:
- Age over 65-70 years old. Age-related changes occur in the body, which can provoke the formation of adenocarcinoma.
- The disease affects black men more often than whites and Asians.
- Influenced by hereditary predisposition. If the father or grandfather had adenocarcinoma, or the mother had breast cancer, then the risk of getting sick is much higher.
- The risk is increased in men who eat fatty foods, especially animal fats.
- Hormone replacement therapy with testosterone can also trigger the growth of adenocarcinoma.
- Bad habits such as alcoholism and smoking increase the risk of prostate cancer.
- It is known that poisoning with chemicals, the use of carcinogens, exposure to radiation, and even poor ecology in the area where the patient lives can become a tumor provocateur.
Unfortunately, even excluding all these factors, it is impossible to accurately prevent the development of prostate adenocarcinoma.
Symptoms of prostate adenocarcinoma
Adenocarcinoma is characterized by slow development, while the tumor does not manifest itself in any way. The first signs of cancer include symptoms of prostatitis, such as urinary retention, weakening of erection. Since patients with adenocarcinoma usually already have a history of prostatitis, they do not pay any attention to these symptoms.
IMPORTANT TO KNOW! 80% of prostate diseases are asymptomatic, and this rapidly leads to dire consequences. If you need powerful protection against prostatitis, experts recommend. Read more >>
Signs of adenocarcinoma of the prostate:
- Urinary disorders: intermittent stream, frequent urge, difficulty urinating.
- Pain and burning in the lower abdomen, which increase during ejaculation and urination.
- Blood in the urine.
- Erectile dysfunction.
- Dramatic weight loss (typical of late stages of adenocarcinoma).
If adenocarcinoma metastasizes, then patients begin to complain of pain in the back and ribs. At the last stage of the disease, lymphostasis develops in the legs, signs of anemia, severe exhaustion of the body and weakness appear.
Cancer diagnosis
It is very important to diagnose adenocarcinoma in a timely manner. But since the disease in the initial stages is asymptomatic, only a doctor can detect it during the examination.
To do this, you need to visit an andrologist's office at least once every 6 months. The specialist palpates the prostate through the rectum. Thus, it can detect seals, a change in the size of an organ, but it will not work to distinguish a malignant tumor from a benign one.
If you suspect the formation of adenocarcinoma, the specialist is assigned the following studies:
- Prostate specific antigen test.
- Biopsy of the prostate.
- Ultrasound of the prostate.
- MRI
- Testosterone test
- X-ray of the pelvis.
- Radioisotope study.
The examination is prescribed by the doctor on an individual basis.
Classification of prostate adenocarcinoma
There are the following types of adenocarcinoma:
- Acinar adenocarcinoma - the acinar epithelium of the anterior part of the prostate is affected.
- Small acinar - difficult to diagnose, since the tumor foci are very small, but the pathology is common.
- Large acinar - very rare, less than 5% of cases.
- Poorly differentiated - cancer develops very quickly, this is the most dangerous type of adenocarcinoma.
- Highly differentiated - the cells are slightly affected, but the tumor reaches a large size.
Depending on the neglect of the disease, prostate adenocarcinoma is divided into the following stages:
- Prostate cancer of the first degree does not show any symptoms, and the pathology cannot be detected by palpation. The only effective diagnostic method is prostate biopsy.
- Adenocarcinoma grade 2 is characterized by spread within the gland. On palpation, the doctor can detect neoplasms, the tumor can be seen on ultrasound.
- Grade 3 adenocarcinoma extends beyond the prostate, accompanied by pain.
- Stage 4 prostate cancer is fatal, the tumor spreads to the pelvic organs and bones. Adenocarcinoma with metastases has the worst prognosis.
Accordingly, the sooner treatment begins, the more favorable the prognosis for the patient.
Prostate adenocarcinoma treatment
The following methods are used to treat adenocarcinoma:
- Chemotherapy;
- Radiation therapy;
- Surgical operation;
- Hormonal therapy.
Radiotherapy is usually used in cases where surgery is contraindicated for the patient.But the most effective method of treatment is prostatectomy, that is, the complete removal of the gland. The doctor also removes the seminal vesicles, the prostatic urethra and the bladder neck.
Sometimes, removal of the testicular parenchyma is also recommended to stop the production of testosterone and prevent recurrence and tumor growth. For the same purposes, hormonal preparations of progesterone and estrogen can be used. They suppress the production of testosterone and inhibit the growth of prostate adenocarcinoma.
USE FOR PREVENTION! An innovative biologically active drug that naturally restores the health of the prostate gland. Experts recommend! Read more >>
For grade 3 and 4 adenocarcinoma, chemotherapy and radiation therapy are used. A method called brachytherapy is often used. In this case, a radioactive drug is injected into the prostate, which locally irradiates the tumor, causing the death of cancer cells.
Other therapies for adenocarcinoma are also being explored:
- Cryotherapy - treatment of a tumor with liquid nitrogen.
- Laser therapy - burning a tumor with a laser beam.
- Focused ultrasound therapy.
- Hyperthermia.
The last three methods involve burning cancer cells. All these methods of treating prostate adenocarcinoma are innovative and non-invasive; they are not yet used in all clinics in the country.
Prevention
Prostate adenocarcinoma is a very serious and life-threatening disease. To reduce the risk of developing cancer, you need to eliminate the factors that provoke it, following these recommendations:
- Eat right, do not abuse animal fats, refuse food with preservatives, dyes and other harmful additives.
- Quit alcohol and smoking.
- Have sex regularly to reduce the risk of developing congestive prostatitis.
- Protect yourself from genital infections, always protect yourself.
- Do not contact with chemicals, radiation. If necessary, you need to work in a protective suit.
- Do not take testosterone supplements without a doctor's prescription for muscle gain.
- Regularly examined by an andrologist for timely diagnosis of prostate pathologies.
A healthy lifestyle and regular consultations with a doctor can significantly reduce the risk of developing prostate adenocarcinoma.
The prognosis for prostate adenocarcinoma depends on the type and stage of pathology. A differentiated form of the disease with timely diagnosis is successfully treated. Poorly differentiated and undifferentiated adenocarcinoma often provokes a fatal outcome, but with timely diagnosis, the chances of a five-year survival are quite high.
Conclusion
Adenocarcinoma is a very insidious disease that does not manifest itself for a long time. If a man has already been diagnosed with prostatitis, this does not mean that he does not need to go to the doctor. In any case, it is necessary to be regularly examined in order to detect the tumor in time and begin its treatment. Otherwise, the probability of death is high.
Treatment of prostate adenocarcinoma: effective methods
Prostate adenocarcinoma is one of the most common types of malignant epithelial formation. It is classified as cancer. It occurs in 90% of cases among patients with prostate cancer. Other types of cancer are diagnosed less frequently. Symptoms at an early stage are practically absent, which makes self-diagnosis of the disease difficult.
Acinar adenocarcinoma of the prostate
What is acinar adenocarcinoma of the prostate? This is a histological feature of prostate cancer, the most common being adenocarcinoma. It is divided into large-acinar, small-acinar.
Small acinar - the most common type of adenocarcinoma. It occurs in 95% of cases of prostate cancer. Large acinar adenocarcinoma has an atypical structure, as well as a high malignancy of the tumor. Forecasts with such a diagnosis are usually disappointing.
Acinar adenocarcinoma in most cases is diagnosed in men over 50 years of age. The disease first affects the acinar epithelium of the peripheral zone of the prostate. Usually reduces the patient's life expectancy by 10 years.
Treatment of acinar adenocarcinoma of the prostate in the third and fourth stages of the disease is hampered by the rapid growth of the tumor.
Causes, stages, symptoms of adenocarcinoma
Adenocarcinoma is preceded by the following conditions:
- atypical hyperplasia, in which tissue growth and changes in its structure are observed;
- Intraepithelial neoplasia, in which new pathological cells and tissues are formed.
Pathology stages
The first stage is difficult to diagnose, structural changes are minimal and are detected only during a biopsy. Analyzes at this stage are usually not informative.
In the second stage, some parts of the gland and membranes are affected. Detectable during research due to the appearance of tumor markers in the blood, urine.
The third stage is characterized by active tumor growth. Cancer cells affect the vesicles of the prostate gland and can affect neighboring organs.
Metastases spread to neighboring organs of the genitourinary and digestive systems, sometimes affecting almost all organs.
Causes of the disease
Many factors influence the development of adenocarcinoma. Most common:
- senile changes in the body;
- hereditary predisposition;
- chronic cadmium poisoning;
- overweight;
- XMRV virus;
- hormonal imbalance;
- chronic inflammatory diseases.
Symptoms
Pathology may indicate:
- frequent urge to urinate;
- discomfort, pain in the groin area;
- after urination, there is a feeling of incomplete emptying of the bladder;
- impeded urine outflow;
- blood in urine, semen;
- frequent urinary tract infection;
- prostate enlargement;
- urination is performed only after a strong tension of the abdominal muscles.
The last stages of the development of the disease are characterized by pain in the anus, legs while walking, a feeling of heaviness in the pelvis. This indicates the growth of the tumor outside the prostate. Due to the spread of metastases, the lymph nodes in the groin may swell, and severe pain will be felt in the bones.
Prostate adenocarcinoma: treatment
Early stages allow you to cure the disease without surgery. In later cases, medical and surgical treatment is usually used. Commonly used treatments for adenocarcinoma:
- prostatectomy - a method of removing a tumor;
- endoscopic prostatectomy;
- radiotherapy;
- cryotherapy;
- chemotherapy;
- hormone therapy.
Prostatectomy
This is a surgical intervention with the complete removal of the prostate gland. The operation is performed under general anesthesia, preoperative preparation, as well as postoperative support, and a rehabilitation period are necessary. The most successful stages for the operation are the first, second and third stages without metastasis outside the prostate gland.
- intolerance to anesthesia due to diseases of the heart, blood vessels;
- blood clotting disorder.
During the operation, the gland, its capsule, adjacent tissues, and lymph nodes are removed.
Laparoscopic prostatectomy
Laparoscopic prostatectomy using endoscopic techniques is considered one of the modern methods. Also, surgery is carried out using the Da Vinci operating complex.
During the operation, the surgeon makes three small incisions in the anterior abdominal wall, injects a gas mixture and an endoscope with a video camera and manipulators that display the image on the monitor.
This operation is less invasive and less traumatic than open surgery. Laparoscopy allows you to save the nerve bundles that control urination and urinary retention, sexual arousal, erection.
After an open prostatectomy, the patient must stay in the hospital for 2-3 weeks. After the laparoscopic method - 10 days. In the first days after the operation, urination occurs through a urinary catheter. The patient is also prescribed antibiotics to prevent infectious complications and a diet aimed at unloading the intestines, preventing constipation, gas formation.
Walking is allowed on the second day after the operation. After 3-6 months, endurance and former activity gradually return.
In order to strengthen the muscles of the pelvic floor, to restore the general condition, the patient should do therapeutic exercises. With the permission of a doctor, you can do Kegel exercises.
Cryotherapy
During cryotherapy, alternating exposure to low and high temperatures occurs on the affected prostate tissues, leading to their death. When frozen, the cell membrane is pierced by ice crystals, damaging the blood supply, the supply of tissue with oxygen, and nutrients.
The procedure is performed under local anesthesia, as well as general anesthesia. Cryoprobes are inserted into the prostate and are monitored by transrectal ultrasound. Through them high and low temperatures are supplied. The procedure is controlled by a computer with a monitor.
It is often impossible to exclude the nerves that are responsible for erection from the freezing area during cryotherapy, which leads to erectile dysfunction. Six months after the procedure, 80% of men suffer from a lack of potency, after 2 years the percentage drops to 76%. In 5% of cases, cryotherapy can lead to urinary incontinence.
Hormonal therapy
Treatment involves taking drugs that suppress hormone levels in the body or block their effect on cancer cells. It is also possible to remove organs that normally synthesize such hormones (orchidectomy): 90% of testosterone is synthesized by the testicles. But usually men prefer drug therapy.
Therapy is divided into:
- adjuvant - antihormonal drugs are prescribed in the postoperative period to prevent the recurrence of the disease;
- neoadjuvant - hormonal drugs are given before surgery to reduce the size of the tumor.
In case of adenocarcinoma, hormonal therapy is connected in the later stages as a background during irradiation.
The prospect of recovery depends on the stage of the adenocarcinoma. The appearance of the slightest alarming signs is a reason for an urgent consultation with a doctor. The first two stages respond well to treatment, and there is also a high probability of maintaining labor qualities and erectile function. Advanced stages with signs of damage to internal organs can lead to death.



























