ADS:
Cephalexin Interactions with Alcohol
The potential interactions and precautions associated with alcohol consumption should be taken into account when taking cephalexin, a bacterial infection medication, due to its high sensitivity. Cephalexin is an antibiotic that works by disrupting the formation of bacterial cell walls, which in turn leads to cell death and ultimately eliminates the infection. Even though it is not completely safe to consume, the medication can also result in adverse effects that could affect its effectiveness or cause significant health problems when consumed with alcohol.
Bronchitis, pneumonia, skin infections, and UTIs are among the most frequently treated by Cephalexin. While treatment is typically good, patients frequently ask if they can indulge in some wine or beer. The cephalexin-alcohol interaction will be the subject of this article, which will also discuss potential risks and safety precautions for safe treatment.
The impact of cephalexin on the interaction with alcohol can be influenced by various factors, including age and weight as well as liver function or medical history. Prior to consuming antibiotics, patients should inform their healthcare provider about their alcohol intake and avoid using it. Sometimes, the physician may modify the amount of cephalexin or prescribe alternative drugs that are less risky to take when consuming alcohol with other substances.
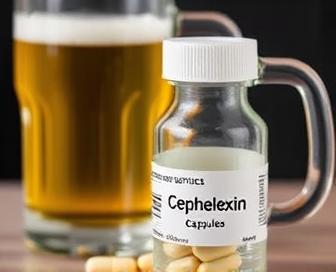
The main issue with cephalexin when drunk is the elevated risk of negative gastrointestinal reactions, including nausea, vomiting, and diarrhea. Some cases of this mixture may lead to severe consequences such as liver impairment or blood loss, which may require hospitalization.
Taking cephalexin without alcohol may result in a less severe interaction for different individuals. Some individuals with moderate drinking (1-2 standard drinks per day) can tolerate the effects without significant complications, whereas excessive or binge alcohol consumption may lead to serious health consequences.
The safety and efficacy of cephalexin-alcohol treatment depend on knowing how cefexine interacts with alcohol and taking appropriate precautions. Just as with medications, it's important to follow your doctor's advice and never mix anything with alcohol (e.g., an overdose of Ritalin)—or else, you may end up drinking heavily or mixing too much with something like vodka or wine. Awareness of these possible connections can aid patients in participating fully, promoting the healing process, and helping to reduce the risk of side effects.
Cephalexin: Understanding Its Interactions
Various medications and substances can interact with Cephalexin, a widely used antibiotic for treating bacterial infections. The impact of cephalexin may either be minimal due to these interactions or significantly higher in terms of toxic effects. The patient undergoing this treatment must be cognizant of any potential drug interactions, dietary restrictions, and other precautions.
Interactions with Medications
The effects of Cephalexin can be observed on multiple medications.
- Blood thinners (warfarin): Increased risk of bleeding.
- Probenecid: reduced excretion and increased toxicity of cephalexin.
- Side effects of Azithromycin, Clarithromy, and Epsteinon.
- Methotrexate can lead to toxicity.
- Norfloxacin and other fluoroquinolones exhibit reduced efficacy in cephalexin.
- Oral anticoagulants (acenocoumarol): Increased risk of bleeding.
- Efficacy of hormonal birth control could decline.
Food and Beverage Interactions
Specific types of food and drink can alter the function of cephalexin or trigger potential adverse reactions.
- The calcium binding in milk and yogurt causes a decrease in absorption.
- Antacids containing aluminum (e.g., Maalox): Delayed excretion and increased toxicity.
- Side effects of antihistamines (diphenhydramine) may be worsened.
- High levels of caffeine in beverages can result in side effects such as agitation, anxiety, and insomnia.
- Alcohol: Enhanced potential for liver damage.
Precautions and Monitoring
to reduce risks of cephalexin interactions,
- Avoid consumption of aluminum-containing antacids and dairy products during treatment.
- Inform your doctor about all medications, supplements, and herbal remedies you use.
- Avoiding moderate alcohol consumption can lead to damage to the liver.
- If you are on blood thinners, look for signs of bleeding, such as bruising or developing petechiae.
| Drug/Agent | Interaction Type | Description |
|---|---|---|
| Blood Thinners (e.g., Warfarin) | Potential for increased bleeding risk | Closely monitor INR levels and adjust warfarin dosage as needed. |
| Antacids containing Aluminum (e.g., Maalox) | Delayed excretion and potential toxicity increase | Avoid antacid use within 2 hours of cephalexin dosing. |
| Norfloxacin and other Fluoroquinolones (e.g., Ciprofloxacin) | Potential reduction in cephalexin efficacy | Monitor infection response and adjust antibiotic regimen if necessary. |
To ensure safe and effective treatment, it is essential to comprehend the interactions between cephalexin and medications, foods, and beverages. Always seek advice from your doctor before taking or modifying any medication regimen, particularly when using cephalexin.
Alcohol Consumption Risks
The antibiotic cephalexin is used to combat bacterial infections. As with any drug, risks come with the risk of drinking alcohol. The interactions should be understood before deciding whether to drink alcohol while on cephalexin.
- Dizziness, drowsiness, and nausea are potential side effects of Cephalexin. These symptoms, such as headaches, stomach upset, and fatigue, may be amplified or replaced by alcohol.
- The liver is responsible for the impairment of Cephalexin. The consumption of alcohol beyond its normal limit can cause this organ to become irritated and lose the ability to break down cephalexin. The risk of adverse reactions may be raised by the presence of an increased quantity of the antibiotic in your bloodstream.
- Against bacteria, Cephalexin targets immune compromised cells. Drinking alcohol can hinder the immune system and make it more difficult for your body to recover from infections, potentially decreasing its ability to treat certain types of infections like cephalexin.
- Enhanced risk: Both cephalexin and alcohol can cause stomach pain, which may lead to heartburn as well as nausea, vomiting (including passout), along with diarrhea. Combining these substances may increase this risk significantly.
Remember to follow your doctor's advice not to drink when taking cephalexIN. Broadly, abstain from drinking or engaging in any other activity during the use of this antibiotic to minimize the risk of harmful interactions and maximize its effectiveness in combating bacterial infections.
Antacids and Proton Pumps
Some drugs that Cephalexin can mix with may also change the levels of stomach acids. Tums, Rolaid, and Maalox are antacids that are often prescribed to neutralize excess acid in the stomach. Properly regulated proton pump inhibitors (PPIs), such as omeprazole (Prilosec) and lansopraclomid (Prevacid), both reduce stomach acid production.
Antidepressants, like cephalexin, can reduce their penetration into the body when combined with other drugs. Hence, this may reduce the effectiveness of treating bacteria. Precisely because of its higher interaction with PPIs, cephalexin is the opposite. They can also increase the absorption of cephalexin by reducing the levels in the stomach, which in turn increases the concentration of cetacids.
Even though cephalexin may provide benefits, it's important to keep a close eye on the use of PPIs and cefloxynin together. Some PPIs can cause additional side effects, such as bone fractures or infections caused by Clostidicule dissipation (C. diff). Additionally, high doses of PPIs may interact with other medications taken concurrently.
Always seek advice from your doctor before using cephalexin with antacids or PPIs. They can help determine the appropriate dosage and monitoring plan based on individual circumstances. The risks associated with these treatments are often lessened under appropriate guidance.
Methotrexate Combination Concerns
The effectiveness of methotrexate may be reduced if it is taken in combination with other medications or substances, which can lead to an increased risk of side effects. Among these, cephalexin, another antibiotic from the cephalocarpimylazine family (often called ceftoxin), may interact with methotrexate.
It has been established through strong evidence that cephalexin can dramatically elevate serum levels of methotrexate by preventing it from leaving the body. Due to its high toxicity, there are serious adverse effects such as bone marrow suppression, liver damage (leading to senescence), and bleeding (which can be fatal).
Research has indicated that the risk of severe adverse effects can be raised by as much as 50% due to the concurrent administration of methotrexate and cephalexin. When taking both medications at the same time, patients may experience symptoms such as fever and chills, fatigue, and shortness of breath. Sepsis or organ failure can be caused by this interaction in severe cases.
The prescribing of cephalexin for methotrexate treatment requires heightened caution from healthcare professionals. The most important step is to closely monitor patients for signs of toxicity and consider other antibiotic options that are less likely to interact with methotrexate.
It is important to discuss with your doctor if you have received both methotrexate and cephalexin and he/she hasn't told you whether your condition will change or if you show up with side effects. In order to minimize the potential harm caused by this potentially harmful interaction, it is important to carefully consider the benefits and risks of these medications.
Kidney Function and Dosage Adjustments
If you are taking Cephalexin, keep in mind that it's for your kidneys and that the medication is excreted from your bladder or bowel. Dozens of the drug may need to be adjusted if patients have an impaired kidney and want to avoid having it stored in their system for an extended period. Uncontrolled dosing can result in severe toxicity and potentially fatal side effects.
Patients who have a weaker kidney should seek medical advice before taking Cephalexin. In order to minimize risks of impaired excretion, the doctor will adjust the dose as needed and consider the individual's current renal status. It's also important for these people to monitor their urine output closely and immediately report any changes to their doctor.
A separate dosing regimen is recommended for dialysis patients under close medical supervision. Keeping Cephalexin levels within therapeutic ranges can be achieved through regular blood tests. If you're taking other medications that may impact kidney function, such as diuretics or blood pressure medications, it's essential to discuss these with your doctor before starting Cephalexin.
If you observe any indications of an allergic reaction or alteration in your urine while on Cephalexin, make sure to consult a doctor immediately. It's also important to follow the dosage instructions carefully and not stop taking the medication without consulting your healthcare provider first – even for mild side effects like nausea. Your doctor should provide you with personalized advice if you're uncertain about your kidney function and feel that Cephalexin could be harmful.
Cephalexin can interact with other antidepressants like Lexapro in some cases. If you're unsure about potential interactions or have questions about your medication regimen, don't hesitate to ask your doctor for clarification. Your healthcare provider and you will work with you to monitor your kidney function and, if necessary, provide an effective approach to managing infections while minimizing the risks associated with Cephalexin use.
Monitoring for Side Effects
The side effects of Cephalexin, like any antibiotic, can vary in their severity. Monitoring your body's reaction to the medication during treatment is vital. Keep an eye out for changes in taste, stomach discomfort, or dizziness caused by a food allergy; also watch out when you have: low temperature, fever (high), chills and chilling, nausea, and vomiting from fever followed by any joint pain or soreness.
If you notice any of these side effects, please notify your doctor. While mild symptoms may not affect the rest of the body, they can cause severe symptoms that require adjusting to your current treatment plan or sometimes necessitating hospitalization.
| Common Side Effects | Severity Level | Action Required |
|---|---|---|
| Diarrhea, nausea and vomiting, headache, dizziness | Mild to moderate | Monitor closely, may require over-the-counter medication for symptom relief |
| Rash or itching, stomach upset, fever, chills | Moderate to severe | Contact your healthcare provider for guidance on managing symptoms and potential treatment adjustments |
| Allergic reactions (hives, difficulty breathing, rapid heartbeat) | Severe | Seek immediate medical attention in an emergency situation |
Rarely, cephalexin can cause more serious side effects, such as liver damage or seizures. In case of emergency, contact medical professionals if you encounter any unusual symptoms or your condition worsens while using this medication.
We recommend you read it
Find out how to pronounce Cephalexin with this informative page.
- See the Cephalexin 500mg price here.
- Learn how much Cephalexin is necessary for a tooth infection with this informative site.













