Home >
Erectile Dysfunction >
Chronic prostatitis symptoms
Chronic prostatitis symptoms
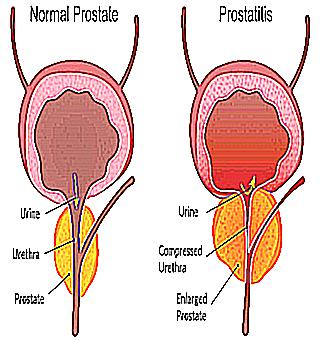
Chronic inflammation of the prostate may be the result of the absence or untimely treatment of the acute stage. However, in many men it develops immediately and is characterized by "blurred" symptoms. Among the main features are:
- low-grade fever (occasionally)
- mild pain in the perineum
- discomfort during urination
- scanty discharge from the urogenital canal during bowel movements
In general, the clinical picture changes over time, differs in intensity in different patients and can turn into a latent form when trying to self-medicate. Symptoms of a chronic disorder may include a burning sensation in the urethra, pressure in the perineum, dysuria, impaired sexual function, and general fatigue. Against the background of problems with potency, mental depression, irritability and anxiety arise. Fear of impotence leads to the development of complexes, but at the same time, most men tend to postpone going to a urologist because of a sense of shame. Primary chronic prostatitis develops over a long period. Blood congestion in the capillaries (prostatosis) provokes the initial stage of non-bacterial inflammation, which leads to the appearance of the disease. In infectious etiology, the cause of the disease is a chronic inflammatory process against the background of infection with Trichomonas, ureaplasma, chlamydia or gonococcus. The primary infection masks the signs of prostatitis, and treating it does not correct the inflammation of the prostate. Often, the addition of a concomitant problem remains invisible for a man. Let us consider in detail the three main symptoms of chronic prostatitis:
- Urinary disorder (dysuria). The inflammation increases the volume of the prostate gland, which causes the ureter to be compressed. With a decrease in its lumen, there are frequent urges to urinate and a feeling of not completely emptying the bladder. Dysuric disorders in many men occur in the early stages of prostatitis. The compensatory mechanism during this period is manifested in hypertrophy of the muscles of the bladder and ureters, which reduces the symptoms of dysuria, but with the development of inflammation, they increase again.
- Pain syndrome. There are no pain receptors in the tissues of the prostate. Pain occurs when the inflammatory process spreads to other organs of the small pelvis and their nerve pathways. The sensations range from weak and aching to very intense, which interfere with the night's rest. Increased discomfort occurs with ejaculation, sexual abstinence, or excessive sexual activity. Pain is given to the perineum, sacrum, scrotum and sometimes to the lumbar region.
- Violation of potency. Lack of treatment in the early stages of prostatitis can lead to dyspotentia, when a man has frequent nocturnal erections, deterioration in the quality of orgasm and accelerated ejaculation. In different patients, these signs appear with different intensities. Premature ejaculation occurs due to a decrease in the excitability threshold of the orgastic center. In this case, the patient has painful sensations, which leads to the development of pain expectation syndrome and a gradual refusal of sexual activity. In the absence of a comprehensive treatment with the study of the mental factor of the disorder, sexual dysfunctions are increasingly aggravated. Ignoring the need to seek medical help for prostatitis often results in impotence.
The degree of sexual dysfunction varies depending on individual factors. Some men are so afraid of erectile dysfunction that their disturbances arise more from suggestion than from objective physiological factors. In particular, psychogenic dispotency is observed precisely with increased anxiety and obsessive complexes. The very thought of possible male health disorders is hard for such patients. This greatly affects their character and communication with others. Irritability, hypochondria, grossness and depression appear.



























