Home >
Erectile Dysfunction >
Cramps and painful symptoms in the urethral canal after urination
Cramps and painful symptoms in the urethral canal after urination
Pain in the urethra in men with cuts and other discomfort is of a peculiar nature. Unpleasant symptoms may occur during urination, after urine drainage, or constantly.
What makes you feel uncomfortable
Resi in the male urethra, as well as in the female, have the same reasons. Gender differences have little or no effect on differences in symptom factors.
This is usually:
- Inflammatory process of the urinary canal - nonspecific urethritis. The disease can be triggered by enterococcus, Haemophilus influenzae, staphylococcus, Klebsiella, pathogenic fungi.
- Infected specific flora - mycoplasmos, Trichomonas, gonococcus, chlamydia.
- Injury during medical examination (instrumental examination of the urethra).
- Radiation or toxic intoxication.
- Weakened immunity.
All these reasons provoke pathologies in the urethral tissues with the occurrence of focal inflammation.
The urethra of the female body is an order of magnitude shorter, but wider than the male urethral canal. In women, this pathology is more common.
Resi, pain in the urethra in men occurs in the presence of several reasons. For example, when catheterization was performed on a patient with a weakened immune system.
The urethral canal may hurt after the passage of stone formations.
Etiology of urethritis
Often, pain in the urethra occurs during the inflammatory process. There is an infectious and non-infectious pathology. Infectious urethritis can be provoked by cocci, fungus, gonococcus, Escherichia coli, mycoplasmosis, chlamydia.
The disease is secondary and primary. Secondary pathology can be triggered by other diseases (cystitis, prostatitis, vesiculitis). Since the female urethral canal is shorter and wider, microorganisms reproduce there worse.
Female pathology has a number of reasons:
- catheterization;
- infection through unprotected sex;
- poor quality hygiene procedures;
- irritation of the mucous membrane after gels, soaps;
- germs from neighboring organs.
Symptoms for acute urethritis include:
- pain in the urine channel during urine excretion;
- inflammation;
- redness;
- traces of pus in the urine;
- itching;
- burning sensation;
- Sometimes secretion with pus is noted.
Urea inflammatory process
When the urethra hurts in females and males, this indicates an inflammation of the bladder. Harmful bacteria penetrate the urethra, blood, lymph. The most common agent is Escherichia coli.
The urine can become inflamed for some reason:
- hypothermia;
- chronic infectious diseases of the genitourinary system;
- pathology of the urinary mucosa;
- hormonal disorders;
- pathological failure of the central nervous system;
- medical procedures (catheterization, cystoscopy);
- chemical intoxication of the body;
- frequent colds, respiratory diseases;
- impaired microcirculation;
- physical inactivity;
Acute cystitis at a young age can be triggered by neglect of the rules of intimate, hygienic procedures. In acute cystitis, pain occurs when urinating, frequent urge to use the toilet (25-30 times), painful sensation in the pubic area. Unpleasant symptoms most often appear after sexual intercourse. The spasmodic sphincter and severe pain reflexively stop urination.
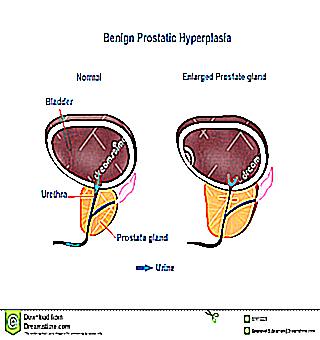
Pain in the inflammatory process of the prostate
Painful syndrome in the urethral canal warns of prostatitis. This is the most common disease among the male population. Most often, pathology pursues men aged 28-47 years. Often, due to untimely treatment started, the disease from an acute form turns into a chronic one.
Acute catarrhal process has a milder course. When it is noted painful urination, increased urge, especially at night, a feeling of heaviness in the middle.
Follicular prostatitis is caused by difficult urination, pain during bowel movements, fever, pain in the perineum, radiating to the genitals and anus.
In a difficult situation, there is an acute retention of urine, a deteriorated general condition. In acute prostatitis, pain appears in the urethral canal.An outbreak of prostatitis in men is possible against the background of the impossibility of regular intercourse for various reasons, unprotected sexual intercourse and intimacy with partners in whom he is not sure, physical inactivity, the use of a catheter, the presence of cracks in the anal canal.
Additional causes of pain when emptying urine
Pain syndrome can provoke non-infectious pathologies. Such pathologies include diseases of gout, tumors, urolithiasis, pubic lice. The main causes of pathologies are the use of an alkaline detergent, soap, a condom with a lubricant, and powders. Painful syndrome is similar to allergic reactions. Sometimes patients feel renal colic, with sharp, acute symptoms, radiating to the groin area, genitals. With urolithiasis, renal colic is the most common manifestation.
Feelings of soreness are triggered by stones in the urinary tract or urethral canal. When the urea is emptied, sand and stones are excreted through the urethral canal. This phenomenon injures the mucous layer of the urethra.
Urolithiasis is provoked by metabolic disorders.
However, there are predisposing factors:
- poor nutrition;
- inflammatory processes in the urinary and reproductive system;
- injury;
- gout;
- harmful work.
When a third of the urea is blocked at the bottom of the organ, the symptoms resemble acute cystitis and urethritis.
Diagnostics and therapy
Treatment of pathologies in which a painful outflow of urine occurs should occur under the supervision of a urologist. The scheme of therapeutic therapy is selected according to the clinical picture of the patient, in each individual case, the treatment is different. The disease is first diagnosed. To do this, the doctor examines the patient, takes anamnesis, and takes swabs from the urethral canal. The study of urine is carried out on 600 ml of urine. Additionally, you may need ultrasound examinations of the prostate gland, kidneys, general blood and urine tests, cystoscopy of the ureters.
To determine the disease for infection, it may be necessary to study the bacterial culture. Women are referred to a gynecologist for examination. If urolithiasis is detected, conservative or surgical treatment may be prescribed.
With conservative treatment, a dietary ration is recommended, the use of medicines (Phytomedics, Allupurinol, Hypothiazide). The choice of the drug depends on the type of stone formations. The treatment regimen provides for the use of physiotherapy procedures.
Large stones are promptly removed or lithotripsy is performed. Some patients receive advice on the use of antibacterial agents. Infectious inflammation of the prostate can be cured with antimicrobial drugs, medications, antispasmodics (No-shpa, Drotaverin), pain relievers, rectal suppositories. In case of remission, physiotherapy procedures are performed. With congestive prostatitis, you should normalize your sex life, avoiding promiscuous sexual intercourse.
If a tumor is detected, it is possible to carry out surgery, radiation therapy, chemotherapy. When pain in the urethral canal is provoked by fungal infections, antifungal medications are used (Ketaconazole, Itraconazole). When the painful syndrome does not disappear for a long time, you should consult with your treating urologist.
Medical therapy is necessary at the first sign of discomfort (slight burning sensation). This will avoid complicated situations. The initial form of any disease is treated very quickly, in an advanced stage - therapeutic therapy has a longer period, with considerable financial costs.



























