Home >
Erectile Dysfunction >
Excision of the prostate
Excision of the prostate
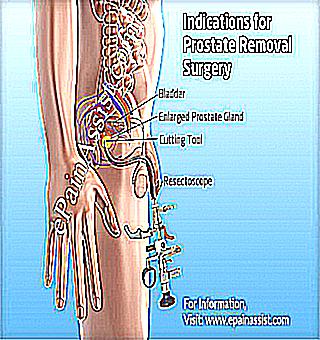
The prostate is a vulnerable organ of the male reproductive system. Pathologies of the prostate gland in men threaten the general health of the body. Therapeutic therapy can be drug and operational.
The operative technique of the prostate is a partial removal or complete excision of the glandular organ. Removal of the prostate gland can be recommended by a specialist, both in the oncological process and in adenoma (benign formation).
Definition of prostate adenoma
Another name for prostate adenoma is hyperplasia. This disease is caused by single or multiple nodular formations, which can increase in size over time. Adenoma is the most common pathology in the male half of humanity after the age of 45.
Benign formations are dangerous because they can degenerate into a tumor of a malignant nature. Adenoma is detected during the diagnosis of the analysis of the dog, which shows the amount of antigen produced by the cells of the glandular organ.
Often, men are faced with an oncological process of one type or another of severity. PSA testing helps determine the onset of a cancerous process. Removal of the prostate for cancer is performed in more serious cases. A surgical solution is not the only way to treat patients with an oncological process, sometimes specialists carry out therapeutic therapy, which is prescribed based on the stage of the oncological process.
After removal of the prostate in men, postoperative recovery is prescribed, which may consist of:
- radiation therapy;
- chemotherapy;
- hormone therapy.
What techniques are performed during surgery
Elimination of the prostate is carried out in several ways:
- Transurethral resection - excision of a small area of the male gland by introducing a special instrument.
- Incision - widening of the lumen through a vertical incision (urethral penetration).
- Radical prostatectomy - The main method of therapy, during which not only the tissue of the gland is removed, but also the capsules, seminal vesicles, iliac lymph nodes. It is allowed to remove the prostate with such a technique only in cases where metastasis is not yet detected. For more advanced cases, palliative therapy is provided, which is carried out under general anesthesia. Such a method of treatment: removal of the prostate has consequences for men's health, therefore, there are contraindications in some cases.
- patients of the age category after seventy years of age.
- cardiovascular pathologies.
Before prescribing surgery, the doctor consults with the patient about how to remove the prostate gland.
What are the features of prostatectomy
Before performing a prostate resection, it is required to identify the features that imply the determination of a suitable access to the organ.
How to prepare for a prostate excision
Before carrying out an operation, a specialist assigns research:
- testing the dog;
- ultrasound;
- palpation of the prostate;
- biopsy;
- blood and urine tests.
Before the prostate is removed, the patient should stop using medications that increase the risk of bleeding. Food intake is stopped the day before the intervention. After the operation, the patient needs to rest in stationary conditions.
What can be the consequences after the operation
Despite the fact that the surgery is carried out using high technologies, the consequences of removing the prostate still exist.
These include:
- sclerosis of the urea neck;
- detection of a dog in plasma;
- suppuration, weakness, inflammation;
- retention of urine or incontinence - causes of occurrence: blood clots after surgery, physiological changes in the canal (edema, renal failure of an acute course);
- leakage or incontinence - 1 to ten percent of patients, such an unpleasant phenomenon may occur (the reason may be in, not completely removed tissue), reoperation is encouraged;
- inflammation - the process manifests itself on the occasion of an infection, an individual characteristic of the body (painful symptoms, fever, discharge of pus, an unpleasant odor are felt);
- soreness - the pain syndrome after surgery lasts for a week, however, if the soreness is of a longer duration, consultation with the attending physician is necessary;
- retrograde ejaculation or lack of seminal fluid is a common complication that involves the transfer of semen into the ureter.
Violation of potency is the most important complication that all representatives of the strong half of humanity fear. Such a complication occurs after surgery to remove the prostate for cancer and adenoma. However, doctors say that such a change is possible only after operations are carried out at a later stage of the pathology (cancer), and in this case, patients think more about staying alive.
Sometimes patients have exceptions, but they are not permanent. To avoid serious consequences, it is necessary to follow all the recommendations of a specialized specialist regarding the preparation of the body for the procedure.
Some of the more rare complications are:
- allergies;
- sepsis;
- questionable thoughts about complete excision of the lesion.
Any surgical procedure has a risk of large blood loss, as such cases are very common. To correct this effect, the patient is given a plasma transfusion.
After transurethral resection, patients may experience water intoxication. This can happen due to irrigation with an antiseptic solution during the procedure.
For any reaction, doctors consider this a deviation from the norm, therefore, for any manifestation, a doctor's consultation is required. During the elimination of the tumor process at the initial stage of its development, the chance of leading a full life for ten years increases. If the cancer is more serious, complications cannot be avoided.
When a high level of antigen or metastasis is found in a patient, physiological functions cannot be preserved, specialists fight the disease in order to prolong the patient's life.



























