Home >
Erectile Dysfunction >
Spermatocele why does a man get sick and how to treat it
Spermatocele - why does a man get sick and how to treat it?
Benign testicular neoplasms are more common than is commonly believed in society. But in the overwhelming majority of cases, they can be eliminated without negative consequences for the potency and fertility of a man. A spermatocele is an accumulation of sperm and other locally circulating body fluids in a randomly formed tissue sac next to the testis. Such a tumor is dangerous only by inflammation and suppuration with a sharp decrease in immunity. Like all diseases of the reproductive system, it brings psychological discomfort many times more than physical.
Testicular spermatocele - what is it?
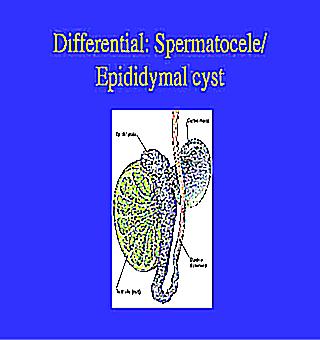
The testes are involved in the production and maturation of sperm. The white ejaculate, with which they are ejected during ejaculation, is produced by the prostate gland. They mix into a single substance just before orgasm. To get into the prostate located much higher and connect with its ejaculate, sperm still need to stay not dry, but in a liquid, just not yet similar to semen environment.
The biological path for them is represented by the vas deferens. They lead one from each testicle into the prostate, and the already united duct from it opens into the urethra. And the appendage in men is the lowest segment of the indicated tubules that covers it. It produces enough cerebrospinal fluid so that when sperm are needed, they can freely flow into the ducts of the prostate.
Normally, the synthesis and outflow from the appendage of the fluid that was not "useful" is balanced. Spermatocele in men occurs when, for some reason, a relatively or completely isolated capsule of fibrous tissue has formed in the tissues of the epididymis.
Reasons
Spermatocele can be congenital or acquired in nature. In the first case, the reason for its appearance is the same as with an inguinal hernia. During intrauterine development, the processus vaginalis of the peritoneum must lower the testicles into the scrotum through the inguinal canal (the gap between the abdominal muscles in their lower part), form one of the membranes of the baby's testicles and grow higher, around the spermatic cord, separating the abdominal cavity from the scrotum.
Its incomplete overgrowth (obliteration) becomes the cause of congenital hernias, seminal cysts, dropsy of the testicle. This variant of the spermatocele often affects the left testicle, and neoplasms on both sides are found in isolated cases. In adulthood, the anomaly is acquired by men due to:
- hitting;
- pressure of tight underwear and clothes;
- non-standard sexual pleasures (such as threading the scrotum).
The causes of spermatocele may also lie in complications of inflammatory processes nearby:
- vesiculitis - sepsis of seminal vesicles;
- epididymitis - infection of the epididymis itself;
- orchitis is almost always a secondary testicular inflammation.
Such a bubble fills mixed contents - cerebrospinal fluid and mature spermatozoa, their unripe precursors and leukocytes
Spermatocele: symptoms and signs (photo), diagnosis
Small, congenital and proceeding without complications spermatocele does not give subjective sensations. But many of them grow over the years, especially during periods of maximum hormone activity (in adolescents under 15 and in the premenopausal 45-50 years).
In boys under 7 years of age and men at the peak of fertility, there are almost exclusively traumatic neoplasms. They are found on unintentional palpation (personal hygiene, sex). As you can see in the photo below, it is palpable and looks like a dense, not painful, movable ball over the testis.
Symptoms of spermatocele in men appear when the tumor reaches more than 3.5 cm in size. Patients begin to worry about one-sided heaviness in the scrotum, the feeling of a foreign object when wearing clothes and tight underwear. With its further growth, the pressure on the testis and excretory canal increases, complaints of pain while sitting, walking and having sex occur.
To make a preliminary diagnosis, a repeated examination with palpation in the clinic is sufficient. But a benign cyst must be distinguished from cancer of the spermatic cord, epididymis and the testicle itself. Their differential diagnosis is based on:
- mobility - malignant neoplasms are usually fused to the surrounding tissues. But strength increases over time and may be subtle at first;
- presence or absence of near metastasis - to the inguinal lymph nodes. Finding a group of enlarged nodules nearby with a 100% probability indicates cancer stage 2 or higher;
- transillumination - transillumination of the body of spermatocele with red rays. A benign tumor should let them pass well.
Ultrasound and computed tomography are used to clarify the size and location of the formation.Histology (biopsy) is hindered by the likelihood of a breakthrough of the watery "body". It is carried out only because of a solid suspicion of cancer.
Treatment
Uncomplicated cysts up to 2.5 cm in diameter require conservative treatment. Most often, it allows you to temporarily reduce the amount of fluid accumulated in the bag. After therapy, the tumor regains its size in a period of 1-6 months. The reason for this low efficiency is the inability of common funds to "dissolve" the connective tissue capsule that forms.
Surgical treatment of spermatocele refers to dynamically developing, large neoplasms in men showing dangerous signs - acute compression of the seminiferous tubules, heaviness, inflammation, purulent fusion
Spermatocelectomy (surgery)
Excision or spermatocelectomy does not require general anesthesia - only local anesthesia. A small incision is made on the skin above the focus of stagnation and all altered tissues are removed. In the course of treatment, magnifying devices are necessarily used. The procedure does not affect the functional parts of the appendage. Following the results of treatment, the patient is prescribed for 2-7 days:
- wearing a supporting and protecting wound dressing - suspensor;
- ice packs to control swelling;
- mild oral pain relievers and non-steroidal anti-inflammatory drugs - Ketanov, Ibuprofen, Analgin (all except for the coagulation reducing and therefore contraindicated after Aspirin operations).
Even if there is no doubt about the diagnosis, the extracted fragments are examined for malignant changes and bacterial and fungal microflora. After treatment, a man should abstain from sexual activity for 3-6 weeks.
Other ways and means
Procedures close to the operation in their meaning are:
- aspiration - puncture and suction of the liquid contents of the spermatocele with a special needle;
- sclerotherapy - immediately following aspiration. The bottom line is to inject sclerosant into the emptied connective tissue sac, a drug that causes it to shrink and stick to prevent relapse.
The period of recommended abstinence from sex after them does not exceed 2 weeks. A cyst overgrown after an operation of this type is considered safe.
Folk remedies are indicated for use only by men with simple cases of spermatocele. The effect of them differs little from palliative treatment due to their inability to destroy the already existing walls of the capsule without surgery.
Aftermath
Stable formations of this type can spontaneously (or due to conservative measures) dissolve without consequences
Influence of spermatocele on potency
With a medical history not complicated by other defects of prenatal development, immunodeficiencies or repeated trauma, spermatocele in men does not affect sexual function in any way: libido, erection, potency.
Spermatocele in men: prevention
Patients with such a diagnosis (current or history) are not recommended only intense sex in unusual positions, as well as with increased trauma. Favorable conditions for stagnation of cerebrospinal fluid in the pelvic organs are also created by hypodynamia. Accordingly, it is useful to engage in any sport to your liking, at least 3 times a week when training from 45 minutes to an hour.



























