Home >
Erectile Dysfunction >
Spermatozoon what is it its functions and structure
Spermatozoon what is it, its functions and structure
The cell in the male reproductive system that serves to fertilize the female gamete is called the sperm. From ancient Greek it is translated as seed and life. This terminology is used to characterize micro gametes that are unusually mobile. They are characterized by a type of sexual process in which there is a draining of sharply different sex cells.
Spermatozoa are smaller in size than the female egg, since they do not have such an amount of cytoplasmic fluid in their structure. But a huge amount of them is produced in the male body.
The very meaning of sperm, it is important to distinguish from the word sperm, since the latter has a wateriness, which includes the male gametes themselves. In addition, there is a certain concentration of epithelial cells in the semen coming from the urethral canal.
Discovery History
The first to describe the male gamete was the Dutch scientist Anthony van Leeuwenhoek. The discovery dates back to 1677. As the microscopist himself reported in his treatises, his friend Johann Gamm told him about spermatozoa. Formally, he is the discoverer, but it was he who examined and made sketches in detail of the sperm, namely Levenguk.
Since the discovery of human sperm, other male gametes have been found in most mammals. For almost 100 years, it was believed that seed animals, and this is what the discoverer called them, were considered a parasitic form of microorganisms in the human body. Sperm differentiation, appeared in medical sources only in the 19th century.
Functional features and structure
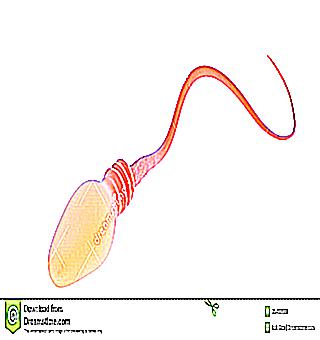
What is a sperm and what is it? The sperm cell is a specific cell, the structure of which enables it to perform the function of overcoming the female genital tract intended by nature, subsequently penetrating the female egg, introducing the genetic material in it.
In the process of fusion of a sperm with an egg, fertilization and the formation of a zygote occurs. The sperm is about 55 microns long, making it the smallest cell in the human body. The upper part, called the sperm head, is 5.0 µm in length and 3.5 µm in width. The middle part and special tail are about 4.5 and 45 microns in length, respectively.
Such small sizes are due to the fact that the male gamete needs to move as soon as possible along the female pathways to the egg. In the process of maturation of the male gamete, a decrease in size occurs due to the transformation and compaction of the nucleus, and the cytoplasmic fluid is ejected to a greater extent. Thus, only the most needed parts of the sperm are left.
The male gamete contains the X and Y chromosomes. Those containing Y in the chromosome are called androspermia, and the X chromosome in gynospermia. Fertilization of an egg occurs with only one sperm, and the likelihood that it will be andro or gynospermia is equal, which in turn does not give clear guarantees to guess the future sex of the baby .
Components
The head of a sperm in a male human body is presented in the form of an ellipse, compressed on both sides. One side has a small indentation, which gives reason to talk about the spoon-shaped head of the male gamete.
The head contains a number of cellular structures, which include:
In addition, the middle part and the neck are distinguished in the sperm. Next is the tail. The entire middle part of the male gamete has a tail cytoskeleton, but in the middle part around the tail there is a mitochondrion. It represents one large mitochondrion in the form of a spiral, entwining the cytoskeleton of the tail. It is this mitochondrion that allows the flagellum to move through the synthesis of adenosine triphosphoric acid.
The tail is located immediately behind the middle part, has a thin structure. The process of movement of human sperm is provided by the tail, or flagellum. When making a movement, the male gamete moves, making revolutions around its axis. The movement speed can reach up to 30 cm in 60 minutes.
This is where the fertilization process takes place. Being in the male body, sperm cells are in standby mode, not showing their activity, and the movements of their tails are barely noticeable. The excretion of spermatozoa along with the semen occurs due to the compression of the muscle fibers of the ducts and the beating of the ciliary parts of the cells located in the ducts.
Male gametes begin to show their activity after the ejaculation process has occurred. The reason for their activation is a special prostatic fluid containing enzymes.
Important! On the genital tract of the female body, sperm move only against the flow of fluid
The speed of movement of sperm is 2-5 millimeters in 60 seconds.This type of movement and speed allows you to reach the anterior third of the oviduct for 6-10 hours.
How long do sperm live?
After the maturation process is over (about 65 days), the male gamete can remain in the body for up to 30 days. In semen, the ability to survive depends on environmental factors (light, room temperature, humidity) up to one day. In the vaginal cavity, gametes die within a few hours
In case of pathological conditions in the body of a man, the number of sperm in the seminal fluid may change. It also happens that mature germ cells are absent during a special analysis, spermogram.
High temperature, ultraviolet radiation, acidic environment, salts of heavy metals can kill male gametes. In addition, radiation of a radiation nature, alcoholic beverages, nicotine, narcotic substances, antimicrobial drugs and potent medical substances have an adverse effect on male gametes.



























