Home >
Erectile Dysfunction >
What is vesiculitis and how to treat it
What is vesiculitis and how to treat it
What is chronic vesiculitis in men and how to treat it?
The appearance of acute pain in the sacrum, anus and genitals may indicate the presence of vesiculitis - an inflammatory disease of the seminal vesicles.
The chronic form of the disease reduces the number of active spermatozoa and minimizes the chances of a successful conception.
The development of the disease can lead to loss of fertility and serious health problems.
What is chronic vesiculitis in men
Chronic vesiculitis: what is it? A urological disease called vesiculitis (an alternative name is spermatocystitis) has an infectious nature of appearance in the body, therefore it often develops against the background of infection with a sexually transmitted or other infectious disease.
Although the pain syndrome caused by vesiculitis can radiate to the lower back, it should be understood that the seminal vesicles are located next to the rectal zone (only the wall separates), but the glands themselves are located in the abdominal cavity, directly in contact with the bottom of the bladder and located above the prostate gland, near the vas deferens. The appearance of the gland is a bumpy spindle-shaped surface.
What are the reasons for the appearance and who is at risk?
In addition to getting into the body of infections - chlamydia, gardanella and gonococci, the influence of opportunistic microflora - Pseudomonas aeruginosa and Escherichia coli, influenza virus, staphylococcus can also lead to the appearance of the disease. The penetration of these microorganisms is also possible through sexual contact, in which a barrier method of contraception is not used.
Vesiculitis - adverse conditions:
- lack of physical activity;
- prolonged hypothermia;
- excessive sexual activity;
- low immune resistance of the organism;
- frequent constipation.
Given these factors in the development of the disease, doctors note the similarity of the causes caused by vesiculitis and prostatitis. For this reason, clinic staff often diagnose these diseases at the same time. Another reason is the proximity of the organs of the genitourinary system, which are capable of spreading inflammation from one area to another.
Symptoms and manifestations of the disease
The chronic form develops after an acute form of the disease, in which fever, chills and sharp pain radiating to the lumbar region are diagnosed.
The chronic course of vesiculitis can also include similar symptoms, but differ in pain intensity (moderate or mild pain is present).
Has symptoms of chronic vesiculitis:
- appearance of aching pain;
- potency reduction;
- decreasing the intensity of orgasm or its complete disappearance;
- discharge of purulent fluids and blood with semen.
You can read more about the symptoms of vesiculitis in this publication.
Against the background of the progression of the disease, urination disorders also develop and involuntary ejaculation appears. After sexual activity, mild pain occurs, lasting up to three hours.
Consequences and possible complications
The seminal vesicles create a fluid that contains the nutrients needed to saturate the spermatozoa. Receiving a powerful influx of energy due to the release of fructose, spermatozoa are able to maintain motor activity for a long period of time. Violation of the function of this gland leads to depletion of the composition of sperm and the appearance of a large percentage of non-viable seminal cells.
In advanced situations, cancer cells may appear, which quickly pass to the pelvic organs. The consequences of the pathological process are cancer of the prostate and bladder.
An operable form of the disease is formed as a result of suppuration of the glands, however, in most cases, stages of the disease are diagnosed that do not require surgical intervention.
If chronic vesiculitis appears, treatment is carried out by conservative methods.
Often, a therapeutic solution or substance is administered rectally: the impact on the rectal mucosa allows you to have a beneficial effect on the seminal vesicles.
Traditional medicine
Microclysters with chamomile. Glass with 2 tbsp. l. chamomile is poured with boiling water and cooled to 37-39 degrees. Then a syringe is prepared, the anus is lubricated with petroleum jelly, 50-100 ml of an aqueous solution is injected. In this position, the patient should stay for 10-15 minutes. The daily frequency of use is 1-3 times.
The minimum course is 7 days. To enhance the antibacterial effect on the glands inflamed from vesiculitis, you can use a combination of chamomile and other medicinal herbs - calendula and eucalyptus leaves.
Rectal suppositories with propolis.
1 suppository before going to bed is inserted into the rectal area, lubricated with oil or petroleum jelly.
The general course of treatment is from 2 to 4 weeks.
Castor oil. Castor bean oil is used as an aid in vesiculitis to eliminate constipation (constipation). It is taken for the treatment of vesiculitis in the morning, 1 tbsp. l. on an empty stomach for several days. After normalization of the stool, vesiculitis ceases to bother.
Recipe for a natural antibiotic. Parsley root, honey, lemon, olive oil are mixed in equal proportions (250 g each) with a blender. The resulting consistency is sent to the refrigerator and taken 1 tbsp. l. every morning. A folk remedy is also used to treat cystitis and prostatitis. The course of treatment of vesiculitis in this way is carried out for at least two weeks.
Sage. The course of treatment is 2 weeks. Hemostatic, antibacterial and anti-inflammatory effects alleviate the condition of the patient with vesiculitis.
Recipe: 10 grams of sage are poured with boiling water and boiled over a fire for 30 minutes. Take 100 ml 2 times a day.
Dill water. Prepared by infusing pre-crushed parsley seeds in a glass of boiling water. The broth should be infused for at least 2 hours, you can cook in a water bath. The infusion is an excellent diuretic that allows you to enhance the cleansing of the urinary tract if vesiculitis is accompanied by inflammation of the bladder.
Treatment of vesiculitis: drink on an empty stomach a third of a glass 2 times a day or 90-110 ml five times a day (for 7-10 days).
Drug treatment
The treatment of chronic vesiculitis with medications depends on the nature of the occurrence of spermatocystitis.
Erythromycin. The antibiotic destroys bacteria of conditionally pathogenic microflora (staphylococcus, streptococcus) and inflammatory processes, including those occurring in the inguinal region. Once in the blood, the active substance inhibits protein synthesis and allows you to remove the inflammation of the seminal vesicles. The course of treatment varies from 10 to 14 days, during which 200 mg of the substance is taken two or three times a day. Taboo on admission: sensitivity to macrolides, jaundice, functional disorders of the liver.
Sumamed. An antibiotic similar in effect to Erythromycin. The scheme and course of treatment of chronic vesiculitis: the first day is used 2 times 500 mg in the morning and evening, the next 4 days - a similar dosage 1 time per day. Restriction on treatment with this medication: combining the intake with dehydroertotamine and ergotamine, severe disorders of the functioning of the liver and kidneys.
Regulax. It is prescribed for patients suffering from spermatocystitis due to chronic constipation.
Contraindications: bleeding in the digestive tract, peritonitis, hernia with pinching. It is taken for at least three days, if an intestinal disorder develops, then therapy should be discontinued.
Mironem. The strongest antibiotic indicated for men infected with ureaplasma, gardnerella or chlamydia. One day, immunomodulatory medications are taken, then Miranem is taken for 7-10 days, 60 mg 3 times a day. Conditions for limiting admission: individual intolerance.
Benzylpenicillin. An injectable drug prescribed for patients with gonorrhea, syphilis and vesiculitis that has developed against their background. From 3 to 9 million IU is administered intramuscularly for no more than 7-10 days in the treatment of vesiculitis. With the development of sepsis, the duration of the course increases to 60 days. Prohibited use: bronchial asthma, renal dysfunction, hay fever.
Trental. The drug is used to treat vesiculitis caused by congestion. Trental enhances blood circulation in the arterial vessels of the lower extremities, thereby eliminating inflammation caused by vesiculitis. The general course of treatment is 3 weeks, the dosage varies from 100 to 400 mg. Contraindications: severe bleeding, retinal hemorrhages, impaired hemoglobin synthesis, hemorrhagic stroke, acute myocardial infarction.
What lifestyle should be followed during treatment? In sexual terms, moderation should be observed - avoid long breaks in intimacy and excessively long intercourse.
Prevention and general recommendations
- have sex regularly;
- wear warm underwear in the cold season;
- visit a urologist at least once every 6 months;
- Treat other diseases of the urogenital area in a timely manner.
Blood stasis can be prevented not only by regular trips to the gym, but also by the introduction into the habit of exercising every day and doing warm-ups (turning the torso and squats) after sitting at the computer for an hour.
Vesiculitis destroys a full-fledged sex life and brings discomfort to the pelvic area.The goal of most therapeutic measures is the rehabilitation of foci of infection, used to eliminate inflammation of the seminal vesicles. After a course of therapy, the disease can disappear forever and - subject to preventive measures - no longer bother a man.
For more information about vesiculitis in men, see the following video.
Vesiculitis: symptoms, causes, diagnosis and treatment
Vesiculitis in men is usually a complication of some other disease or infectious process in the body. Despite the fact that the diagnosis of vesiculitis is quite rare, the consequences and complications without appropriate treatment can lead to infertility and a purulent-inflammatory process in the seminal vesicles.
What is vesiculitis
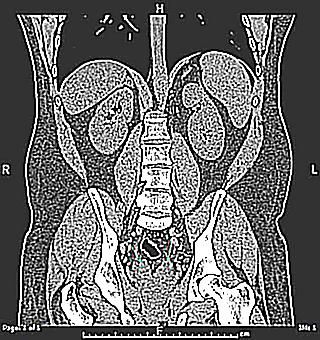
Near the prostate gland there is a special paired organ - vesicles (or seminal vesicles). The main function of these bubbles is to store the secret that is produced by the prostate. They communicate with the vas deferens through which spermatozoa are carried out. The inflammation of these vesicles is known as vesiculitis.
Structure and functions of seminal vesicles
Let's talk more about the structure of the seminal vesicles. This paired glandular organ is located on the side of the vas deferens, above the prostate. Its front surface is in contact with the bottom of the adjacent bladder. Behind the seminal vesicles are in contact with the ampulla of the rectum. And only the upper part of the bubbles is covered with peritoneum. Depending on the volume of fluid in the bladder, the location of the seminal vesicles may change.
The shape of this paired organ is spindle-shaped, its thickness can reach 2 cm, the width is usually 2-4 cm, and the length is about 5-6 cm. Each seminal vesicle consists of three elements - the base, the body and the excretory duct, which connects with vas deferens. This is how the ejaculatory duct is formed, which penetrates the entire thickness of the prostate, and then opens on the seed mound with a common duct (on each side).
The blood supply to the organ occurs through the descending branch of the artery of the vas deferens, and the branches of the arteries of the bladder. Outflow is carried out to the vesical venous plexus and to the internal iliac vein. Lymph outflow - to the internal iliac lymph nodes. Innervation - nerve branches of the plexus of the vas deferens.
The seminal vesicles perform several important functions. First, they provide the sperm with energy resources, and second, they protect them. And finally, the third task of the bubbles is to dispose of the remaining seminal fluid.
More than half of semen consists of a secret formed in the seminal vesicles. An important component of this secret is fructose. This nutrient provides sperm cells with sufficient energy, which is necessary for metabolic processes and active movement. The fructose content makes it possible to assess the hormonal status of the patient and draw conclusions about how capable he is of fertilization. When analyzing the semen of a healthy man, the fructose content usually reaches at least 13-15 mmol / l.
The secret formed in the seminal vesicles is combined with the secret of the testicles. Since it has a pH of 7.3, a protective colloid is formed, which significantly increases the resistance of spermatozoa and improves their survival during the long journey to the egg. If sexual intercourse is realized, the seminal fluid containing spermatozoa enters the vesicles, and is disposed of there. Utilization of spermatozoa in the seminal vesicles is carried out by their absorption by special cells, which are known as "spermophages".
Why vesicles become inflamed. Causes of vesiculitis
Vesiculitis cannot be attributed to common male diseases. Inflammation of the seminal vesicles is quite rare due to the special location of this paired organ. They are located deep in the small pelvis, and it is not so easy for pathogenic microbes to get there.
The primary inflammatory process in the vesicles is an extremely rare occurrence. It is considered to be purely academic, since it is usually encountered only in the pages of educational medical literature. In practice, the seminal vesicles become inflamed as a result of an inflammatory process in another organ. Usually, vesiculitis develops as a result of urethritis, epididymitis (inflammation in the epididymis), or chronic prostatitis. In some cases, vesiculitis is associated with a general infectious process that has arisen outside the genitourinary system. These can be diseases such as osteomyelitis (an inflammatory process in the bone marrow), tonsillitis and even the common flu.
This list of factors that can provoke the development of vesiculitis is not exhausted. In order to get sick with this disease, it is not necessary to transfer a sore throat or flu.Sometimes the reasons can be very banal - a sedentary lifestyle, a tendency to constipation, long breaks in sexual activity, a decrease in immunity. The combination of these moments (or even one of them) is a good basis for the development of the inflammatory process in the seminal vesicles.
That is, the factors underlying vesiculitis can be divided into two groups: infectious and congestive. Infectious causes of the development of the inflammatory process in the seminal vesicles can be specific and nonspecific. Specific include: gonorrheal, trichomonas, tuberculosis, mixed. Nonspecific - viral and bacterial, associated with chlamydia, mycoplasma and ureaplasma, candidiasis (thrush in men) and gardnerella.
Congestive vesiculitis (i.e. congestive) develops when there is stagnation of secretion in the prostate or seminal vesicles. Another possible cause is venous congestion in the scrotum or pelvic area.
How does inflammation of the seminal vesicles occur?
In the vast majority of patients (up to 80%), the inflammatory process is due to a deterioration in the natural protective function of cells. Immunity is reduced, first of all, under the influence of such reasons: overheating, cooling, lack of physical activity, trauma. The action of these factors makes the bubbles susceptible to pathogenic microbes, and they begin to multiply freely, causing inflammation.
Possible ways of infection and development of vesiculitis
Infection with vesiculitis can occur in the following ways:
Hematogenous. In this case, pathogenic microbes enter the vesicles along with the blood. Sources of infection can be very different: pneumonia, caries, sinusitis, sore throat. In such cases, vesiculitis is usually associated with staphylococcus, streptococcus.
Lymphogenic. Microbes are spread along with the lymph. Possible sources are boils, prostatitis, balanoposthitis. Pseudomonas aeruginosa, cocci, and proteus act as causative agents of infection.
Ascending. In this case, the infection spreads up the mucosa of the urinary tract. This method of spread is typical for Escherichia coli, as well as sexually transmitted infections.
What happens with inflammation of the seminal vesicles (vesiculitis)
In this disease, hypertrophy of the mucosa develops, and the lumen of the vesicles begins to narrow. During the period of the acute course of the process, the outflow of contents from the vesicles is difficult, since the mucous membrane swells strongly. Due to a prolonged inflammatory process, the epithelium begins to grow, the mucosa becomes thicker. There is swelling of the gland and an increase in its size.
In place of the cells responsible for the formation of the secret, connective tissue appears. Due to its excessive growth, the secretory function of the vesicles suffers. The epithelium that produces the secret begins to atrophy. In semen, the amount of organic components necessary to maintain the activity of spermatozoa decreases. The sperm itself becomes more viscous.
As a result of a deep inflammatory process, the adventitial (or outer) membrane undergoes atrophy. The main function of this contracting plate is squeezing out the secret of bubbles during orgasm. If she is amazed and cannot fully cope with her task, the gland will become much larger in volume. Moreover, congestion can cause suppuration. A man has erectile dysfunction.
Types of vesiculitis
Inflammation of the seminal vesicles are classified depending on the changes occurring in this organ. There are 4 types of vesiculitis.
Superficial catarrhal spermatocystitis
The superficial form is manifested by redness on the mucous membrane. At the same time, the mucous membrane swells. And on the epithelial layer lining it, damage appears. Inside the bubble there is a purulent-mucous liquid, inclusions of blood may be noted. The size of the organ is increased, and the shape is slightly stretched.
Deep vesiculitis
In patients with deep vesiculitis, inflammation passes to the submucosa, as well as the muscle tissue of the vesicles. With this form of inflammation, they also increase in size, swelling and hyperemia appear. The walls thicken, and in the lumen there is a little serous secretion with a purulent admixture.
Paravesiculitis
A serious complication of deep vesiculitis is paravesiculitis. It is characterized by the spread of the inflammatory process beyond the boundaries of the bubbles - to the fiber. Sometimes deep inflammation causes atrophic sclerosis of the vesicles.
Empyema of the seminal vesicle
If deep spermatocystitis has developed under the influence of pyogenic microorganisms, the seminal vesicles are filled with pus, and in fairly large quantities. This is how a disease known as empyema occurs.
By the type of course, vesiculitis can be both acute and chronic.Acute inflammation in the vesicles (as in any other organ) manifests itself unexpectedly. The disease begins with a sharp rise in temperature, the sick person is overcome by weakness, pain occurs in the pelvic area. Discomfort increases during bowel movements or when the bladder is full. Most often occurs in men suffering from prostatitis, and therefore can be perceived as its complication.
Chronic vesiculitis is the more common form. It is considered a complication resulting from Acute inflammation. Patients complain of erectile dysfunction, impaired ejaculation, aching pain in the pelvis and perineum. In such patients, there are qualitative changes in the composition of sperm.
Symptoms of vesiculitis in men
In many men, the inflammatory process in the seminal vesicles does not manifest itself with pronounced specific symptoms and may be ignored. The disease often develops against the background of prostatitis, and it is difficult for the patient to distinguish the symptoms of vesicle damage from the symptoms of inflammation of the prostate gland. Sudden fever (up to 39 degrees), increased pain in the perineum, and more pronounced problems with urination suggest thoughts about vesiculitis. Feeling discomfort in the pelvic area during intercourse. Another alarming sign is the appearance of bloody inclusions in the semen. In addition, with a bowel movement and a full bladder, the pain will begin to increase.
If you notice such symptoms (or at least some of them) in yourself, a visit to the urologist should not be postponed. After all, inflammation of the seminal vesicles is a rather serious medical problem that can lead to extremely unpleasant complications. Do not ignore suspicious symptoms or try to attribute them to chronic prostatitis. It must be remembered that vesiculitis is a much more serious disease than chronic inflammation of the prostate.
How is vesiculitis diagnosed
It is not too difficult to diagnose an inflammatory process in the seminal vesicles. At the first stage, after listening to the patient's complaints, the doctor performs a rectal examination, the purpose of which is to identify pain in the anterior wall of the rectal ampulla. Then the patient is prescribed laboratory tests for an accurate diagnosis.
The general blood test is not very informative. It can only show that somewhere there is an inflammatory process. More accurate results will not give a laboratory study of urine. For accurate diagnosis, it is necessary to perform seeding of the contents of the vesicles. Using a special prostate massage, the doctor selects the material for analysis in a test tube. Then the contents of the bubbles are sown in a special medium containing nutrients. During a certain period, colonies of microorganisms grow, making it possible to diagnose bacterial vesiculitis.
While waiting for test results, the patient is offered to undergo an ultrasound examination of the pelvic area. Ultrasound is performed using a special sensor, through the rectum. This method makes it possible to determine the presence of an inflammatory process in the wall of the bubble. Ultrasound is classified as an indirect method. However, its results often become a sufficient basis for the diagnosis of vesiculitis (both acute and chronic).
The standard examination method for inflammation of the seminal vesicles is vesiculography. Such a diagnosis makes it possible to exclude other diseases: tuberculosis and sarcoma. The procedure is invasive. It is done in this way. An incision is made in the scrotum to expose the vas deferens. Then, using a special needle, a contrast (iodolipol, verografin) is injected into the lumen of the duct. Then they take an x-ray.
Modern diagnostic methods include CT and nuclear magnetic resonance. They give an accurate picture of the state of the diseased organ. But such procedures are much more expensive than traditional methods of examination. Therefore, they are rarely resorted to.
How is vesiculitis treated
If the disease was diagnosed in the early stages, the patient is shown a course of active antibacterial treatment. For this purpose, a wide range of macrolides, penicillins, cephalosporins and fluoroquinolones are prescribed. Although all of these remedies are available over the counter without a prescription, you should not self-medicate. You can take drugs only after consulting a doctor, who must make an accurate diagnosis and determine the treatment regimen.
Antibiotic treatment regimens for vesiculitis
For vesiculitis associated with traditional pathogens (white staphylococcus aureus, E. coli), the following treatment is indicated:
Erythromycin: 200 mg per day, 2-3 doses, a course of a week to two.
Sumamed: the first day 500 mg in the morning and evening, the next 4 days once a day, 500 mg.
Doxycycline: 100 mg twice a day for 10-12 days, on the first day once 200 mg.
Metacycline: 300 mg twice a day (the whole course is 5-10 days).
Furagin: 50 mg 2 or 3 times a day with meals for 7-10 days.
Bactrim: 2 tablets twice a day after eating, for 5-14 days.
If vesiculitis is caused by rare pathogens (such as Klebsiella, Proteus) or urogenital infections (ureaplasmas, chlamydia, gardnerella, mycoplasmas), therapy is carried out according to a different scheme.
In the first day, an immunoprotector is prescribed. And three days later, a course of antibiotic treatment (macrolide or tetracycline plus biseptol) is carried out, which should last 10 days. In total, it is desirable to carry out at least two ten-day courses using antibiotics of different groups.
For specific infections (syphilis, gonorrhea, tuberculosis), the following therapy is indicated:
Benzyl penicillin IM 3 9 million units
For patients with congestive vesiculitis, the recommended treatment regimen is:
Trental: 100-400 mg, twice a day, the course lasts 2-3 weeks.
Obzidan: 1 tablet 2 or 3 times a day for three weeks.
Aescusan: 1 tablet three times a day, duration of administration - from 10 to 20 days.
UHF is also often prescribed for vesiculitis. In this case, the electrode is inserted rectally to a depth of 10 cm. One session lasts about 15 minutes, procedures are performed every day.
For enema use chamomile (or sage), novocaine. First, a cleansing enema is done, and then a microclyster. During this time, the patient should lie in a calm position for at least 30 minutes for the medicines to work well.
With the help of antibiotics, you can act on the microbes that caused the disease. But they, unfortunately, will not remove unpleasant symptoms. Therefore, the patient is usually prescribed symptomatic treatment - painkillers and antipyretics (in the form of tablets or injections). First of all, these are drugs such as Indomethacin and Diclofenac.
Laxatives can significantly alleviate the patient's condition. Under their influence, the patient does not experience pain during the act of defecation. But, unfortunately, their reception is inconvenient to combine with bed rest, which is recommended for men with an acute form of the disease.
The described treatment is prescribed for acute vesiculitis. In the chronic nature of the disease, some other surgical and therapeutic methods are additionally used. So, with purulent forms of vesiculitis, an operation is necessary, the purpose of which is to drain the vesicles. But they can also resort to a more gentle method - washing the cavity of the bubbles through the urethra.
Vesiculitis prevention
In order for the disease not to recur, much attention should be paid to rehabilitation measures. One of the best ways to prevent relapses is to stay in a sanatorium where mud procedures are applied. In addition, physiotherapy is very useful.
Recent medical studies have confirmed that physiotherapy can prevent recurrence in many cases. The scientists who conducted the study claim that the likelihood of a recurrent episode of the disease after physiotherapy is almost halved.
For reliable prevention, it is necessary to deal with local causes that caused acute vesiculitis. As already noted, the inflammatory process in the seminal vesicles may be associated with chronic prostatitis or urethritis. Therefore, it is simply impossible to do without sanitation of primary foci. To do this, prescribe preventive antibacterial courses and local antiseptic treatment.
To prevent the recurrence of the disease, it is necessary to be attentive to personal hygiene. It is necessary to change underwear frequently and to toilet the genitals regularly. This rule is relevant for the prevention of any disease of the urogenital area.
Sometimes the source of inflammation is the source of infection, located at a great distance from the bubbles. Therefore, not a single focus of purulent inflammation in the body can be ignored. This applies even to caries-affected teeth.
In addition, we must not forget that the complete absence of foci of infection is not a guarantee that there is no risk of vesiculitis. In medical practice, there are cases when the disease occurred in perfectly healthy men as a result of severe hypothermia.
Treatment of vesiculitis with folk remedies
It is unrealistic to cure an infectious disease without antibiotics. Therefore, it is not worth getting involved in folk methods to the detriment of traditional treatment. Otherwise, the condition of the diseased organ may deteriorate greatly. Herbal remedies can be used only with the consent of the doctor, as an addition to the main treatment. In this case, baths with the addition of St. John's wort, chamomile, nettle, calendula, fennel and some other herbs can be recommended.
Consequences of vesiculitis in men
A serious consequence of vesiculitis is suppuration in the vesicles. The development of such a complication is indicated by severe pain in the sacral and inguinal regions, fever, chills, severe weakness.Such a patient needs to be urgently placed in a hospital for surgical treatment. An operation is indispensable, since there is a high risk of involvement of other organs in the infectious process. As a result, sepsis can develop, which is fatal.
Another serious complication of vesiculitis is infertility. Vesiculitis can cause the seminal vesicles to dry out and no longer be able to perform their function. Also, there are problems with erection, the quality of orgasm worsens.
Vesiculitis in men - symptoms and treatment
Vesiculitis (spermatocystitis) is an inflammatory process in the seminal vesicles in a man, a very insidious disease, often without visible symptoms. A late visit to the doctor leads to serious complications.
What is vesiculitis
Vesicles or seminal vesicles are a paired glandular organ located above the prostate and below the bladder. Their location may vary depending on the filling and emptying of the bladder. The vesicles are spindle-shaped and have a bumpy surface. Their length is about 5-6 cm, width - 2-4 cm, and thickness - 1-2 cm. The body, base and excretory duct stand out in the vesicle itself, connecting with the vas deferens.
The functions of seminal vesicles include:
- sperm protection;
- providing them with energy resources;
- production and disposal of residual seminal fluid.
Approximately 50-60% of the volume of sperm is their secret. And with unrealized sexual intercourse, spermatozoa are absorbed by spermophages located in the vesicles.
When the vesicles become inflamed, all these functions are disrupted, which negatively affects the well-being and fertility of a man.
Causes of inflammation
It should be noted that primary vesiculitis is extremely rare. It usually accompanies other pathologies of the genitourinary system: for example, orchitis, prostatitis, epididymitis or urethritis. Sometimes it can be a complication of other diseases: for example, SARS, sinusitis or tonsillitis.
In the first case, the cause of vesiculitis is the causative agents of sexually transmitted diseases: for example, chlamydia, mycoplasma, ureaplasma, gonococcus or Trichomonas. Infection through the vas deferens enters the vesicles. In the second case, the pathogen can penetrate into the vesicles with the blood flow from the affected organ.
The factors that provoke the development of the disease are:
- a sedentary lifestyle and resulting congestion in the pelvis;
- hypothermia;
- irregular, disharmonious sex life;
- too infrequent or excessive sexual activity, regular practice of coitus interruptus;
- frequent constipation due to malnutrition and lack of activity;
- the presence of chronic infections in the body, including caries;
- alcohol and nicotine abuse.
Stages of the disease and possible complications
Modern medicine distinguishes between two types or stages of vesiculitis - acute and chronic. Acute vesiculitis begins suddenly and is characterized by a rapid increase in symptoms. Often it develops as a complication of chronic prostatitis, so the patient perceives it as an exacerbation.
Chronic vesiculitis is diagnosed much more often and is usually a complication of an acute one. Symptoms with nm are not so pronounced, so patients often delay going to the hospital. This leads to erectile dysfunction, problems with ejaculation, changes in the composition of sperm.
A very dangerous complication of vesiculitis is suppuration of the seminal vesicles. If the acute process is not cured in time, fistulas with the rectum may form. This leads to a deterioration in the patient's condition, an increase in temperature up to 40C. This process requires surgical treatment.
Signs and symptoms
The most characteristic symptoms of acute vesiculitis:
- Pain in the groin and deep in the pelvis, radiating to the sacrum. Usually it is unilateral, even if both vesicles are affected, since the degree of damage to them is not the same;
- Pain when filling the bladder and during the act of defecation, during ejaculation;
- The appearance of an admixture of blood in the semen;
- Sickness, fever and headaches.
In chronic vesiculitis, the following are observed:
- Pain during erection and ejaculation, within 2-3 hours after intercourse;
- The appearance of wet dreams (involuntary ejaculation);
- Change in sensations during orgasm;
- Pain in the sacrum;
- Infrequently, urination disorders are recorded.
Often, chronic vesiculitis is completely asymptomatic, and the patient comes to the doctor with the only complaint of blood impurities in the semen. Also, the discharge of pus with urine (pyuria) or with sperm (pyospermia), a decrease in the number of spermatozoa (azoospermia) is also periodically recorded.
Diagnostic methods
The diagnosis of vesiculitis is made on the basis of a study of symptoms and a urological examination. A digital examination of the prostate through the rectum is mandatory, it is performed with a full bladder. The patient should be in the lying position on the right side with the knees pressed to the stomach. In the normal state, the vesicle is not palpable, but in the presence of pathology, the doctor may notice:
- In catarrhal spermatocystitis - slight swelling and soreness near the vesicles;
- With deep spermatocystitis, vesicles are easily palpable and feel like dense, elastic, rounded formations;
- In empyema (complicated by purulent vesiculitis), the seminal vesicles are palpable as painful, springy, pear-shaped or sausage-shaped formations.
- With paravesiculitis (inflammation of the tissue around the seminal vesicles), a painful diffuse infiltrate is palpated, which, when pressed, spreads to the sides. It is impossible to determine the contours of the vesicles.
Digital examination of the prostate allows the diagnosis of vesiculitis
Also, when diagnosing inflammation of the seminal vesicles, a bacteriological study of the secretion of vesicles is carried out. It may contain erythrocytes, leukocytes, epithelial cells, hematoidin crystals, spermatozoa.
To confirm the diagnosis and for the purpose of differential diagnosis, the doctor may prescribe:
- Ultrasound of the small pelvis, which allows to determine tumors, cysts and some other pathologies of the genitourinary system;
- Vesiculography or x-ray with contrast;
- Blood test for Wassermann reaction, as syphilis can also lead to an increase in the volume of vesicles.
In addition, OAC, OAM, and a study of the hormonal profile are usually prescribed.
In acute vesiculitis, the patient must be hospitalized and treated in a hospital. In the most difficult situations, surgical intervention is required. With a simple form, you can limit yourself to using folk methods.
Traditional medicine against spermatocystitis
In the conditions of the urological department of a hospital, a patient with acute vesiculitis is prescribed a half-bed rest and a special light diet that does not overload the body and relieves constipation. In addition, thermal physiotherapy is prescribed:
- hot sitz baths 2-3 times a day for 15 to 20 minutes;
- warmers on the crotch area;
- microclysters with warm (40C) water with 0.5-1 g of antipyrine 2-3 times a day.
Symptomatic therapy is also carried out:
- bromine preparations for sexual arousal;
- painkillers, including in the form of candles;
- antipyretic;
- laxative for constipation.
A broad-spectrum antibiotic is also prescribed, for example, from the group of penicillins, macrolides, fluoroquinolones and cephalosporins. After acute inflammation is stopped, a special massage is performed to obtain the secret of the seminal vesicles. Its bacteriological and microscopic examination is carried out. Then the prescribed treatment can be slightly adjusted, an antibiotic that is more suitable in this situation is chosen.
In acute vesiculitis, such a massage is contraindicated, therefore, treatment is prescribed based on the patient's history and well-being. In chronic vesiculitis, regular urological massage, a variety of physiotherapy, such as mud therapy and paraffin therapy, are recommended. Also carry out instillations of silver nitrate 0.25-0.5% in the back of the urethra. Antibacterial drugs are injected directly into the seminal vesicles. In the most advanced situations, surgical treatment, such as vesiculectomy, is recommended. But in most cases, the treatment is successful and leads to a complete recovery of the patient.
Modern medicine can easily cope with vesiculitis
Folk remedies
In addition to medical treatment, in simple situations, you can try folk methods, for example, rectal suppositories with propolis, as well as rectal mud tampons and hot microclysters with infusion of chamomile and calendula or mineral water.
In the process of therapy, it is necessary to strengthen the immune system in order to prevent relapses. To do this, you can take tinctures of Echinacea and Eleutherococcus. In addition, there are herbal recipes designed specifically for the treatment of vesiculitis:
- We mix 25 g of burdock root, 15 g of black poplar buds, 10 g of sage and 5 g of St. John's wort. Pour half a liter of boiling water together and leave for about 10 hours in a sealed container. We take this medicine in 50 ml. three times a day for 20 minutes. before meals, preferably warm. The course of treatment lasts approximately 1-2 months, it depends on the severity of the patient's condition.
- You can take a decoction of parsley seeds. To prepare it, you need 2 tbsp. l. grind raw materials, pour boiling water and boil for 15 minutes.Such a medicine will help clear the urinary tract and reduce the symptoms of vesiculitis.
It will also be useful to drink fresh juices daily. They strengthen the body, relieve constipation and provide valuable vitamins.
Lifestyle features
Vesiculitis is one of those diseases that can never be considered completely cured. For any reason, a relapse can occur, so men who have had spermatocystitis have to carefully monitor their health all their lives. It is very important to constantly monitor the condition of the prostate gland, since it is prostatitis that in most cases is the cause of vesiculitis.
Men with chronic inflammation of the seminal vesicles need to monitor their diet. It should be complete and contain all the necessary vitamins and minerals, as well as a lot of fiber, which prevents constipation. Also, hypothermia should not be allowed, especially in the pelvic area. Regular stable sex life is very important.
Sufficient physical activity helps prevent vesiculitis
Prevention
Since there is no underlying cause for vesiculitis, it is not easy to talk about preventing it. However, modern urologists have developed methods for the prevention of acute spermatocystitis:
- Remove the causes of inflammation. Usually it is preceded by such chronic processes as urethritis and prostatitis. Timely treatment of these diseases will help prevent vesiculitis. In addition, it is necessary to monitor the health of all organs. Even unbaked caries can cause inflammation of the seminal vesicles.
- Healthy lifestyle and no hypothermia. You need to eat right, move enough and eliminate bad habits.
- Careful personal hygiene. Regular toilet of the genital organs is an indispensable element in the prevention of any diseases of the genitourinary system.
Vesiculitis or inflammation of the seminal vesicles is a dangerous disease that can lead to the destruction of a man's reproductive function and even his death due to sepsis (the spread of a purulent infection throughout the body). This disease rarely appears on its own and is usually a complication of other inflammatory processes. Therefore, in order to avoid it, you must try to keep your body in shape and treat any infections in time. If it was not possible to avoid vesiculitis, then treatment is carried out with antibiotics and symptomatic therapy and physiotherapy.



























