Home >
Erectile Dysfunction >
Causes of prostatitis at 60
Causes of prostatitis at 60
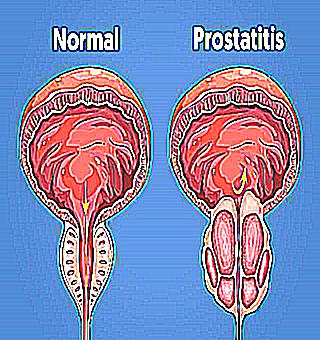
According to statistical studies, seventy percent of men at the age of sixty have a disease such as prostatitis. This is primarily due to the aging process and its numerous biochemical changes, which also affect the prostate gland. Acute prostatitis is mainly characteristic of men between the ages of twenty and forty. At the age of sixty, this disease is already acquiring a chronic form, with periodic exacerbations.
Factors of manifestation of prostatitis after 60 years
The first reason contributing to the appearance of the disease is an unstable hormonal background. There is an imbalance between the hormones estrogen and androgen. All this, in turn, affects the enhanced multiplication of prostate cells. It also affects the life time of each of the cells. Hence the first reason, which in most cases is indicated when prostatitis is detected, is a stagnant phenomenon of the prostate gland that appears when there is a failure in the blood circulation.
At the age of sixty to sixty-five years, the main factor in the manifestation of prostatitis is a number of age-related changes in a man's body, which affect the outflow of urine. Violation of the blood circulation process appears as a result of a sedentary lifestyle, the presence of cardiovascular diseases and a number of other diseases that have a chronic form. You should also take into account the factor that various pathogenic bacteria enter the prostate gland.
The main reasons for the manifestation of prostatitis in men aged sixty should be highlighted:
- Various infectious diseases acquired as a result of intercourse;
- Weak immune system;
- Lack of physical activity;
- Various injuries in the groin area;
- Having bad habits;
- Prolonged exposure to cold;
- Lack of balanced nutrition;
- Hereditary factor.
The main symptoms of prostatitis manifestation
In the initial stage, the disease is manifested by the following most common symptoms:
- Increased body temperature;
- Feeling chills and weakness in the body, like a cold or flu;
- Occurrence of pain in the spine or sacrum;
- Occurrence of mood changes and general depression;
- Severe sleep problems or no sleep at all.
A very important factor at this time is to seek help from a medical representative, as the symptoms can become more pronounced and painful. Also, you should not resort to self-diagnosis and treatment, which only aggravate the situation.
Prostatitis also includes the following specific symptoms of the disease:
- Having trouble urinating;
- The urge becomes more frequent, and the urination itself becomes difficult;
- There is also pain when using the toilet;
- The volume of urine excreted decreases and the shade also changes;
- Mucus particles may appear in the urine.
In the absence of proper medical treatment, pain symptoms increase and spread to the intestines and lower abdomen.
Also, for men at the age of 60, it should be remembered that prostatitis can proceed in an asymptomatic form, without showing itself in any way. However, this does not mean that the disease does not develop. Therefore, it is so important to periodically take urine tests to identify leukocytes and bacteria.
Methods for preventing prostatitis at age 60
To prevent this disease, a man must follow the following rules:
Treatment of prostatitis at age 60
Inappropriate treatment or its complete absence can translate an acute process into a chronic one. Chronic prostatitis does not have very pronounced symptoms, but as a result of a prolonged inflammatory process, damage to the tissues of the prostate gland and the vessels adjacent to it begins. And this, in turn, contributes to the complete loss of the prostate gland.
Also, another most common phenomenon is an abscess, which is accompanied by purulent inflammation. The cure of purulent inflammation is a rather long and difficult process, which in some cases ends in unfavorable prognosis.
Therefore, in the presence of existing chronic prostatitis, the following rules must be observed:
- Regular use of medications prescribed by the attending physician;
- Normalization of sexual activity;
- Compulsory exercise therapy;
- Complete rejection of bad habits;
- Having a full-fledged rational diet;
- Periodic testing of PSA or prostate specific antigen, which is capable of detecting the development of a malignant disease. At the age of 60 to 70, the norm for PSA is 4.5 ng / ml, no more.
Spicy, fatty, fried foods, alcohol, sweets, soda are prohibited foods that must be discarded.
The effectiveness of treatment primarily depends on the timing of seeking medical help. Therefore, when the first signs appear, it is better not to postpone until later, but to start treatment in time, since in the last stages it can be absolutely useless. A qualified specialist should definitely deal with the treatment of prostatitis.
Therapeutic measures are carried out by the following drugs:
- Rectal suppositories, to ensure normal metabolism;
- Injections necessary to maintain good immunity;
- Non-steroidal drugs are prescribed to slow the inflammatory process;
- Herbal enemas;
- Local instillation drugs;
- Broad spectrum antibiotics required for inaccurate pathogen detection.
These drugs have both positive and negative aspects, therefore, independent use and prescription is strictly prohibited.
For prostatitis, alternative methods of treatment are also used, which can not only strengthen the body as a whole, but also greatly facilitate the process of urination. One of the most popular are pumpkin seeds, which have a fairly high content of trace elements. Also, a positive effect in the treatment is given by parsley seeds, used in their pure form, and aspen infusion, which has a beneficial effect on blood circulation.
However, it should be remembered that traditional methods will not replace professional treatment and they must also be agreed with a doctor.



























