Home >
Erectile Dysfunction >
Peculiarities of bacterial prostatitis treatment
Peculiarities of bacterial prostatitis treatment
Chronic bacterial prostatitis is a type of infectious disease of the prostate. Medical therapy of this form is recommended by doctors to be carried out in hospitals with the appointment of antibacterial drugs. This technique helps to eliminate pathogenic microorganisms, accelerating the healing process.
Chronic bacterial prostatitis most often occurs in patients at a young age, accompanied by local and general symptoms.
Causes of the disease
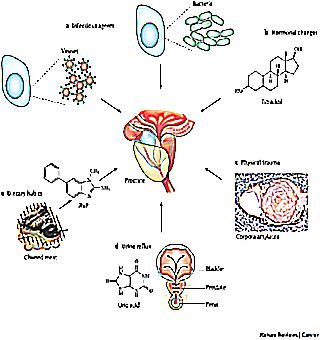
Chronic prostatitis of bacterial origin occurs against the background of the activity of harmful bacteria, viruses and fungi in the male gland.
The onset of the inflammatory process is due to penetration:
- staphylococcal bacillus;
- enterococci;
- enterobacter;
- intestinal bacteria;
- protea;
- Pseudomonas aeruginosa infection;
- Klebsiella.
The entire list of bacteria is called pathogenic flora. In a normal environment, these bacteria do not cause discomfort. Harmful microorganisms begin active life in a certain environment.
This includes:
- phimous pathology of the prostate;
- urinary tract infection;
- having sex with an infected partner;
- acute epididymitis;
- immunosuppression;
- surgery without antibiotics;
- change in the process of passing urine;
- chronic, bacterial diseases.
When microorganisms are activated, an inflammatory infiltrate is produced, which accumulates in the lumen of the glands. The active multiplication of bacteria provokes progressive inflammation. During the not started therapy of the acute stage leads to chronic, bacterial prostatitis. Chronic bacterial prostatitis is a consequence of the reproduction and growth of pathogenic flora. Treatment of this form of prostatitis begins with the identification of provoking factors for the selection of therapy.
Signs of bacterial prostatitis
Acute bacterial prostatitis begins with acute symptoms.
Treatment of bacterial prostatitis is prescribed based on the clinical picture of the stage of the disease.
At the initial stage, called catarrhal, inflammation is seen on the ducts of the prostate. Patients experience pain in the perineal area, which is given to the sacrum. Urination becomes frequent and painful.
The second stage is called follicular (damage to the lobes of the prostate). Characterized by strong painful sensations, which are marked by lumbago in the anal passage. Patients experience difficulty in emptying the urea, the stream is thin and intermittent, sometimes urine does not leave at all, which threatens the collection of biological material in the body. At the same time, the patient constantly has a subfebrile temperature.
The third stage is called parenchymal. During this process, both lobes (tissues) of the prostate gland are inflamed. During this process, a man feels severe intoxication, a rise in temperature to high levels. The disease is accompanied by acute urinary retention, sharp throbbing pains in the perineal area, severe constipation.
Diagnosing bacterial prostate pathology
It is very simple to diagnose the prostate gland for a bacterial disease. The patient cannot remain silent about problematic symptoms. Rectal examinations are necessary in cases of a non-exacerbated course of the disease.
A specialized specialist examines the prostate by palpation and takes the secret of the male gland for analysis. After that, the taken material is sent for bacterial sowing. Acute (bacterial) prostatitis is also examined by urine culture. This method allows you to detect harmful organisms that have led to the inflammatory process. This analysis determines the tolerance of the infection to medications (antibiotics).
Digital rectal examination is not permitted when patients have an acute form with fever and generalized intoxication. In these cases, rectal examination can provoke the spread of harmful microorganisms through the plasma with the development of sepsis. In addition, such an examination is not possible, since the patient feels severe pain.
When a patient says that he cannot reschedule a rectal examination, specialists choose another method.
This could be:
- urine analysis;
- sowing of the urethra epithelium for PCR studies;
- general clinical picture of blood;
- urine test;
- Plasma PSA (distinguish bacterial prostatitis from prostate cancer).
Investigations with an ultrasound apparatus are recommended for a detailed examination of changes in the structure of the gland. This method is carried out when acute inflammation has already been removed.
Treatment techniques
Treatment of bacterial prostatitis is not possible without taking antibiotics. These medicines help to destroy the pathogenic flora that caused the inflammatory process that led to the complication.
When diagnosed with acute bacterial prostatitis, treatment is prescribed only by a specialist. Recommendations for taking antibiotics are selected according to the severity of the pathology. Spontaneous therapy leads to exacerbation. The fact is that antibiotics are prescribed for certain types of microbes (the quick healing process depends on this). Microbes have a certain immunity (addiction to drugs) and for the effect to be effective, the agent is selected according to the sensitivity of microorganisms to the active substances of the drugs.
It will not be possible to cure bacterial prostatitis with drugs alone. You must adhere to a dietary diet.
How to treat bacterial prostatitis with nutrition?
Androgen deficiency is treated with a dietary regimen. You should use foods from the list.
- Vegetable oils containing fat-soluble vitamins. These are corn oil, cod (liver), fish oil;
- Preference should be given to a product with a large amount of vitamin A (carotene). These are pumpkin porridge, tomatoes, carrots, beets, persimmons;
- Protein foods with a high concentration of minerals and electrolytes. These are Eggs, young veal.
It is required to give up smoked, salty, spicy foods, seasonings, sauces, alcoholic beverages.
You can not lead a sedentary lifestyle, completely exclude hypodynamia. It is recommended to give preference to physical activity, to engage in physical culture.
The high efficiency of antibacterial treatment depends on the correct identification of pathogens. Severe exacerbations of prostatitis are treated with broad-spectrum antibiotics. The chronic form is treated with antimicrobial drugs macrolides, tetracycline, aminoglycoside, cephalosporin subgroup.
Prostatitis, provoked by staphylococcal bacillus, with a severe course, is difficult to treat. For treatment, antistaphylococcal antibiotics (Fusidin) are selected in combination with modern beta-lactam antibiotics.
Medicines of nitrofurans, interferons, sulfonamides showed good results of treatment. They are used in complex therapy.
Improvement of microcirculation, metabolism, biochemical process with an increase in the tone of the male gland is achieved using therapeutic exercises, thermal procedures, electrophoresis, mechanotherapy, rectal massage.
Massage Treatment
The most effective remedy in the treatment of Chronic prostatitis during remission of the disease is massage. The procedure is carried out every other day, in the future, sessions can be done less often (2 times a week). The full course takes a two month period. If the disease has an aggravated form or complications appear, the sessions are terminated.



























