Home >
Erectile Dysfunction >
Prostatitis and its manifestations
Prostatitis and its manifestations
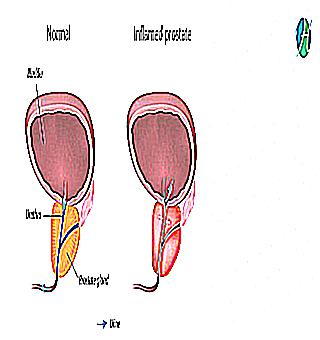
Prostatitis is a common disease among the stronger sex, such a diagnosis is noted in more than 80% of men, of which one third is diagnosed before the age of 45. According to statistical studies, it is known that every first patient out of ten suffers from prostatitis.
How is the disease characterized?
Prostatitis is a disease in which the prostate gland, called the prostate, becomes inflamed. It is located under the bladder, enveloping its neck. The appearance of pain during urination depends on the location of the prostate, since the urethra - the urinary canal passes through the prostate. With the inflammatory process, the prostate enlarges, the urinary tract is compressed, which causes pain when urinating.
In the stronger sex over 35 years old, enlargement of the prostate is often observed, which is considered a typical physiological phenomenon characteristic of many men. They usually have prostatitis when the genitourinary system is impaired, that is, with inflammation of the prostate gland.
Causes of prostatitis
The main reason for the development of prostatitis is considered by doctors to be a violation of blood circulation from a sedentary lifestyle, high weight, these factors cause an enlargement of the prostate.
Another reason for the onset of prostatitis is infection, it can get into the body as a result of a venereal disease in gonorrhea or urethritis, sometimes prostatitis develops as a result of complications after colds such as flu, tonsillitis, as well as from tuberculosis. Blood, lymph and unprotected intercourse can carry the infection.
Sometimes the cause of male disease is trauma to the pelvic organs and their soft tissues in case of impaired blood circulation. As a rule, drivers are most exposed to this insidious ailment, whose work is associated with constant vibrations, shaking, and increased stress on the muscles of the perineum. Frequent hypothermia with low physical activity also contribute to the development of the disease, chronic diseases of the genitourinary organs, hormonal imbalance with irregular sexual activity play a negative role.
Local symptoms of prostatitis
Prostatitis is characterized by indistinct symptoms. What are the first symptoms of this insidious male disease? Are there any bells that can be used to identify the problem that has arisen?
Prostatitis manifests itself variably. But in any case, there are basic symptoms of the disease that should alert men. However, prostatitis may not manifest itself for a long time, and then suddenly develop. Its symptoms also manifest themselves in different ways: in some patients there are several basic ones, in others in a whole complex of symptoms. Consider the symptoms that characterize the disease.
Pain syndrome
The most basic prostatitis syndrome is pain. Pain in the perineum or groin can be of a different nature: pulling, cutting, aching and pressing or bursting. In terms of intensity of manifestation and sensations, they are barely noticeable, and sometimes intolerable. With a complication of prostatitis, patients feel pain even without the act of urination.
Some people experience pain during bowel movements. The reason for this is that the prostate gland is constantly irritated by the products of the inflammatory process. There is pain of a aching, pulling or dull character. However, pain in prostatitis in men is localized not only in one place, they appear either in the perineum, in the groin or in the anus.
Increased body temperature
When an acute form of prostatitis begins, the process is accompanied by intoxication of the body, the appearance of a feverish state, and the temperature may rise. With purulent prostatitis at an early stage, its level reaches 40 degrees. In the late stage, on the contrary, the body temperature can drop to 35 degrees. Such a decrease is also dangerous for a person with the appearance of DIC. Identification of such symptoms of acute prostatitis requires timely treatment.
If the decision on the appointment of therapy is delayed, the disease can become chronic, then the treatment will require a long time and a lot of money.
Urinary Disorder
A number of symptoms of male disease are replenished with urinary disorders. In healthy people, the urge to urinate usually occurs about 5 times a day, but does not exceed 10-12 times. An adult releases about 1000-2000 ml per day. urine. When the volume of urine reaches 120-170 ml, a person begins to feel the urge. If urine accumulates more than 350 ml, there is a stronger urge to empty the bladder. When the prostate becomes inflamed, it enlarges and may obstruct the urethra, making it difficult to empty the bladder.
Inflammation of the prostate causes irritation of the receptors in the walls of the bladder, as a result of which disorders appear in urination:
- Frequent urination (pollakiuria) is observed, although there is no increase in daily urine volume;
- Urination occurs with effort and in small portions, sometimes in drops. The stream of urine is lethargic and intermittent. The products of the inflammatory process give false signals to the receptors of the bladder, but after coping with a small need, the person does not feel a sense of relief;
- Sore urination (stranguria) as the urethra narrows due to inflammation of the prostate;
- Urination is difficult due to squeezing of the urethra by an inflamed gland, in some patients ischuria develops in the impossibility of emptying the bladder;
- The urge to urinate occurs at night (nocturia phenomenon).
Suffering from prostatitis, when urinating, there is a burning sensation in the perineum. Urethral light discharge is observed.
Sexual Disorders
In addition to problems with urination, a characteristic expression of male disease is a disorder of sexual function, which manifests itself in various signs. Men are worried about erectile dysfunction during intercourse, and prolonged erections are often noted, especially at night. In addition, such patients have premature ejaculation, and the orgasm is significantly reduced. In the acute period of male disease, sexual disorders are of a temporary type and disappear.
However, in the chronic form of the disease, disorders in the genital area become permanent. Frequent signs of sexual dysfunction in chronic prostatitis are expressed in the form of painful erection, loss of sexual desire, and the presence of blood in the semen. Launched prostatitis threatens infertility. From these unpleasant problems, men experience nervous stress, becoming desperate. Their mood often changes, a feeling of apathy appears, in some, nervousness is expressed as a manifestation of aggression. Patients suffer from sleep disturbances, frequent insomnia.
Blood in urine and semen
The appearance of blood in urine and semen is considered a rare, but very dangerous sign, it is called a symptom of hematuria.
There are several causes of hematuria:
- When the prostate tissue melts with the release of pus, the process captures an area close to the blood vessel, while the vessel is perforated into the cavity of the urethra.
- When inserting a catheter into the bladder.
- For prostatitis complicated by tissue hyperplasia, often malignant.
Laboratory tests to confirm symptoms of the disease
To check for prostate inflammation, blood and urine tests are done in a laboratory.
Instrumental diagnostic methods are also used
All these methods with the patient's history will help create a picture of the development of the disease.
Symptoms of acute prostatitis
Like other diseases, prostatitis has an acute and chronic form.
What symptoms characterize the acute form of the disease?
- The most important symptom is pain when urinating.
- The patient begins to feel unwell and weak.
- Frequent headaches are accompanied by fever for no apparent reason.
- Pain of a pronounced character in the perineum appears not only during urination, but also during defecation, which is determined in the entire groin area.
- The patient often goes to the toilet, but urination does not bring relief, because it is not possible to get rid of the accumulated urine.
- Severe cases are accompanied by acute urinary retention.
- Stretching discharge appears.
- Erectile dysfunction is noted.
- The patient feels increased irritability and nervous excitability, discomfort.
- Fluids can be seen floating in the urine.
The appearance of at least one of the listed symptoms should alert men.
Chronic prostatitis symptoms
The chronic form of the disease differs from the acute one in its course without symptoms. It mainly proceeds secretly, the characteristic signs of the disease are not clearly manifested. Symptoms of a chronic course are poorly expressed, representatives of the stronger sex do not always pay due attention to the feeling of discomfort and are in no hurry to go to the urologist.
- In the chronic form of the disease, pains localized in the perineum and groin pass quickly and are poorly expressed.
- There is a change in the duration of sexual intimacy, both in the direction of decreasing and lengthening, the brightness of intimate relationships dims. In the morning, you can see white discharge from the urethra, and you can find the presence of whitish or yellowish flakes in the urine.
- In the inflammatory process, the lumen of the urethra narrows, for this reason, the act of urination is disrupted. The stream of released urine is lethargic and weak, without pressure, urine is sometimes excreted drop by drop. Emptying becomes difficult at the beginning and at the end. Patients do not feel complete emptying of the bladder.
- Patients have more frequent urination, but in small portions, especially at night. This leads to the irritating effect of the inflammatory process on the nerve endings of the bladder.
The identification of these symptoms shows that an insidious and dangerous disease develops, requiring immediate treatment. No need to self-diagnose and self-medicate. Only an experienced specialist - a urologist will make an accurate diagnosis and prescribe the correct treatment. In the absence of timely medical care, sexual desire may fade away, reproductive function may be impaired, prostatitis not cured in time can lead not only to infertility, but also to complications in the form of a secondary infection of the genitourinary organs and urinary tract, in particular to chronic renal failure.
The bladder is also threatened with the development of acute urinary retention. With the progression of prostatitis, the outflow of accumulated urine is disturbed, which can lead to hardening of the walls of the bladder.
These are the symptoms inherent in acute and chronic prostatitis, which cannot be ignored, but must be responded to immediately. Very often a person does not want to admit that he needs to be treated, but that the appearance of problems with potency and nervousness are trying to be explained by the lack of proper rest and fatigue. Therefore, for the timely detection of the disease, it is necessary to undergo medical examinations every year, according to the results of which it is possible to establish the presence of the disease and begin treatment in the early stages of development.
Men should be aware that prostatitis can be asymptomatic. The inflammatory process in the prostate does not always manifest itself clearly, and the diagnosis can only be made by urine and blood tests. In order not to be mistaken with the diagnosis and classification of the disease, it is necessary to undergo a thorough examination in several medical institutions. In no case should you self-medicate prostatitis. After the detection of the disease, complex treatment should be started immediately, saving on health and delaying prostatitis is impossible!



























