Home >
Erectile Dysfunction >
Removed from the bladder for prostatitis
Removed from the bladder for prostatitis
If you have any discomfort in the area of the drained organ, do not hesitate to consult a doctor. Many urological operations end with temporary or permanent drainage of the organ
The system used for temporary and permanent drainage of the urinary tract also includes urinals. Their patient or his relatives can pick up at the pharmacy. Urine bags with a capacity of 1500-2000 milliliters are usually attached to the bed, ottoman - the patient's sleeping place with the help of special fasteners, or a bandage, or large safety pins.
For constant wear, these urinals are heavy, uncomfortable, it is better to use smaller ones, with a capacity of 750 milliliters. They are attached to the thigh with self-adhesive Velcro tape, and best of all with canvas belts.
This is primarily provided by the catheter heads and balloons mentioned at the beginning
It needs to be changed periodically (once a week). And if urine leaks, change it daily. When you leave the hospital, the doctor explains how to deal with it. But it is better if this procedure is done by a doctor or nurse. When this is not possible, one of the relatives can master it, since it is inconvenient for the patient himself to do this.
But this does not mean that you can not contact the urologist for so long. A patient with a drained renal pelvis, for example, would like to see a specialist at least every 7-10 days
For washing, a warm solution of furacilin is used. At home, you can dilute 2 tablets of furacilin in 400 milliliters of boiled water. Strain the solution through a double layer of gauze. A 3% solution of boric acid is also suitable.
Pre-boil the syringe, rinse the syringe with boiling water, and between procedures keep it in a disinfectant solution: 3% chloramine or 2% chlorhexidine. They are sold in pharmacies. After the introduction of portions of the solution, remove the syringe from the catheter. The rinsing solution will flow freely into the substituted basin or tray.
How often should this procedure be repeated? If a therapeutic effect on the mucous membrane of the bladder is required, washings can be daily. And if there is a need to periodically flush out mucus and salts from the bladder, these procedures are performed less frequently. How often - the doctor will say.
The urinal must, of course, be kept clean. As it fills, it is emptied and washed. It is best to use a slightly pink solution of potassium permanganate for this. The adapter and the urinal can be rinsed with running water by substituting the adapter of the urinal under a stream of water from a water tap. With the accumulation of salts, hard-to-wash plaque on the bottom and walls, it is advisable to replace the urinal with a new one.
Sometimes stones form in drained cavities, which is manifested by pain in the area of the kidneys or bladder, and when the stone leads to the activation of the inflammatory process, the body temperature also rises. In this case, you should immediately consult a doctor, since the process of stone formation can disrupt drainage, the catheter will come out of the drained organ, and the fistula, especially in young people, can even close within a few hours. Then you have to resort to repeated surgical intervention. Try to prevent this and if you experience any discomfort in the area of the drained organ, consult a doctor.
Suprapubic urinary catheter
An epicystostomy is a special catheter for removing urine from the bladder.
A urologist installs an epicystostomy if the patient has problems emptying the bladder and if it is impossible to do this through the urethra or if a urinary catheter is needed for a long time.
An epicystostomy is inserted through the anterior wall of the lower abdomen into the bladder. Epicystostomy is the best alternative to an indwelling bladder catheter. The catheter is held either by a special balloon filled with liquid and located at the end of the catheter, or the catheter is attached to the skin of the abdomen with sutures. For the best fixation of the catheter, a patch can be used as an additional attachment.
Epicystostomy does not create any restrictions in movement, does not cause rubbing of the urethra. Also, epicystostomy allows you to monitor the possible recovery of spontaneous urination after urinary retention.
As a rule, an epicystostomy is connected to a urinal bag. With the permission of the urologist, the catheter can be closed with a special stopper.
What is the most important and what should be observed when an epicystostomy is placed?
The most important thing in caring for an epicystostomy is cleanliness.
- Wash your hands thoroughly with soap and warm water before and after touching the epicystostomy catheter, urinal bag, or catheter stopper.
- Avoid touching the inside of the catheter, the parts connecting the catheter to the urinal bag, and the sealing surface of the catheter stopper.
- The insertion site of the catheter in the lower abdomen should also be kept clean. Wash the skin around the catheter with warm water and soap or wipe it with a swab moistened with water 2 times a day.
- You can take a shower. Saunas, baths and swimming should be avoided.
- Check every day that the catheter is well secured. It is also important to pay attention to the condition of the skin around the catheter.
- Check every day for any discharge from the catheter site. If the presence of secretions is detected, then the catheter entry site should be covered with a thin and breathable bandage.
- The dressing must be removed before showering. Apply a new bandage after washing. Before applying a new bandage, it is recommended to leave the skin around the catheter uncovered for 10 minutes (the so-called air bath).
- If there is no discharge and the skin around the catheter does not show signs of inflammation, then the dressing and patch can be omitted.
How to properly handle the urinal bag?
When connecting the catheter to the urinal bag, secure the latter so that the catheter does not stretch and neither the catheter nor the urinal bag is double-folded.
When walking and standing, make sure that the urinal bag is secured at a level below the bladder (for example, with a tape or strap on the thigh or with a special bag). If you are lying down, the urinal bag should be at a level below the surface of the body (for example, on the side of the bed), but not on the floor. This position will ensure unimpeded discharge of urine into the bag and will not allow urine to flow out of the urinal back into the bladder.
Use a urinal bag that can be emptied through the valve (cork) at the bottom of the bag.
The urinal bag should be changed at least once a week, if necessary (for example, damage to the bag or blockages) more often.
Adequate fluid intake
- If drinking a lot of liquid is not contraindicated for you due to some other illness, then try to drink more during the day;
- The amount of fluid you drink per day should be at least 1.5-2 liters;
- Increased fluid intake ensures a constant flow through the urinary tract and catheter, thereby helping to avoid inflammation and sediment.
Using a catheter stopper
- If your doctor advises you to try emptying your bladder naturally, a stopper can be placed on the end of the catheter instead of a urinal bag.
- When the catheter is plugged, try to empty your bladder naturally.
- If you managed to empty your bladder, then measure the amount of urine remaining in your bladder. To do this, remove the stopper from the catheter and release the remaining urine into the measuring dish. If the amount of remaining urine does not exceed 100 ml, then inform your doctor about this.
- If it is not possible to empty the bladder naturally, then do this by removing the plug from the catheter every 4-5 hours. Urine should be drained into a measuring dish or into the toilet.
- If desired, you can always reconnect the urinal bag to the epicystostomy catheter.
- Used bags and corks are disposed of in the same way as normal household waste.
- New urinal bags and stoppers can be purchased at the pharmacy.
Possible problems
The following problems are possible with epicystostomy:
- Increased body temperature;
- Pain in the lower abdomen;
- Reduce urine output;
- Changes in the color of urine mixed with blood or sediment, turbidity, an unpleasant odor is also possible;
- Clogging or damage to the catheter, slippage of its bladder.
If you experience any of the above problems, please contact:
- With your family doctor;
- Admission department of the nearest hospital;
- Your doctor or urology nurse;
The need for a catheter in the epicystostomy, its removal and replacement is decided by the doctor or nurse, guided by your condition. The above procedures are carried out only by a urologist or a trained nurse.
More information can be found on the website www.urology-MChS.rf
Urinary catheter care
Responding to your letters My husband has a permanent urinary catheter. Please tell me how to take care of him.
The presence of a permanent catheter in a patient to remove urine from the bladder provides for careful hygienic care and compliance with the optimal drinking regimen for patients.The patient needs to drink fluids more often, reducing the concentration of urine and thus reducing the likelihood of developing a urinary tract infection. Hygiene measures should include care for the perineum and the catheter itself. To care for the patient's perineum, you will need: rubber gloves; towel; oilcloth; napkins or paper towels; garbage bag; dirty laundry bag; cotton swabs; clip; a jug or basin for washing; soap. The procedure is performed as follows: lower the head of the bed so that the patient lies horizontally on his back; cover the patient with a blanket, leaving the pelvis and legs open; put an oilcloth under the buttocks of the patient and put a vessel on it. Ask him to bend his knees and lift his buttocks. If he is unable to do this, turn him over on his side and spread the oilcloth, then turn him over again on his back; pour warm water into a pitcher; put on gloves; stand to the right of the patient, take a clamp with a cotton swab in your right hand, and a jug of warm water in your left hand. Start processing the perineum from top to bottom: from the genitals to the anus (cotton swabs need to be changed after each movement from top to bottom); dry the skin of the perineum in the same direction with a dry cloth; using cotton swabs, wash and dry 10 centimeters of the catheter, starting from where it exits the urethra
Urine excretion in this case is carried out through a rubber catheter. The catheter is changed once a month, as it can become clogged with urinary salts, crack when replaced or removed, and tear. In the presence of epicystostomy, the patient needs periodic washing of the bladder (at least 2 times a week). At home, care for epicystostomy and urine collection during the day is carried out as follows. When caring for the skin around the epicystostomy: the skin around the epicystostomy is washed with warm boiled water or a solution of furacilin (a weak solution of potassium permanganate can also be used); the surface of the skin is dried with napkins; Lassar paste or other ointment recommended by the doctor is applied to the skin around the epicystostomy; after absorption, the remnants of the ointment are removed with a napkin. When caring for an epicystostomy, it is necessary to monitor the functioning of the drains. It is important to notice in time the appearance of traces of blood in the urine, the cessation of the outflow of urine through the drainage, as this may be due to blockage of the drainage, prolapse or bending of the catheter.
Bladder flushing It is best to entrust this procedure to a medical professional. If it is not possible to constantly seek the help of a specialist, ask your doctor or nurse to tell you in detail and demonstrate how this procedure is performed. Our recommendations can only serve as an additional reminder. To wash the bladder: put on sterile gloves; draw 200 ml of a sterile solution of furacilin at a concentration of 1:5000 into a sterile Janet syringe (it is better to purchase a ready-made solution in the production department of a pharmacy, rather than prepare it at home on your own) or a 3% solution of boric acid; disconnect the catheter from the urinal; insert the end of the syringe into the opening of the catheter; carefully injected into the bubble 30-40 milliliters of solution; disconnect the syringe from the catheter; substitute a tray or other container under the flowing liquid; The procedure is repeated until clean wash water appears. To collect urine during the daytime, the outer end of the catheter is lowered into the urinal, which in walking patients is hung under clothing near the abdomen or thigh. At night, and also, if the patient does not walk, the outer end of the catheter is lowered into a container attached to the bed.
General recommendations Patients with epicystostomy require very careful care. They are recommended full regular and sufficient, but not excessive, nutrition. Spicy and salty foods and alcohol are excluded from the diet. It is advisable to stop smoking, or at least significantly reduce the number of cigarettes smoked. Encourage the patient to special therapeutic exercises and walks, help them to do them. Be very tolerant of the whims of the patient.
Installation and care of a cystostomy and catheter for prostate adenoma
A catheter for prostate adenoma is used for internal administration of anti-inflammatory and therapeutic drugs, as well as improving the function of urination.
A catheter for prostate adenoma is installed in the postoperative period. Required immediately after surgery. Catheterization reduces pressure and irritation on tissue damaged during surgery.
Draining the bladder for BPH has the following benefits:
- Unhindered entry of medicines and antibiotics. After the operation, washing with furacilin is mandatory. The solution reduces tissue irritation, accelerates wound healing and prevents the spread of infection.Entering the drug into the bladder using a catheter increases the effectiveness of drug therapy.
- Removal of blood clots and dead fragments of the prostate. During surgery, 30% of the prostate gland is removed. Most of it is removed through the endoscope. The remaining particles exit through the urethra. Dead tissue is the cause of sepsis in the body. Flushing the bladder through a catheter speeds up rehabilitation and reduces the likelihood of complications after surgery.
- Reducing the load on injured tissue areas. A surgical operation, regardless of the type of operation (vaporization, ablation or TUR), injures healthy tissues. The body's defense mechanism is activated, aimed at restoring the normal function of internal organs. There is blood flow to the prostate gland, which leads to swelling, as in the case of a severe bruise. Often, after surgery, the urethra is compressed to such an extent that going to the toilet without a catheter becomes impossible.
Methods of installing a catheter for prostate adenoma
The methods of catheterization are different, they differ in purpose, the risk of complications and are prescribed strictly according to individual indications:
Traditional catheterization - with this solution, a Foley catheter is placed. The device has the form of a flexible tube with a special balloon at the end. After insertion through the urethral canal, the bladder is inflated to secure drainage in the bladder. A reservoir for collecting urine is attached to the other end of the Foley tube, usually fixed to the patient's leg. Through the catheter, antiseptics and antimicrobials are injected into the prostate, and the remnants of dead tissue are removed. The device is effective for short-term use
For this, a small incision is made in the abdominal cavity, where drainage is inserted. An installed cystostomy with prostate adenoma without proper care becomes the cause of infection, complete sepsis of the body or an infectious disease
The duration of the catheter installation in prostate hyperplasia is determined by the degree of invasiveness of the operation performed, the patient's condition at the time of surgery and the speed of postoperative recovery of the body:
- Type of surgery: Minimally invasive techniques: vaporization and ablation require short-term catheterization lasting no more than a day. Manipulations to install and remove drainage are carried out during mandatory hospitalization for 2-3 days.
- After TUR, the period of wearing increases to 2-3 days.
- The skin around the entrance is regularly washed with boiled water, a solution of potassium permanganate or furacilin.
- The skin area is wiped dry and smeared with Lassar paste.
- Control the constant outflow of urine
- Care of the catheter is also required inside the drainage system located in the bladder. Regular flushing of the system is required. This way, you can prevent clogging of the catheter with sand and ingestion of infectious agents. For washing, they take the Janet device with a washing solution filled into it: 3% boric acid or furacilin, at a concentration of 1k 5000. The urinal is disconnected from the system, a syringe is connected and about 40 ml of the substance is injected , after which the syringe is disconnected from the system
- Replacement of the system is carried out 4-8 weeks after installation. The first time manipulations are carried out in the clinic. Re-replacing is done by yourself.
The skin around the catheter may grow when worn for a long time, which leads to loss of drainage. There is a slight leakage through the hole around the inserted catheter, which requires constant treatment of the skin area with special solutions. If the situation does not correct itself, qualified medical assistance will be required.
How to change a catheter for prostatic hyperplasia
The catheter is reinserted after 4-8 weeks. The replacement is performed by a urologist. If the patient is immobilized, manipulations are carried out at home.
But studies have shown an extremely negative effect of this approach on the immune system and bladder flora. The replacement technique does not allow the body to get used to the action of antibiotics, which is especially important in case of an infectious lesion.
At the same time, the correct operation of bag-shaped urinals is required. The recommendation is to empty the container when it is about half full. After a week of use, replace the urinal with a new one.
After the appointment of catheterization, the attending physician is interested in the shortest possible time for draining the patient's bladder. Long-term wearing is indicated only in extreme cases and is fraught with complications.
Unlike a conventional catheter inserted through the urethra, the bladder cystostomy is inserted through the abdominal wall directly into the urinary bladder.A special device is used in case of pathology or damage to the urinary canal, when urine output is impossible in other ways.
What is a cystostomy?
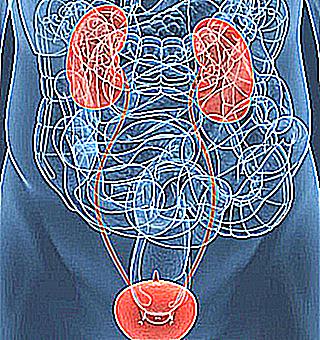
In the absence of pathology, urine passes independently through the urinary system and is freely excreted from the body. This movement is performed from the kidneys through the ureters to the bladder, after which it is excreted through the urethra. When there is a disturbance in the genitourinary system that affects normal urination, a drainage system (catheter) is placed. It carries urine
Due to the physiological characteristics of the body in men, the installation of a urinary device is carried out much more often.
Indications for use
A bladder cystostomy is placed when:
A cystostomy of the bladder is installed for injuries, obstruction, stagnation of urine, after complex operations.
- Urethral surgery required.
- the canal was injured, which made it impossible to remove urine through the urinary canal;
- there is an acute violation of the outflow of urine;
- there is an obstruction (dysfunction of muscle tissue, prostate enlargement);
Back to index
Contraindications for bladder cystostomy
In certain cases, the installation of a cystostomy is not possible. There are 2 types of contraindications for such a procedure. Manipulation is not carried out with such pathologies:
- cancers in the urinary system or in nearby organs;
- malformations - features of the structure of the urinary organ, when it is impossible to visualize or palpate the organ for the procedure.
With the following pathological abnormalities, the decision of the possible installation of a cystostomy is made by the doctor:
- poor blood clotting;
- after operations in the abdomen;
- prostheses of bones, artificial tissues in the pelvic area.
Back to index
Cystostomy procedure
All manipulations are carried out with the use of painkillers at the incision site. There is no need for further hospitalization of the patient. The operation takes place in several stages:
The importance of proper care
The following care is required for a cystostomy:
- inlet processing;
- bladder lavage;
- replace fixture.
You can process and wash the device at home. Its replacement is possible only in a medical institution. It is held once a month. Daily manipulations include the treatment of the area near the incision. To do this, use:
- disinfection of the skin around with alcohol or special solutions;
- bandaging.
Washing of the cystostomy occurs depending on the change in the color of the urine, usually 1 time in 2-3 days. Perform this manipulation several times until the color of the outgoing liquid becomes transparent. Then connect the urinal back.
Caring for a bladder cystostomy requires external sanitation, rinsing and replacement of the device.
To restore the normal outflow of urine, you need to train the urinary system. Bladder training goes through the stages:
- periodic compression of the drainage system;
- attempts to urinate normally.
Back to index
Removal of cystostomy
The procedure is performed when the outflow of urine is fully restored. Removal of the device is done in the hospital in a stationary mode. This procedure consists of several stages:
If the wound looks normal, then a special bandage is applied to it or stitched. She heals on her own. If there is suppuration, then additional therapeutic measures are required for its treatment and healing. Removal of a cystostomy does not take much time; after the operation, the patient can immediately leave the hospital.
Possible consequences
Complications after such a procedure can cause:
- improper care of the cystostomy;
- development of an infectious purulent lesion;
- inflammatory process;
- Bleeding and perforation of the colon.
Often, the installation of a cystostomy causes psychological consequences. Due to the constant discomfort, the procedure can lead to depression. It is important to understand that this device saves lives, and it is installed only when there is no other option to fix the problem.



























