Home >
Erectile Dysfunction >
What are the signs of prostatitis and adenoma recognition
What are the signs of prostatitis and adenoma recognition
An inflammatory process in the prostate can occur in almost every member of the stronger sex. The condition of the prostate is responsible for a stable erection, sexual activity, urinary tract function, procreation. Most often, men suffer from prostatitis or adenoma. These pathologies affect the urinary and genital areas of patients. Diseases are not related. What signs of prostate and adenoma are observed in patients, how to avoid diseases?
By what signs is prostatitis recognized
Inflammation of the prostate is called prostatitis. Pathology occurs in acute and chronic form. The bacterial course of the disease is marked by a painful syndrome in the pelvic area, and an outbreak of asymptomatic disease occurs, which the patient does not even know about. Acute inflammation of the prostate gland, most often occurs due to the penetration of harmful microorganisms along the pathways of the ascent of the urethra or through the blood from the focus of chronic infection. Signs of prostatitis and adenoma are similar.
Factors provoking inflammation of the glandular organ:
- pathological processes of the rectum (cracks, proctitis);
- STI diseases;
- frequent freezing;
- inflammation of the urethral canal;
- sedentary work, sedentary lifestyle;
- urolithiasis;
- irregular sexual activity;
- diseases of the upper and lower respiratory system;
- stagnation of blood in the organs located in the pelvis.
Acute prostate has the following clinical picture of symptoms:
- pain, dysuria against the background of intoxication;
- temperature rise;
- weakness;
- sluggish;
- chills;
- painful emptying of urine;
- pain syndrome in the perineum, groin, testicles;
- frequent urge to use the toilet;
- painful discomfort in the sacro-lumbar spine;
- painful symptoms of the abdomen, pubic area.
Patients suffering from acute prostatitis observe impaired urination with the appearance of dysuric phenomena:
- painful sensations of the urethra;
- burning sensation;
- frequent outflow of urine;
- increased urge;
- turbid consistency of the rejected liquid with characteristic impurities.
Impaired outflow can provoke acute urinary retention.
Additional symptoms of prostatitis
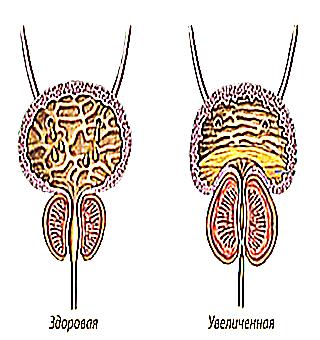
With prostatitis, an increase in the size of the glandular organ occurs. When a large size is reached, the surrounding tissues are compressed, while constipation, pain during stool, rejection in the form of characteristic discharge from their urethral canal are observed.
The objective symptoms of an acute form of prostatitis is an enlarged gland, which is found on rectal, digital examination. During palpation, the density, soreness of the organ is determined. According to the analysis of urine, transparency, leukocytes, sediment are examined.
Symptoms of prostatitis and adenoma are carefully investigated by urologists. When testing the secretory fluid, pus or blood may be detected. This indicates the occurrence of catarrhal prostatitis. If treatment is not carried out on time, the pathology can turn into follicular, and then into parenchymal prostatitis. The acute form is dangerous by the transition to the inflammatory process of urea, pyelonephritis, sepsis.
How chronic inflammation manifests itself
The chronic process differs from the acute one, it manifests itself as exacerbations with improved health. In chronic pathology of a bacterial nature, pain is felt in the area of the scrotum or the lower abdominal cavity. Among the symptoms, there is a disturbed process of emitting fluid with pain, signs of weak potency appear.
Patients with chronic inflammation in the prostate during the eruption of seminal fluid do not feel the fullness of the sensuality of orgasm.
Nonbacterial prostatitis is manifested by persistent pelvic pain that lasts for months. The painful syndrome radiates to the groin area. Some men do not feel anything at all, since the pathology proceeds without recognizable symptoms. It is possible to diagnose such an inflammatory process only after collecting anamnesis (instrumental examination, analyzes).
What are the signs of adenoma recognition
Signs of male prostatitis and prostate adenoma are diagnosed by differential diagnosis. Adenoma of the glandular organ is called benign hyperplasia. Adenoma and prostatitis are classified as a benign pathological process. Basically, the disease manifests itself in older men (after 45 years). The older the patient's age, the more the risk of adenoma of the gland increases.
The main factor in the onset of a benign process is old age and a malfunction of the endocrine system (hormonal calapse in estrogens and androgens).In patients with adenoma, urination is impaired due to obstruction of the fluid pathways.
Patients highlight signs of obstruction:
- reduced head during outflow;
- intermittent jet;
- decreased daily emptying;
- delayed urinary excretion;
- difficult and painful urination.
Other signs of BPH:
- nocturia;
- increased urge to use the toilet;
- rarely incontinence.
At the first disturbing signs and discomfort, you need to contact your specialist doctor. The specialist will conduct a number of studies and prescribe adequate treatment. Adenoma is dangerous for its complications.
What says about the onset of adenoma?
The disease is recognized in three stages:
Important! A benign neoplasm forms very slowly, so men often simply do not pay attention to the discomfort that appears. Patients go to a medical facility when problematic trips to the toilet appear.
Symptoms of prostate adenoma cannot be ignored, it is dangerous by the transformation of a benign process into a malignant one.
What are the dangers of a patient with prostate adenoma
The consequences of prostate adenoma without timely therapy have disappointing forecasts.
The disease provokes the emergence of new pathological processes in the form of:
- urolithiasis;
- constantly overflowing urine;
- cystitis;
- renal or urethral inflammation;
- chronic renal failure.
These diseases are not fatal, but they significantly impair the usual life.
How is the diagnosis done
A narrow-profile specialist conducts diagnostics. This is usually done by a urologist. The doctor asks the man for symptoms, listens to complaints, after which a thorough examination is prescribed.
The first symptomatology in a patient with an adenoma is similar to other inflammatory processes occurring inside the urinary and genital area.
To clarify suspicions, a number of measures are being taken:
- urine and plasma testing (general);
- ultrasound diagnostics;
- rectal palpation of the glandular organ through the anal canal.
Prescribing therapeutic manipulations
If the first manifestations of adenoma appear, the doctor prescribes the use of drugs to inhibit the formation of the tumor process and relieve puffiness. Large tumors that can cause complications (blockage of the fluid outflow canal) are removed. The surgical method is used for stage 2-3 inflammation.
After surgery, patients may experience:
- worsening sexual condition;
- blood loss;
- an outbreak of inflammation against the background of infection.
These complications are not permanent, after the patient's rehabilitation, they disappear on their own.
How is inflammation of the glandular organ treated
The male gland is designed to produce secretory fluid, which is a constituent of semen. The prostate is responsible for the regularity of urine flow. It is a trapezoidal organ, about the size of a walnut. The gland also prevents bacteria from entering the organ.
At the slightest problems with the performance of the prostate gland, irreversible pathological processes occur.
In general, a conservative technique is recommended for the treatment of the prostate. The urologist prescribes combination therapy. The use of antibiotic agents (fluoroquinols, tetracycline group, macrolides), medications with analgesic effect, alpha-blockers, enemas is recommended.
The patient is advised to enter sexual rest, proper diet, organ stimulation. Acute fluid retention is treated with catheterization. Antispasmodics, immunomodulatory drugs, vitamin complexes, physiotherapy procedures are prescribed.
Hyperplasia is treated with adrenergic blockers, inhibitors, alpha-reductase agents. In an advanced situation, surgical assistance is offered in the form of transurethral resection or prostatectomy. Despite the similarity of symptoms of prostatitis and adenoma, different treatment methods are prescribed.
To control his health, a man must conduct regular scheduled examinations, then the pathological process can be prevented at an early stage of development.



























