Home >
Erectile Dysfunction >
Operative help for prostatitis
Operative help for prostatitis
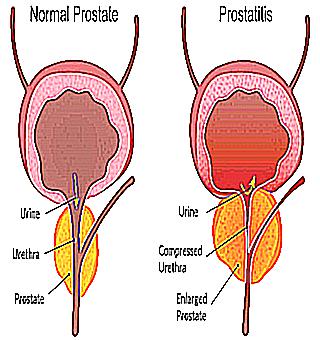
Surgery on the prostate is carried out after weighing the entire risk, both by the patient and the doctor. Any surgical decision is an ordeal, with unpleasant, risky and fraught complications. Inflammation of the prostate gland is called prostatitis. The prostate is located under the urethra, around the urethra. With a normal prostate gland, the urine channel is free for urine to drain, and the enlarged prostate gland constricts the urinary channel.
When is the operation indicated
Operation prostatitis is the removal of excess growths of prostate tissue. Surgical intervention is carried out in cases where other methods of therapy have proven meaningless.
Surgery is indicated when:
- constricted urethra obstructs urine flow;
- inflammation in the seminal vesicles with impaired outflow;
- prostate sclerosis;
- prostate enlargement leading to kidney failure;
- for male gland volumes exceeding 75 mm.
Prostatitis surgery is not performed on patients with liver failure, cirrhosis, cardiovascular pathologies, mental disorders, diabetes mellitus, serious respiratory diseases.
Before surgery, specialists take urine and blood for analysis. With the help of an anesthesiologist, the type and dosage of anesthesia is determined. The day before the operation, an enema is done to cleanse the intestines.
Taking tissue for research in laboratory conditions
After applying the surgical intervention, some problems are possible:
- there may be bleeding and clots at the surgery sites;
- problematic passage of urine through the canal, urinary retention or urinary incontinence);
- inflammatory symptoms.
Very often, urologists prescribe the use of the drug Prostodin to restore and prevent prostatitis in men. This is a natural preparation made on the basis of bee honey, a complex herbal collection (peony, chamomile, mint, plantain, nettle, fireweed, hazel). Sbiten contains vitamins of group B, PP, C. Thanks to this amazing composition, unpleasant symptoms leave the patient in a short time.
The product eliminates the inflammatory process in the prostate, improving health is noted after the first use. According to doctors, patients should adhere to a healthy diet, not overload with physical activity, and transfer sexual intercourse until the moment of complete recovery. For the first two days, the patient has a catheter to remove plasma from the urea. Upon receiving positive tests, the patient is discharged from the hospital.
Types of surgery
Surgery to remove pathology is possible in several ways.
Removal: prostatitis transurethral surgery (resection)
This technique is designed to remove the inside of the prostate. This technique is considered the most popular in surgery. The same method is used to treat benign hyperplasia. This surgical solution has alternative methods.
Before surgery, a standard study is prescribed: urine, plasma - general, biochemical analysis, coagulation study. The procedure is performed under general anesthesia or inserted into the spinal cord. It depends on the patient's state of health.
On the day of the operation, food and water should not be consumed, this may affect the perception of anesthesia.
TURP does not have a long recovery period after surgery, which cannot be said about prostatectomy (open exposure), there are practically no complications after a treatment session.
The only drawback after the surgery is the pain when urinating, which manifests itself in the first days after the procedure.
Prostatectomy
This operation is performed under the condition of a strong enlargement of the prostate gland, in case of complications, damage to the bladder. An incision is made in the lower peritoneal region (retropubic intervention), sometimes between the scrotum and the anus (perineal intervention), part of the prostate or the entire organ is removed.
- Before the surgical solution, an ultrasound examination is performed, cystoscopy, magnetic resonance imaging are done, some tests are taken: blood, urine, prostate-specific antigen (PSA), an examination by an anesthesiologist.
- Do not eat or drink water on the day of surgery.
- Prostatectomy is an effective therapy that heals the prostate gland by eliminating associated problems.
- The technique has its drawbacks: long postoperative recovery after surgery (30 days or more). The patient is in the hospital for the first seven days after surgery.There is a threat of high blood loss, damaged nerve fibers affect the manifestation of a normal erection. Complete erectile dysfunction sometimes occurs.
Laser resection of the prostate
The newest progressive method, which is carried out using endoscopy. The operation under consideration allows you to remove the adenoma with a laser. Resection is similar to TUR, but it takes less for a session, moreover, this method of treatment is completely bloodless and sparing. After the session, the patient's body quickly recovers. Patients are not hospitalized. Laser vaporization takes place by evaporation of damaged tissues by laser action. The patient gets complications in very rare cases.
This could be:
- urinary incontinence;
- erectile dysfunction;
- inability to ejaculate.
During the operation, the affected tissue is destroyed, the size of the prostate gland decreases. The bloodlessness of the operation is due to the sealing of blood vessels that do not bleed. Before the operation, tests (blood, urine) are taken, an ultrasound scan, a biopsy is done. Food and water are not consumed on the day of surgery.
The instrument penetrates into the urethra without incision, this does not lead to bleeding and prolonged inpatient stay. After the operation, the recovery period lasts for three days. During this time, symptoms disappear, the quality of life improves.
Abscess drainage
The urological surgeon cuts the closed abscess through the anal canal or perineum, a rubber drain is inserted into the dissected cavity of the purulent filling.
Before the operation, a transrectal examination is carried out, tests (blood, urine) are taken, a proctologist is visited.
After the operation, there is no need for a long rehabilitation period, moreover, there is no loss of sexual activity. In some cases, there is a risk of incomplete removal of the abscess, in which bacteria can enter the body.
Notes
Any surgery for prostatitis in all men has risks and benefits. Risks include:
- reaction to anesthesia;
- bleeding;
- infection;
- fused urethral lumen.
Bleeding
The most common complication after prostatectomy (open surgery). There is a network of blood capillaries around the prostate gland, which leads to the fact that patients lose from 06-0.7 ml of plasma during the operation. Sometimes there is more blood loss. Then a blood transfusion is required.
Infectious signs
Fever, swelling, chills, drainage from the incision site.
After the surgery, a non-random urine leak occurs, which stops after a few days. Older men (after age 65) may develop persistent incontinence.
Possible complications after a surgical solution
After prompt action, complications are possible that affect:
- urine outflow disorders;
- traces of plasma in urine;
- bleeding when urinating;
- pathology of acute urinary retention;
- manifestation of infection.
However, the patient's attitude has a great influence on the result of the surgical operation. All difficulties with complications are temporary and go away on their own. The body is restored gradually. After the operation, therapeutic therapy is required only after the infection, during the intervention.
Traces of plasma appear a couple of weeks after the procedure, this is due to the rejection of the crust, which is formed in the area of resection. Initially, at first, the plasma in the urine does not bother the specialized specialist. Even when the urine is pretty bloody. Severe bleeding is treated with plasma transfusion.
Laser surgery reduces the risk of blood loss by 85%. In case of acute urinary retention, catheterization is performed. Most often, the complication does not happen, since catheterization is carried out immediately after the procedure, this is necessary in order to eliminate clots from the urinary canal.
The onset of infection after surgery occurs in only 15% of patients. Such cases occur in cases where men do not adhere to the doctor's recommendations. To eliminate the incidental situation, the patient is prescribed therapy, taking into account the agent of penetrated microorganisms.
During postoperative recovery, men are advised to observe intimate hygiene and proper nutrition. Healthy foods are fresh vegetables and fruits that have a relaxing effect on the intestines. Sexual dysfunction after surgery occurs very rarely, when the pathology was severely neglected.



























