Home >
Erectile Dysfunction >
Peculiarities of carrying out transrectal ultrasound
Peculiarities of carrying out transrectal ultrasound
Many factors indicate that timely, correct and accurate diagnosis of the existing pathology leads to a positive outcome in the treatment of each pathology. And, of course, in addition to the fact that the diagnosis must be accurate, every man wants to undergo a therapeutic course painlessly and effectively.
In order for a man to be guaranteed to get rid of diseases associated with the pelvic area, it is necessary to resort to a timely transrectal examination of the prostate gland.
Concept of ultrasound examination of the prostate
The prostate gland is the male reproductive gland (prostate), which fell to play the most important role during the formation of the normal sexual existence of a male.
According to anatomical features, the prostate gland is located adjacent to the bladder, as well as the ampulla of the rectum. That is why the prostate gland is most often exposed to the influence of foci of infection.
One of the most common methods for diagnosing prostate diseases is ultrasound. This study is associated with an affordable, painless and cheap high-level prostate examination.
Transrectal ultrasound of the prostate (TRUS) is a method of sound diagnostics using special rectal sensors. Previously, during examinations of the prostate gland and organs in the vicinity, ultrasound examination with abdominal access was used.
This technique assumed the passage of sound beams from the anterior abdominal wall, adipose tissue, bladder, only then revealing muscle tissue and visualizing the prostate gland. Even in the absence of excess weight in a male individual, the distance from the sensors to the examined prostate gland was about ten centimeters, that is, it was almost impossible to examine the pathology of the organ.
When the patient had obesity, the distances increased four times, therefore, due to the excessive attenuation of the ultrasound signals from the sensors due to the passage through the adipose tissues, the images of the prostate gland obtained on the computer display were indistinct, therefore, did not carry information. p>
Benefits of TRUS of the prostate
Medical researchers, in search of an answer to the question of how it is possible to bypass the influence of adipose tissue on the ultrasound result, have solved the question in an original way. The answer was simple - it was necessary to change the place of the contacts of the sensors for better visualization and get a Transrectal ultrasound of the prostate gland.
Considering the fact that the anatomical location of the prostate gland is adjacent to the rectum, and there is virtually no adipose tissue between them, the method of using rectal sensors has become the most effective. This innovation had a positive effect on the high-quality visualized image of the prostate gland, since it became not blurry, more informative.
Another positive one, for a male individual is the main factor of transrectal Ultrasound examination - the technique does not imply invasive intervention, that is, no needle is used, no surgical intervention is used, and if the device is used correctly, the technique is absolutely painless.
List of indications for the use of transrectal ultrasound
Considering the positive side of the technique, we can conclude that the list of indications for transrectal ultrasound of the prostate area is extremely wide in terms of ultrasound.
In this case, such indications are:
- impaired performance of male power;
- painful, difficult or frequent urination;
- pain in the perineal region, pain above the pubis, in the lower abdomen, sharp lumbar pain;
- the presence of plasma in semen;
- suspicion of not having children;
- violation during ejaculation processes;
- having clinically proven renal area insufficiency;
- painful intercourse.
List of existing contraindications to the use of transrectal ultrasound
Contraindications include a list of such acquired pathologies:
- conditions after resection of the rectum;
- recent surgery near the rectum;
- inflamed organs in the form of hemorrhoids;
- pathology of urinary incontinence (dysuria).
How to properly prepare for the study
There are no organs in the area between the prostate gland and the rectum. Therefore, it is extremely easy to prepare for a transrectal ultrasound examination.Before going for a transrectal prostatic ultrasound, it is necessary to cleanse the rectum with an enema or the use of a laxative medication.
Some medical researchers, in order to accurately determine the amount of urinary residue, recommend that males come for examination with a filled urine. Therefore, one to two hours before the start of the ultrasound examination, a liter and a half of water is drunk. Avoid carbonated and canned liquids.
Principles of transrectal ultrasound technique
Ultrasonic sensors are inserted into the anus of a man who is lying on a bed. The sensors are inserted with axial planes five centimeters deep. It must be remembered that all the processes of the examination are painless, they can bring a minimal feeling of discomfort, which can be compared with an ordinary manual examination.
If a male individual has a concomitant disease in the form of a crack in the anus, the patient is advised to postpone the transrectal ultrasound scan until the existing wounds are completely healed. Ultrasound examination takes twenty to forty minutes over the period. But they will be spent with invaluable benefits for the body.
Quite often, during TRUS, a biopsy (sampling of cells with a needle) of the prostate gland is performed. In order to avoid pain and discomfort, before taking a biopsy, under the control of a monitor, anesthetize the areas where the biopsy needle is planned to be inserted.
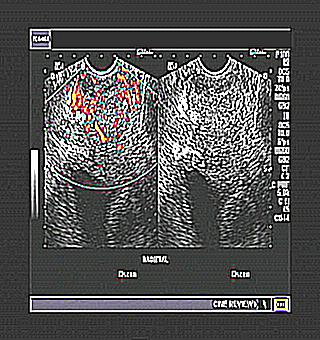
What doctors observe during prostate TRUS
When transrectal ultrasound of the prostate is performed, the prostate capsule is visible on the monitor. In the case when an oncological tumor of the prostate gland is suspected, the correct outline, as well as the integral appearance of the capsule, is the most important diagnostic criterion. Malignant tumors grow through the region of the capsule along the vascular bundles of nerves, therefore, with TRUS they are easily visualized.
Along with a symmetrical appearance, a geometric mirror of the border of the prostate, medical researchers evaluate the internal structuring of both the prostate gland itself and the pathological changes that have been found. Only with the help of transrectal ultrasound can the border of growths in adenomas be visualized.



























