Home >
Erectile Dysfunction >
Transrectal ultrasound of the prostate for what
Transrectal ultrasound of the prostate for what
Transrectal ultrasound of the prostate: description, preparation and recommendations
In recent years, the incidence of pelvic cancer has been growing rapidly. This is due not only to the fact that oncological pathologies are more common than before. First of all, the reason for the increase in the incidence is the improvement of diagnostic methods. Now almost every person over 50 years of age will periodically take tests to determine cancer markers. In addition, if such diseases are suspected, high-quality instrumental diagnostics is performed. One of the methods is Transrectal ultrasound. It is carried out for both men and women with suspicion of oncological and inflammatory processes in the pelvic organs. Compared to abdominal ultrasound, this method is considered more reliable, since the sensor is closer to the pathological processes. Therefore, it will be better to consider the organs.
What is transrectal ultrasound?
This method is based on the action of ultrasound. As you know, this imaging method refers to non-invasive procedures. Ultrasound waves are able to reflect on the tissues of the human body, as well as pass through them. Transrectal ultrasound (TRUS) does not differ in mechanism of action from other types of research. The only difference is that the sensor is inserted into the rectum, and not installed on the surface of the abdomen.
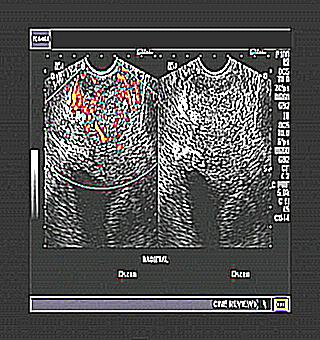
Due to the fact that all tissues have different echo density, the doctor will be able to visualize the organs on the screen. In the presence of inflammatory changes or any seals (formations), the ultrasound picture changes. That is, the density of the organ or its section differs from the norm. Both hypo- and hyperechogenicity indicate the presence of a pathological process, that is, a change in the structure of the tissue.
TRUS is performed to visualize the prostate, rectum, Douglas space, bladder. All these organs are displayed on the monitor and with other types of ultrasound (abdominal, in women - transvaginal). However, when the transducer is placed in the rectum, visualization is better due to the reduced distance between the transducer and tissues.
Indications for transrectal ultrasound of the prostate
Transrectal ultrasound of the prostate is a reliable method for diagnosing prostate diseases. It is the preferred research method, especially when a cancer process is suspected. However, a TRUS appointment does not mean that there is cancer. Therefore, do not panic in advance and draw hasty conclusions. It is worth knowing that with abdominal access, ultrasonic waves pass through many tissues (skin, fatty tissue, muscles). Only after that they get to the prostate gland. Therefore, the diagnosis of pathologies is difficult, especially if the patient is overweight. Transrectal ultrasound of the prostate allows several times to reduce the distance from the sensor to the organ under study. After all, the prostate gland borders on the rectum. Indications for TRUS are the following conditions:
Transrectal ultrasound of the prostate gland is performed if the patient complains of pain in the pubic and inguinal region, extending into the anus. Also, this study is performed in violation of urination and ejaculation, impotence.
Indications for transrectal ultrasound in women
Transrectal ultrasound in women is performed less frequently than in men. Most often, this diagnostic method is carried out with suspicion of oncological pathologies. In addition, TRUS is performed if there is a possibility of inflammatory processes in the Douglas space, abscesses, etc. As you know, the structure of the pelvis in women and men is somewhat different. Given that the examination of the uterus and appendages is carried out more often, transvaginal ultrasound is recommended in most cases. However, in some cases, visualization of organs through the rectum dates more information about the disease.
The indication for transrectal ultrasound in women is the study of the Douglas space. It is a pocket of the peritoneum located between the rectum and the uterus. Thus, TRUS allows assessing the state of pararectal tissue and the posterior fornix of the reproductive organs. It is carried out under the following conditions:
In both women and men, TRUS is used to assess the condition of the urinary organs. Nevertheless, in most cases they are examined using transabdominal access.
Diagnosis of bladder diseases by TRUS
In addition to the organs listed above, the bladder is also located in the pelvic cavity. It is located in front of the rectum. In women, access to it is blocked by the uterus. Therefore, transrectal ultrasound of the bladder is more often performed in men. It is carried out with suspicion of tumor, benign formations and inflammatory infiltrates.In women, TRUS of the bladder is performed if there is an adhesive process in the pelvis or severe obesity. Also, a similar method is used so as not to damage the hymen by inserting the sensor into the vagina.
Contraindications for transrectal ultrasound
In some cases, transrectal ultrasound is not recommended. An absolute contraindication to this diagnostic method is anus atresia. This is a congenital malformation in which there is no anus. A similar developmental anomaly is diagnosed in the first days of life. Other contraindications are relative. This means that in case of urgent need, the study is carried out. Nevertheless, it is better to replace it with other diagnostic methods. Relative contraindications include:
Transrectal ultrasound: preparation for the study
Like any transrectal examination, TRUS requires preparation. To achieve normal visualization of the pelvic organs, the rectum must first be cleaned. For this purpose, a laxative or an enema should be taken a few hours before the procedure. If the indications for the study are diseases of the rectum, it is necessary to exclude spicy foods, carbonated and alcoholic beverages from the diet. Before performing TRUS of the prostate, a preliminary diet is not required. If the object of study is the bladder, it must be filled. For this purpose, the patient should drink 1-2 liters of water before the diagnostic procedure.
Research technique
Transrectal ultrasound is performed in various positions. To have a good look at the prostate gland, the patient is asked to lie on his left side. At the same time, his legs should be bent at the knee joints and pressed to the stomach. Transrectal ultrasound of the small pelvis in women is most often performed on a proctological chair (or gynecological). In the same way, the study of the bladder is carried out. In some cases, the patient is offered to take the knee-elbow position. More often - with suspicion of pathology of the rectum.
Before inserting the ultrasonic transducer into the anal canal, it is lubricated with petroleum jelly or a special lubricant. After that, the device is inserted into the intestinal lumen to a depth of 6 cm. The anal canal, sphincters, and organ walls are examined. Next, the prostate and seminal vesicles are examined. In women, after examining the rectum, the posterior fornix of the uterus and Douglas space are visualized, then the bladder. All results are recorded on the monitor screen. After that, the apparatus is carefully removed from the rectum.
Benefits of transrectal ultrasound
The advantages of TRUS include:
Results of transrectal ultrasound
Thanks to the TRUS method, it is possible to diagnose neoplasms of the pelvic organs, as well as metastases to the pararectal tissue. In addition, using this research method, the size, thickness and location of the prostate and bladder are evaluated. Inflammatory processes and formations are displayed on the monitor as hypo- or hyperechoic tissue areas. The conclusion on the ultrasound picture is performed by a doctor of functional diagnostics, a urologist, a gynecologist.
Transrectal ultrasound
Examination of internal organs by ultrasound is an affordable and safe diagnostic method. For the most accurate assessment of the health status of the pelvic organs in men, a variation of this technique is used - transrectal ultrasound. The procedure is not only highly informative for the doctor, but also safe for the patient, since ultrasonic waves do not have a negative effect on the body.
Survey objects
With the help of TRUS (transrectal ultrasound), the doctor examines the organs of the small pelvis of a man:
- bladder;
- paired glands that secrete a secret for the movement and nutrition of spermatozoa - seminal vesicles;
- prostate gland (prostate);
- venous vessels.
To a greater extent, this study is aimed at studying and assessing the health of the prostate gland. The image obtained on the monitor makes it possible to examine in detail the structure of the organ, localization in the body, boundaries and structure. For women, TRUS is practiced only as a method for diagnosing a malignant tumor of the rectum.
Research Features and Opportunities
Diagnosis of the organs of the male genitourinary system is performed by the transabdominal and transrectal method. In the first case, the ultrasound probe is in contact with the anterior abdominal wall, in the second case, it is inserted directly into the rectum. The transabdominal method is less informative for the study of the prostate and seminal glands, since the sensor is at a considerable distance from the prostate. This method is more effective in diagnosing diseases of the bladder.
With the transrectal option, the sensor is as close as possible to the prostate gland, which allows you to get a clear image and diagnose the slightest changes in the organ. In addition, the method allows you to evaluate the adjacent lymph nodes, peri-intestinal (pararectal) space and intestinal walls
Using TRUS to determine:
- the presence of calculi (stones) in the prostate and bladder;
- the presence of tumor neoplasms of various etiologies (cancer or hyperplasia);
- inflammation of the fiber of the rectum (paraproctitis) and possible fistulas (fistulas);
- pathological changes in the lymph nodes;
- structure and condition of seminal vesicles.
Procedure Assignment
A man receives a referral for diagnosis from an andrologist or urologist (less often from a surgeon). The basis for rectal examination of the pelvic organs are symptomatic complaints presented by the patient or control of therapy for a previously diagnosed disease. The procedure can be done independently in order to prevent diseases of the male urogenital area.
The main symptoms for the appointment of TRUS are:
- Violation of the natural process of emptying the bladder (painful and frequent urination, a decrease in the amount of urine produced, the need for additional muscle efforts during urination, and an increase in the time of the process itself);
- systematic pain in the abdomen and perineum;
- pain in the lumbar region caused by a violation of the outflow of urine (renal colic);
- blood clots in semen or urine;
- STIs (sexually transmitted infections);
- erectile dysfunction;
- standard deviations for prostate specific antigen (PSA), urinalysis and semen analysis;
- inability to conceive.
Rectal ultrasound is indicated in the preoperative period on the pelvic organs, as well as after the operation, in the presence of adenoma (hyperplasia) of the prostate gland and chronic prostatitis (inflammation of the prostate), with unsatisfactory results of rectal palpation examination, men aged 50+ (for prevention).
TRUS can be prescribed for inflammation in the bladder and urethra (cystitis and urethritis). Contraindications to the study are: the postoperative period of surgical intervention in the intestine, hemorrhoids in the acute stage. If you have allergic reactions to latex, you must notify your doctor.
Preparations
Special preparation of the body is necessary for the most comfortable well-being of a man during the procedure, and the maximum optimization of the examination results. The patient is required to fulfill the following conditions. On the eve of the study, dinner should not consist of heavy, indigestible foods. An enema should be performed 2-4 hours prior to TRUS. The volume of injected fluid is from 1.5 to 2 liters.
Since it is difficult to perform this manipulation on your own, you can use the Microlax microclyster as an alternative. Immediately before the study, you should drink at least 1.5 liters of water (or other liquid that does not contain gas) and do not empty your bladder. This is necessary for better visualization of organs. During the rectal examination, the man should feel the urge to urinate.
Two days before TRUS, it is recommended to lighten the diet by excluding foods that cause intense gas formation (cabbage, legumes, yeast baked goods, carbonated drinks), spicy and fried foods, and take carminative drugs (Espumizan, Activated charcoal). The use of alcoholic beverages is strictly prohibited.
Conditions for the procedure
The examination is performed in the position of the man horizontally on the left side, the knees should be tucked up to the stomach. A special thin sensor is placed in a condom or a special gel-treated latex sheath. The transducer is inserted into the rectum at a distance of about 10 cm. Ultrasonic waves are reflected from the examined organs by an echo signal, which is processed by a computer program.
On the monitor, the doctor sees a real image of the internal space of the patient's body. The time interval of the procedure is about half an hour. If necessary, analyze the degree of emptying of the bladder, after the main study, the man empties the bladder, and TRUS is repeated. The transrectal method is not painful, but it can be uncomfortable. Especially unpleasant is the sampling of a biopath (biopsy). However, this lasts for a short period of time.
Decode results
The ultrasound doctor deals with the interpretation of the received image, the data is recorded in the ultrasound protocol.The parameters of the studied man are compared with the standards, on the basis of which a conclusion is made about the state of the prostate gland and adjacent organs. A healthy organ has:
- clear and even outlines (contours);
- non-homogeneous granular structure;
- upper anterior, anteroposterior and transverse dimensions normally correspond to digital indicators: 2.4-4.1 cm; 1.6-2.3 cm; 2.7-4.3 cm; Width, length, thickness: 4 cm, 4.5 cm, 2.5 cm respectively;
- round shape with symmetrical lobes.
The volume of the prostate should correspond to the age of the patient, and is calculated using the Gromov formula: V0.13*B+16.4. (B - denotes age). The resulting number should not exceed 30. If the ultrasound volume does not correspond to the norm, we can talk about the presence of pathology. Permissible sizes of seminal vesicles - no more than 0.1 cm. Absence of tumor formations in the prostate gland and bladder. The bladder should not be deformed, contain sand and calculi. Wall thickness - from 3 to 5 mm. The remaining urine after emptying does not exceed 15 ml.
Venous ducts are not dilated. The vas deferens are examined additionally. Based on the results of the procedure, the attending physician prescribes conservative therapy or decides on surgery. For the diagnosis of diseases of the "second heart" of a man (as the prostate gland is otherwise called), transrectal ultrasound is the most informative method. It can be used to identify pathologies at the initial stage of their development. You should not be afraid of the procedure, or be biased towards it. If the doctor prescribed TRUS, then there are indications for this that cannot be ignored.
Transrectal ultrasound of the prostate: what does an ultrasound rectal examination of the prostate show?
If a disease of the prostate gland is suspected, it is very important for the patient to undergo a comprehensive diagnosis, including examination, laboratory and instrumental methods, as well as a mandatory ultrasound examination.
What is a TRUS of the prostate and how is it done? We will talk about this later.
What is research?
Prostate ultrasound is a fast, modern and highly accurate diagnostic method that allows you to identify a number of diseases of the urogenital area.
Thanks to a special sensor that is in contact with the surface of the body, ultrasound allows you to get an image of the internal organs in real time. During its implementation, the body is not irradiated, as during an x-ray, so the procedure is considered safer.
With the help of a sensor, a doctor can assess not only the condition of internal organs. Thanks to the Doppler effect, it is possible to determine the blood flow in the vessels of the prostate, to assess the condition of the seminal vesicles.
Indications for carrying out
The doctor may prescribe the procedure for the following symptoms:
- burning during urination;
- difficulty emptying the bladder, accompanied by instillation of urine or its retention
Types of diagnostics
Today, in modern clinics, the study is carried out in two ways:
Which method to choose?
Many patients are interested in the question - which study is better? The answer is obvious. Despite the more complex preparation and some discomfort, doctors advise performing a transrectal ultrasound of the prostate, since the study provides the most informative data on the patient's physical condition.
This is due to the anatomical features of the male body. The prostate gland is located in close proximity to the rectum, so it is easier for the doctor to get a clear image on the monitor and easily assess the condition of the internal organs.
We have figured out the transabdominal method and prostate TRUS, what kind of study it is and what is the difference between them. But how to prepare for it and how is it carried out? Read on.
TRUS of the prostate
In order to achieve the most accurate result and reduce discomfort during transrectal ultrasound examination of the prostate, it is very important for the patient to follow the doctor's recommendations for preparing for the study, and listen to the instructions during the procedure.
How to prepare for a TRUS of the prostate? Let's get acquainted with this in more detail.
Preparation
How to prepare for a TRUS of the prostate:
For 2-3 days, the patient must adhere to the correct diet. Exclude black bread, legumes (peas, beans), white cabbage, carbonated drinks, fiber-rich foods, fresh kefir and yogurt from the diet.
Food should be light, fresh, easily digestible. This will help to avoid increased gas formation, stool disorders (diarrhea, constipation). In the evening (on the eve of the procedure) and in the morning before the study, the patient will need to do cleansing enemas. You can use warm decoctions of chamomile for procedures. They soothe the intestines, eliminate spasms.As a rule, a rectal ultrasound of the prostate is prescribed in the morning on an empty stomach. You can't eat before the test. You can drink only mineral non-carbonated water. If the diagnosis is carried out in the evening, the patient can easily have breakfast in the morning, but refuse lunch. The last meal should be 6-8 hours before the visit to the doctor. 1-2 hours before arriving at the clinic, you should drink 3-4 glasses (1-1.2 liters) of non-carbonated mineral water. So, the specialist will be able to determine the amount of residual urine, and if necessary, immediately look at other organs. Before the study, you must tell the doctor about all the medications you take, including ointments and suppositories. 2-3 days before the TRUS, the doctor may stop using rectal suppositories, lactulose supplements (Duphalac, Lactusan), laxatives, and some other medications that can make diagnosis difficult. It is important to warn the doctor about the presence of gastrointestinal pathologies and proctological diseases. With anal fissures in the acute phase of exacerbation, the diagnosis can be transferred or replaced by transabdominal ultrasound. How is a prostate ultrasound done? Consider below:
Technique
Despite some of the complexity of the procedure, a transabdominal ultrasound takes no more time than a transabdominal ultrasound.
How a TRUS of the prostate is done:
Indicators of norm and pathology
In the process of transrectal ultrasound of the prostate, the doctor notes many indicators that can tell about the state of the prostate.
What can reveal?
With the help of transrectal ultrasound, the doctor can recognize the following diseases:
Contraindications
Transrectal ultrasound is not recommended for patients with the following conditions:
How often is the procedure scheduled?
Rectal ultrasound of the prostate gland refers to those types of diagnostics that can be carried out both in case of suspicion of a specific pathology, and for preventive purposes.
A patient can undergo diagnostics annually in order to know about the state of his health, to recognize the development of any pathology in time. It is especially important to visit a doctor and follow preventive measures for men over 30-35 years old, because every year the risk of developing prostate adenoma and prostatitis increases.
And you can find out about harmful and beneficial products for the male organ here.
Conclusion
Now you know everything about Prostate ultrasound, what the study is for and how to prepare for it. The TRUS method is one of the most modern and highly accurate in the diagnosis of prostate diseases.
High-tech equipment allows you to make the procedure painless, minimize discomfort and get clear results during the study. Take care of your health!
Useful video
TrUS of the prostate: what is it? Watch the video:



























