Home >
Erectile Dysfunction >
Performing transurethral resection of the prostate
Performing transurethral resection of the prostate
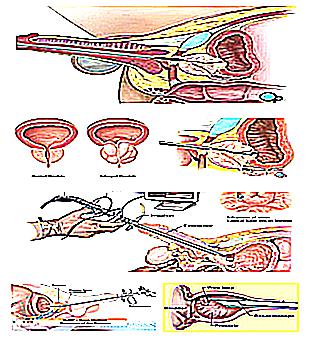
Transurethral resection of the prostate is a bloodless laser surgery with proven benefits over open cavity and other surgical techniques.
When is transurethral surgery indicated
What are the indications for transurethral resection of the prostate?
- Poor quality of life with dysuric disorder due to prostate pathology. When the patient complains of symptoms, consisting in a weakened stream with an outflow of urine, a feeling of incomplete emptying of urea, nighttime urges, a desire to visit the toilet, after a short period of time after emptying the urea, despite medication.
- Chronic and acute urinary retention. In case of acute urinary retention, an ultrasound examination is prescribed if, according to its results, the volume of fluid in the ureter is 650-700 ml.
The technique of performing the TUR operation is a gentle technique, therefore this intervention is allowed for patients with large volumes of the prostate gland and patients with:
- cardiovascular pathologies;
- respiratory diseases;
- for diseases of the thyroid gland;
- concomitant diseases of the urinary and genital area;
- surgical procedures on the urinary tract, intestines, prostate;
- patients who wish to maintain erectile functionality;
- at the time of detection of hyperplasia with recurrent inflammation;
- with detection of oncological pathology.
Due to the fact that, like any other surgical intervention, the technique contains a number of contraindications, permission for this manipulation is accepted by the urological surgeon on an individual basis, taking into account the characteristics of the patient's body.
What types of surgical intervention exist
Removal of prostate pathology is carried out by three types of surgical interventions:
Open method
The technique of the operation by this method is due to the cutting of the skin in the suprapubic zone. The transvesical method is used to extract the hyperplastic prostate. In other words, through the urinary tract (bladder).
The operation in question is associated with many complications, which is explained by the long-term procedure with a significant risk for the man. During open intervention, a large amount of blood loss occurs, which further provokes the onset of anemia in the patient. Such a process significantly increases the terms of rehabilitation recovery. Taking into account the significant areas of alteration (tissue injury) with the risk of postoperative blood loss during the stretching of the walls of the urea due to overflow of urine, specialists use an irrigation system. This is necessary to flush out the plasma clots in preparation for catheter repair and epicystostomy function.
The patient spends about a month in the hospital. Among the complications noted:
- severe impairment of potency (erectile dysfunction);
- urinary incontinence due to damaged urinary sphincter;
- ejaculant without semen;
- narrowed urethral strictures (adhesions);
- inflammation of the urinary and reproductive system (cystitis, orchitis, epididymitis, orchiepidymitis);
- dropsy of the testicles;
- hernia.
Positive aspects of surgery:
- visualization of a regional lymph node with taking a fragment for histological analysis, which must be carried out in case of suspicion of cancer of the glandular organ in a patient. Testing in this way is necessary to determine the course and form of the oncological process, to determine the treatment regimen.
- a radical solution to the problem: open prostatectomy with minimal recurrence of the adenoma that has arisen.
Laparoscopic therapy
Laporoscopy is a surgical procedure that involves removing hyperplasia through small incisions. With this method of treatment, tissue can be taken for a biopsy if the patient is diagnosed with an oncological process. The method has its own complications, including the throwing of sperm into the urinary tract and erectile dysfunction. Other complications after laparoscopy are very rare.
Resection (transurethral)
TUR - excision of the prostate gland (resection of the prostate with a transurethral resectoscope). To carry out this surgical method, the use of a resectoscope (a special instrument of the surgeon) is required. During the procedure, a loop is also used, with the help of which a transurethral resection of the prostate adenoma is performed. The overgrown prostate tissue is excised with a resectoscope under the influence of a laser beam.The surgical procedure is performed under spinal anesthesia, which surgery considers to be a gentle procedure among anesthetic aids for patients.
The operation is controlled by high-precision optics, which provides visualization of manipulations along the canals with a resectoscope. In this case, fluid flows in with an outflow, which relieves injuries in the tissues.
TUR on the prostate is performed with a laser device in two ways:
- laser embolization - with the help of a laser, overgrown tissues in the prostate gland are evaporated;
- enucleation (laser) - the surgeon's scalpel is replaced with a laser beam.
Both types of surgery tour have the same effectiveness: hypertrophied tissue of the gland is excised, thereby improving the outflow of urine. Vaporization (evaporation) is carried out in cases where the prostate gland is small. For larger growths, enucleation is used.
At the end of the surgery, catheterization is performed by the method of penetration through the urethral canal to the urethra in order to create conditions for the normal waste of urine. The catheter remains in the ureter for 3 days, which is much less than after other methods of surgical intervention.
- irrigates the tissues injured by the operation, preventing the formation of blood thickening into lumps, this avoids blockage of the urinary canal;
- allows you to create an empty urinary tract, preventing bleeding.
Considering all the advantages with a minimum percentage of complications and a short period of rehabilitation, it can be noted that surgical intervention is the most effective measure to eliminate the pathology of the prostate. In addition, men do not have an interruption in sexual activity, surgical intervention is allowed to be carried out in patients with concomitant pathologies, to take tissue fragments for biopsy.
Transurethral resection is a highly sought-after surgery for treating male prostate health problems.
How patients are prepared for resection
Before a patient is hospitalized, he undergoes a urological examination. The doctor prescribes to undergo a comprehensive examination, which consists of:
- laboratory diagnostics (blood biochemistry, KLA, tests for HIV, syphilis, hepatitis B, C, syphilis, testing of the prostate-specific antigen of the dog, like an egg-leaf);
- instrumental examination: ultrasound diagnostics (kidneys, urethra, prostate, control of remaining urine, uroflumetry, ECG, FL-graphy);
- consultations of specialized specialists, therapist, cardiologist and others are necessary for patients with comorbidities.
In some cases, an additional study is prescribed: survey and excretory urography, to diagnose the performance of the urinary, reproductive system, kidneys, as well as MRI of organs located in the small pelvis.
Rehabilitation period
Usually, after transurethral resection, patients recover quickly, since the method practically does not cause complications. An inpatient stay of the patient usually lasts 12 days. The independent process of emptying urea after the operation is getting better already on the third day in almost all patients. After the same period, the previously installed catheter is removed. After discharge from the hospital, the patient continues to be monitored on an outpatient basis, using anti-inflammatory therapy.
Possible consequences after surgery
There are practically no undesirable consequences for patients after the tour. However, the laser method is still considered an operation, and as after other methods of surgical intervention it may have some complications (very rarely):
Primary complications
- Postoperative bleeding - to eliminate the pathological phenomenon, doctors prescribe the use of hemostatic drugs (a consequence of ineffectively performed endoscopic diathermocoagulation intervention).
- Water intoxication - occurs during surgery, as a result of the penetration of a large amount of fluid into the bloodstream.
Secondary complications
- Injection of semen into the ureter.
- Urine leakage (incontinence) - drug therapy and therapeutic exercises with a selected set of special exercises are prescribed.
- Urethral strictures - correction is performed using the bougienage method, if efficiency is not achieved, then plastic of the urethral canal is applied.
- The emergence of chronic pathologies of the reproductive system - antibacterial treatment is carried out.
Patients, after surgery, should monitor changes in their health, and after the first negative signs appear, seek medical advice.



























