Home >
Erectile Dysfunction >
Which part of the brain is responsible for potency
Which part of the brain is responsible for potency
Erection and nervous system
An erection is inseparable from the functioning of the nervous system. In order to increase blood circulation in the genitals, an impulse of the nerves extending from the lower part of the spinal cord will be required. Nerves give a signal with the help of a special chemical substance that they secrete as a transmitter. As a result, the muscles holding back the blood vessels relax and the blood flow in the genitals is freed. The spiral blood vessels of the penis begin to pass enough blood for an erection.
All this can be described step by step:
Stage 1. Filling the vessels. Stage 2. Straightening, stretching the vessels. Stage 3. Stretching of the erection tissues, their swelling. Stage 4. The membranes press on the tissues filled with blood. Stage 6. In accordance with the hydraulic mechanism of erection, the penis increases in size and becomes elastic.
The nervous system, which controls the activity of all systems of the human body, is also responsible for the occurrence of an erection. The corresponding nerve centers are located in the brain and lower region of the spinal cord. Nature has provided partial protection in the form of the spine and skull, but sometimes the bones are not able to properly protect a person from serious injuries. Strong physical influences can lead to impotence and even paralysis. To prevent this from happening, you should always remember to observe safety precautions.
An erection can be attributed to one of the following types:
- visual (an extensive group of stimuli, entirely dependent on individual preferences);
- auditory (rapid breathing, exciting voice, whisper, laughter, music);
- irritants of touch or, more simply, all kinds of touches (massage, stroking, touching a naked body, hairline);
- gustatory (taste of genital secretions, saliva);
- smell irritants (smell of skin, hair, perfume);
- a game of imagination (exciting memories, erotic fantasies and dreams).
These six pathogens are all equally important. The absence of any of them can lead to a lack of erection (another possible option is that arousal occurs, but only for a short time).
3. Reflex. It occurs as a result of touching the genital area. The nerve endings of the penis, rectum, bladder transmit impulses to the spinal cord. This reaction is carried out automatically and is of great importance, especially in old age, when the need for physical stimulation increases. The same can be said about certain diseases that impede arousal. The weakening of the positions of mental erection over the years is a completely natural process, however, some men are prone to prejudices regarding physical stimulation, considering it to be something unworthy, a disgrace to a man.
Violation in the male genital area
Incomplete erection makes a man worry. It is necessary to take into account various diseases that reduce sexual arousal. It is not recommended to eliminate the pathology on your own. Stimulant drugs can exacerbate the cause and prolong the recovery process. Potency reduction requires the intervention of specialists.
How a process occurs
To establish the causes of incomplete erection, it is necessary to know the process of formation of sexual arousal.
A man's penis has three cavernous bodies. When arousal occurs, blood is released into the body. They fill with blood, the penis is erect.
Excitation occurs under the influence of nerve impulses. The human brain is complex. Each part of it is responsible for performing separate functions. The release of adrenaline and testosterone activates the part of the brain responsible for arousal. The nerve impulse is transmitted to the endings to the genitals. An erection sets in.
Various failures in the circulatory or nervous system affect the process of erection. The reasons must be sought in the pathologies of the internal organs.
What causes influence
The causes of incomplete erection are various pathological processes that occur in the body of a man. Experts identify the following factors that reduce arousal:
- Neurological disorders;
- Hormonal failure;
- Diseases of the genitourinary system;
- Comorbidities.
Nervous strain leads to the development of depression, apathy and irritability. A man who is in nervous tension cannot fully experience the process of arousal. This phenomenon leads to aggravation of factors and the complete absence of sexual activity. In a healthy person, an erection occurs with any pleasant sensation from the opposite sex. The process is complete. If the nervous load increases, then the release of testosterone into the blood decreases, the erection becomes incomplete.
Hormonal failure affects sexual desire. Testosterone is the main male hormone that affects arousal. Violation of the level of this hormone leads to changes in the genital area. The reduced content of testosterone in the blood causes a decrease in sexual arousal in a man. Erection becomes incomplete or absent.
Diseases of the genitourinary system affect the genital area. Inflammatory processes lead to injury and atrophy of the tissues of the penis. A patient experiencing additional symptoms should seek specialist advice. He will identify the problem and prescribe the necessary therapy.
Comorbidities are present in many people. Cardiovascular disease worsens the condition of the veins of the testicles and the prostate gland. Prolonged violation of blood circulation leads to incomplete erection of the penis. Varicose veins are also a cause of poor arousal. The problem is eliminated surgically.
Diabetes mellitus affects the trophism of the tissues of peripheral organs. Weak and fragile vessel walls cannot deliver the required amount of blood to the cavernous bodies. There is a decrease in the filling of the third chamber and head. Erection does not lead to ejaculation and subsides quickly.
Prostatitis is a common cause of decreased libido. With this disease, there is an overgrowth of prostate tissue. It compresses the urinary and vas deferens. The blood stops flowing to the testicles, the erection disappears. Treatment of prostatitis is long and is carried out with the help of combination therapy.
The age of the patient also affects the state of erection. In adolescence, young people experience arousal with small irritants. This is due to hormonal changes. Testosterone exceeds its norms. Normalization of erection occurs 2-3 years after adolescence. If a violation occurs in a man under 40, then it is necessary to sound the alarm. The reason is the presence of any disease. After 50 years, there is a decrease in the level of the male hormone, an erection occurs rarely and lasts a short time.
Pathology diagnostic methods
A man suffering from an ailment should consult a urologist. The doctor will prescribe a series of examinations to identify the causes. The following diagnostic methods are distinguished:
- Blood for hormone content;
- Smear from the urethra for infection;
- Dopplerography of the vessels of the penis;
- Ultrasound diagnostics.
The blood must be examined for hormone levels. The focus for weak erections is on testosterone and estrogen. Testosterone affects a man's state of arousal, the presence of secondary sexual characteristics. Estrogen is necessary for the patient to maintain reproductive function and normalize the vascular system. If the level of these substances in the patient's blood is lowered, then the cause of incomplete erection is a hormonal failure.
A smear from the urethral canal will help detect pathogenic microorganisms that cause diseases of the genitourinary system. Bacteria have a detrimental effect on the condition of the soft tissues of the genital organs. Identification of the microbe will help to quickly eliminate the cause of the pathology.
Dopplerography is necessary to study the degree of filling of blood vessels. For research, a special liquid is introduced into the vessels. On the screen of the device, sections of the veins that have bridges or damage are clearly visible. Ultrasound diagnostics is a good method for studying the state of the internal organs of the small pelvis. If the doctor detects any changes in the vascular system or urinary organs, he prescribes an additional examination to clarify the diagnosis.
Troubleshoot
Therapy must be selected based on the doctor's diagnosis. If the cause of an incomplete erection is prostatitis or urethritis, it is necessary to undergo a course of treatment with antibiotic drugs. The substance is selected in the laboratory. Experts are studying which antibiotic is effective against the inoculated bacteria. Treatment is accompanied by the use of stimulant drugs. Viagra and Cialis are popular. These substances cause excitement in a man for a long time. It is necessary to take into account the presence of contraindications and side effects. For people suffering from cardiovascular diseases, stimulant drugs are contraindicated.
Venous pathologies can be eliminated in two ways:
Medications normalize blood circulation in the inguinal zone, improve the elasticity of the vascular walls. Treatment with venous drugs is prescribed for mild changes in the vessels. If the pathology cannot be corrected with drugs, the man needs surgical intervention. The operation is performed with a laser. The method eliminates additional bleeding and quickly dries the surgical field. The man fully recovers on the third day after the operation.
Any violations in the sexual sphere require medical supervision. Incomplete erection is eliminated by proper treatment by a specialist.
Neurological causes of impotence - diseases and brain damage
Erectile dysfunction is the inability to achieve or maintain an erection of the penis, making it impossible to have a full sexual desire. Diseases of the nervous system are a common cause of Sexual disorders.
Neurogenic erectile dysfunction originates from the brain and spinal cord (brain damage). Diseases of the central nervous system also often lead to sexual disorders, including Erectile dysfunction.
Neurological causes of erectile dysfunction
Neurological causes of erectile dysfunction of "central" origin (disturbances in the brain) include: brain tumors, trauma, hematomas, epilepsy, infections of the central nervous system, degenerative diseases (for example, Parkinson's disease) and dementia (for example, ).
In contrast, the spinal cord can be damaged by trauma, infection (both bacterial and viral), vascular disorders, cancer, and by altering the demyelination that occurs in multiple sclerosis.
In diseases and injuries of the spinal cord, erectile dysfunction occurs more often than in brain injuries.
Physiology of erection
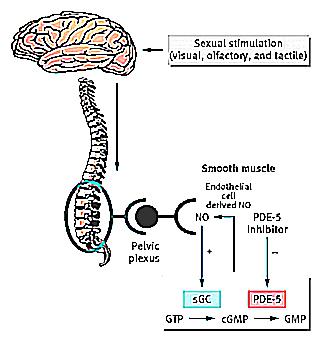
Currently, there are 3 types of penile erection: nocturnal, psychogenic and reflexive. The center of the erection of the penis is located in the spinal cord, at the level of the lumbar region.
The nerve impulse arising in the head (in particular, in the temporal lobe), after checking by the cerebral cortex, is transmitted to the nucleus of the spinal cord and further to the erection center in the spinal cord (section S1-S3), and from here, by special nerves, it is stimulated blood flow to the corpora cavernosa and spongy body, which causes an erection.
All substances or conditions that damage this pathway will have an effect on the occurrence of erectile dysfunction.
Erectile dysfunction of cerebral origin
- Brain tumors, which include not only cancer, but also unusual growths such as abscesses, parasites, hemorrhages;
- Another factor could be brain injury. Injuries are most often the result of movement and secondary cerebral hemorrhages. As a result of damage, there is a weakening of sexual desire and the development of erectile dysfunction;
- Strokes affecting the elderly. It has been proven that erectile dysfunction occurs more often after strokes of the left hemisphere. It is estimated that half of the people after a stroke are able to continue to lead a normal sex life;
- Epilepsy is a common condition in young people who are going through a period of high sexual activity. Sexual disorders are often observed in temporal lobe epilepsy. An additional factor that can increase erectile dysfunction are drugs used in the treatment of epilepsy.
Erectal disorders of spinal origin
Injuries are the cause of erectile dysfunction in 20% of cases. It is estimated that up to half of spinal cord injuries are caused by road traffic accidents.
When an interruption of the intervertebral nucleus occurs as a result of an injury, a complex of symptoms occurs in the form of lower extremity damage, sphincter damage, which is manifested by sphincter control problems, and sexual dysfunction. A person after such an injury, as a rule, is disabled for the rest of his life.
Tumors of the spinal cord
Most often, these are benign tumors, for example, meningiomas, which grow in a rigid structure, however, gradually they cause compression of the spinal cord and a simultaneous violation of its functions. Initially, small paralysis appears, in the final stage, a complete disruption of the continuity of the spinal cord can occur.
Squeezing leads to paralysis, numbness, loss of sensation, as well as lack of erection and degenerative changes in the testicles.
Sexual disturbances are often the first symptom of an enlarged tumor. Treatment in such situations is mainly surgical. Excision of the tumor, if there was no death of nerve cells due to inhibition, makes it possible to completely get rid of the symptoms and restore sexual function.
Multiple sclerosis and diseases of the spinal cord
This is an inflammatory disease of the central nervous system (i.e. the brain and spinal cord). With this disease, demyelination and decay of neurons occurs, which leads to the fact that the nervous system does not function properly. This is the most common cause of spinal cord injury in young people.
Sexual disorders in multiple sclerosis have a cause both in the brain and in the delivery of a nerve signal.Sexual disorders in this disease are very common, in addition, unfortunately, in a significant proportion of cases, the disease begins at a young age, during the peak of sexual activity.
It is assumed that after several years of the disease, erectile dysfunction occurs in 70% of patients. In addition, in addition to the lack of erection, there may be a decrease in libido, difficulties in maintaining an erection of the penis. In some cases, when the disease proceeds in the form of exacerbations and remissions, sexual opportunities may return at the time of remission of neurological symptoms.
Among the diseases of the spinal cord that cause erectile dysfunction, there are:
- Dorsal tabes. This is a form of inflammation of the spinal cord caused by syphilis spirochetes in the later stages of the disease. Erectile dysfunction is one of the symptoms of dryness. At present, due to the widespread use of penicillin treatment, the late nervous form of syphilis is rare.
- Myelitis. Most often, inflammation of the spinal cord is caused by viral infections. Sexual disorders in this case are transient, that is, sexual function returns after the underlying disease has been cured.
- Polio. In the case of polio, erectile dysfunction is quite common. However, at present, thanks to effective and widely used vaccination, this disease is practically not found in developed countries.



























