Home >
Erectile Dysfunction >
MRI diffuse changes in the prostate
MRI diffuse changes in the prostate
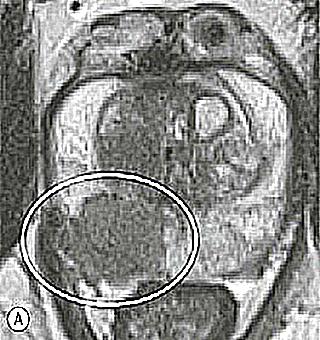
Diffuse changes in the prostate gland: definition of pathology
Diffuse changes in the prostate gland - any degenerative-dystrophic changes in the prostate that are provoked by certain diseases of the organ. It is also the standard medical term most commonly used in ultrasound diagnostics. It is possible to identify such a problem only when visualizing the muscular-glandular organ.
The incidence of Diffuse changes in the prostate increases with the age of patients
The frequency of diffuse changes that are sufficiently pronounced to be detected during ultrasound is approximately 10-15% in the entire male population of a young age (up to 35 years) and more than 70% in the older age group.
Probable causes of the problem
Diseases
The causes of diffuse changes in the prostate are diverse. Among the probable diseases of the organ, the following can be distinguished:
Prostatitis (see here). It is a degenerative-dystrophic violation of the development of the parenchyma of the "second heart" of a man, as the prostate gland is quite rightly called. The pathological process in the vast majority of cases has a metabolic etiology (it is formed due to an imbalance of androgens - male specific hormones).
In more than 50% of clinical cases, diffuse changes in the prostate gland occur due to prostatitis
Prostatitis accounts for about 90% of all clinical cases. And only in 10% of situations is a viral or infectious picture determined, according to European medical research. The disease is characterized by urination disorders (the jet becomes lethargic, insufficient, the process may break off, pollakiuria is observed: frequent false urges to visit the toilet), potency, fertility insufficiency (the man is unable to conceive a child), pain in the anus, pubis, penis (in the projection of the prostate glands). Prostatitis, as the cause of diffuse changes in the organ, is noted in more than half of all clinical cases. prostatic hyperplasia (see here). She's a prostate adenoma. It is characterized by the same symptoms as the classic prostatitis of inflammatory origin, however, in the course of the pathological process, in this case, hypertrophy and proliferation of tissues of the muscular-glandular organ is observed. The result is the formation of persistent complications, including acute urinary retention, renal failure, reflux followed by hydronephrosis, and even bladder rupture.
Diffuse changes in the prostate occur against the background of pathologies
Pathological conditions
Other options are possible when the prostate is still healthy. In this case, we have to talk about the following phenomena:
- impaired blood circulation and trophic tissue of the prostate gland due to smoking, alcohol abuse and more;
- initial stages of metabolic disorders in a glandular organ.
Classification of diffuse changes in the prostate
You can classify the problem based on the degree of trophism of once healthy tissues:
Diffuse changes in the prostate include dysplasia, atrophy and hyperplasia
Dysplasia. In this case, there is a normal or increased trophism (cellular nutrition) with a modification of cellular structures. The cell phenotype changes, rebirth is noted. Malignant or benign - will show a biopsy. Dysplasia can also be observed with long-term prostatitis. This type of diffuse changes is considered the most difficult and prognostically unfavorable. Atrophy. Malnutrition of the prostate. The cellular activity in the organ decreases, the secretory function of the prostate decreases. Hyperplasia. Usually we are talking about excessive tissue growth. A similar variety occurs with prostate adenoma or malignant neoplastic processes. Diagnosis One ultrasound examination of the prostate gland is not enough to determine the nature of the process. Ultrasound allows us to state the fact of diffuse changes, but a deeper examination is required. Additional diagnostic methods:
- Biopsy. With increased proliferative activity of cells, and even more so with dysplasia of the prostate parenchyma, this study is indispensable. Tissues for laboratory morphological and histological evaluation are taken via transurethral access.
- TRUS. Transurethral access can assess the condition of the prostate as a whole. A diagnostic event of this nature allows you to consider tissues, their structure, type, degree of change
With transrectal ultrasound of the prostate, a specialist evaluates the degree of changes
In the complex of these measures, it is enough to make a correct diagnosis and verify it.
It is not the diffuse changes themselves that are subject to treatment, but the underlying disease that caused them. Accordingly, specialized drugs are prescribed. In exceptional cases, surgery may be required with excision of pathological tissues (resection) or total removal of the muscular-glandular organ.
Diffuse changes in the prostate is the general name of the indicator identified during ultrasound diagnostics. What caused them - remains to be seen. This should be done under the supervision of an andrologist or urologist.
Diffuse changes in the prostate gland, types and diagnosis, causes and treatment
If a disease develops in the male body, which is preceded by diffuse changes in the prostate gland - what does this mean, the ultrasound and the attending physician will tell you, who will provide a productive restoration of the affected prostate tissues using the drug method. The disease is not fatal, but in the absence of timely therapeutic measures, it can provoke serious complications not only of the reproductive system, but of the whole organism. Diffuse changes in the prostate parenchyma are a consequence, it is important to find and eliminate the cause of the pathology in a timely manner.
What are diffuse changes in the prostate
If the structure of the prostate parenchyma changes under the influence of provoking factors, this means that there is an extensive pathology that negatively affects the reproductive activity of a man. Such dystrophic changes are called diffuse and require detailed diagnosis and further correction. You should not be afraid of a characteristic ailment, it is important to recognize it in a timely manner - by the method of ultrasound. Diffuse changes in the prostate gland in men include several types of disease, and the severity is determined individually by each clinical picture
How the structure of the prostate changes
A characteristic disease eloquently indicates that the inflammatory process predominates in the body of a man, and it progresses. More often this happens at an older age, doctors even know patients at risk. If treated in time, this means that the risk of negative consequences for the reproductive system and the sexual sphere is minimal. Diffuse changes in the prostate gland are accompanied by the following anomalies in the body that reduce its vital activity:
- metabolic disorders at the cellular level;
- inflammation followed by tissue thickening, formation of fibrosis foci;
- growth of connective, glandular tissue;
- appearance of neoplasms of benign and malignant nature;
- Violation of the systemic blood flow of the penis.
The bladder may be involved in the pathology, which means that the inflammatory process is characterized by the presence of excruciating pain, aggravated by urination, erection, ejaculation. To avoid the development of an abscess or prostate adenoma, it is required to give voluntary consent to a detailed diagnosis, to undergo a series of laboratory tests. Among these, ultrasound of the presumptive gland is welcomed to visualize the pathology zone and further prescribe a conservative treatment regimen.
Ultrasound criteria of the gland
After an ultrasound scan, the doctor often reveals unpleasant signs of atrophy, hyperplasia and dysplasia, when areas of healthy cells are modified into hybrid structures that are not characteristic of the prostate cells. This means that both diseases are dangerous to health, since they significantly increase the risks of making a fatal diagnosis, the formation of a cancerous tumor of the prostate. Typical ultrasound criteria for the gland of a healthy body at the cell level are presented below:
- homogeneous structure;
- selection of five zones;
- volume up to 25 cm;
- clearly defined borders;
- symmetrical;
- allowable density;
- visualization of replaceable bubbles.
If there is a pathology, the ultrasound parameters do not correspond to the normal limits, an additional examination is required. Ultrasound criteria for an inflamed prostate with diffuse changes are presented below:
- the appearance of anechoic zones during the development of a cyst;
- development of fibrous areas;
- pathological decrease or increase in echogenicity;
- combination of hypoechoic and anechoic zones;
- heterogeneous tissue structure, fuzzy contours;
- presence of fibrosis, edema, calcifications, infiltration, pus.
Types of diffuse changes in the prostate
In modern medicine, such a pathological condition of prostate cells has been studied clinically, and it is important to start treatment in a timely manner. For example, diffuse prostatic hyperplasia is prone to a chronic course, so the pathogenesis of a characteristic disease should be established immediately. A pathogenic infection with further abscess and prostatitis could get into the male body.Also, a characteristic health problem is preceded by cancer - malignant neoplasms with deviations from the generally accepted norm.
Before removing diffuse changes in the prostate gland with medication, it is necessary to determine the main causes of such disorders. Anomalies in the structure of tissues can occur as a result of an imbalance of hormones, when the male body does not produce enough testosterone. This is one of the main reasons, however, graduates identify a number of pathogenic factors that can also cause diffuse changes in the prostate gland. This is:
- infection with bacteria, other pathogenic microorganisms;
- the harmful effects of gonococci, Trichomonas, tuberculosis bacteria;
- venereal diseases.
Diagnosis
The main methods of clinical examination are ultrasound and TRUS. In the first case, the real state of the prostate itself is examined for deformation and the appearance of new "structures" of different sizes. When performing TRUS, foci of pathology will not appear, since the purpose of the examination is to study the features of the systemic blood flow of the characteristic zone, to determine the presence of congestion. In the acute phase, the patient is supposed to perform a biochemical and general blood test, pass urine for laboratory testing. Only after that the doctor can recommend treatment.
Diseases indicated by diffuse changes
Based on the characteristic symptoms and changes on the ultrasound screen, logical conclusions can be drawn, which means diffuse changes in the prostate gland. Further therapy can be conservative or operable, and the clinical outcome for a male patient depends entirely on a number of factors. The patient remains under strict medical supervision, and should not resort to self-medication. Below are the diagnoses with a description of what diffuse changes in the prostate can mean:
Video: diffuse changes in the prostate
What are diffuse changes in the prostate and how to treat them
The prostate gland is popularly called the second heart in men, and this is not surprising, because the prostate has a significant impact on reproductive function. Any disturbances in the work of the prostate gland lead to infertility and impotence, problems with the urinary system, which undoubtedly worsens the quality of life of a man.
Diffuse changes in the prostate are several pathologies in which dystrophic changes occur in the gland. Such disorders occur as a result of inflammatory processes and an unhealthy lifestyle. It is very important to timely identify signs of diffuse changes in the prostate and start treatment in order to maintain the function of the organ and normal potency.
Causes of prostate pathologies
Diffuse changes in the prostate do not occur without a reason. The tissues of the organ begin to degrade as a result of the following pathologies of the prostate gland:
Chronic prostatitis
One of the most common male diseases that every second elderly patient faces. For the first time, acute prostatitis can also occur at a young age due to infection of the organ, for example, during promiscuity, during unprotected anal sex.
The inflammatory process injures the tissues of the prostate gland, leads to impaired blood circulation and organ function. If the treatment is carried out comprehensively and timely, then diffuse changes can be avoided. But with a long uncontrolled course of the disease, changes occur in the parenchyma, foci of a dystrophic nature appear.
Stones in the prostate
The formation of stones in the prostate occurs against the background of chronic prostatitis. In a healthy man, the process of urination is established, as well as the release of prostatic juice. In chronic prostatitis, urine does not come out completely, and stagnation of prostatic fluid also occurs. As a result of such a violation, salts, phosphates, epithelial particles accumulate in the organ and thicken, thus forming stones in the prostate.
In turn, calcifications in the prostate squeeze its tissues and injure the organ, causing pain. Large stones necessarily provoke a violation of blood circulation in the tissues of the gland, and as a result, diffuse changes occur.
Benign prostatic hyperplasia
For patients, this pathology is more familiar under the term prostate adenoma. With such a pathology, hypertrophic changes in the gland are observed, that is, the tissues of the organ begin to grow uncontrollably, forming a tumor.
Although BPH is not cancer, it does pose some health risks. The growing tumor compresses the surrounding tissues, in particular the blood vessels that feed the prostate and nerves. As a result of malnutrition, diffuse-focal changes in the prostate are formed against the background of hyperplasia.Also, a large adenoma squeezes the urethra, disrupting the process of urination.
IMPORTANT TO KNOW! 80% of prostate diseases are asymptomatic, and this rapidly leads to dire consequences. If you need powerful protection against prostatitis, experts recommend. Read more >>
Sclerosis of the prostate
Fibrosis or sclerosis of the prostate is a pathology in which healthy gland cells are replaced by dense connective tissue. Adhesions lead to the fact that the prostate tissue shrinks, compresses the urethra and blood vessels, while the nutrition of the gland, the process of urination, impotence occurs.
Fibrosis of the prostate is most often the result of a running process. Also, the cause of the pathology can be hormonal disorders, vascular atherosclerosis, congenital anomalies in the development of the genital organs, as well as mechanical injuries.
As a result of the negative influence, sores, or wounds and microcracks are formed in the gland, which are tightened by the connective tissue, forming dense strands. At the same time, the pathology proceeds for a long time asymptomatically and it is usually detected when the patient goes to the doctor with severe disorders of the genitourinary function.
Prostate cancer
Prostate cancer is the most dangerous disease of the gland that threatens the life of the patient. A growing tumor causes diffuse changes in the prostate, but this is not the worst thing. A malignant neoplasm once begins to metastasize, that is, spread its cells throughout the body. This stage of cancer in most cases is incurable and leads to the death of the patient within a few years, or even months.
It is important to note that moderately diffuse changes in the prostate can also occur in the absence of organ pathology. In this case, the provoking factors are:
- smoking and alcoholism, as a result of which there is a malnutrition of the gland and its dystrophic changes;
- metabolic disorders, obesity, endocrine pathologies;
- lack of sex and a passive lifestyle, resulting in stagnation in the organ.
Thus, the list of causes of diffuse changes in the prostate is quite wide. In each case, the treatment will correspond to the cause of the disease and the stage of the pathology. Therefore, therapy should be carried out under the supervision of a competent specialist.
Signs of diffuse changes in the prostate
Symptoms of diffuse changes are quite non-specific, the patient is worried about:
- pain in the groin that radiates to the perineum and rectum;
- impaired urination, in particular incontinence, frequent urge, weak urine stream;
- erectile dysfunction, pain during ejaculation.
It is important to understand that such symptoms occur with prostatitis, adenoma, and even with prostate cancer, so you should never ignore them.
Signs of diffuse changes in the prostate parenchyma can be seen on ultrasound. Normally, the parenchyma should be symmetrical, homogeneous and with clear contours, normal density, with a size of 30-45 mm.
An echographic sign of diffuse changes can manifest itself in a decrease or increase in echogenicity and the appearance of anechoic zones. In most cases, the sonologist notes that the structure of the parenchyma is heterogeneous.
Ultrasound helps to quickly detect that there are diffuse changes in the prostate according to characteristic features, but this method of examination will not accurately answer the question about the nature of the pathology. Therefore, the doctor will prescribe additional diagnostic methods:
- biopsy;
- Truzi;
- prostate secretion analysis;
- spermogram.
A comprehensive examination will help to accurately identify the cause of diffuse changes and prescribe adequate treatment.
Diffuse nodular hyperplasia
Diffuse prostatic hyperplasia is a proliferation of organ tissues and the formation of nodules and tumors. Neoplasms are benign in nature and do not metastasize, but in rare cases they can become malignant, that is, transform into cancer.
Focal or diffuse-nodular changes in the prostate are slow and almost asymptomatic. A large number of small nodules are formed in the organ, which are interconnected. Over time, problems with urination and urinary incontinence occur.
Treatment of focal hyperplasia can be conservative and surgical. Conservative therapy is aimed at eliminating the symptoms of the disease and reducing the likelihood of tumor transformation, but the patient cannot be completely cured in this way. The following drugs are prescribed:
- Alpha blockers, such as Omnik. They help to improve the process of urination by relaxing smooth muscles.
- Antineoplastic hormonal agents, in particular Finasteride. The drug helps to reduce the growth of education.
Surgical treatment is prescribed in such cases:
- in case of urinary retention, if the catheter cannot be inserted;
- on the background of renal failure;
- with severe infection against the background of a tumor;
- if it is not possible to be treated with drugs;
- with the threat of oncology.
Unfortunately, not every patient with diffuse focal changes can undergo surgery, because due to advanced age there are contraindications to surgery and general anesthesia.
Prostate dysplasia
Dysplasia is the most common form of diffuse changes in the prostate. Pathology is the degeneration of healthy prostate tissue into an atypical one. Dysplasia is not cancer, but the disease is rightfully classified as a precancerous condition, since if left untreated, dysplasia often transforms into oncology.
Dysplasia is widespread among men over the age of 70, and after 45 years, the disorder is diagnosed in about 20% of patients who seek help with characteristic symptoms of diffuse changes.
The treatment of dysplasia is complex. Prescribe drugs that help stop the growth of atypical cells, as well as symptomatic drugs: alpha-blockers to normalize urine outflow, painkillers. If urination is disturbed, the catheter is removed.
Surgical treatment is prescribed if indicated. As a rule, the operation is indicated in a severe case, when the outflow of urine is disturbed, there is a risk of oncology. Various methods are used, for example, in less advanced cases, TUR of the prostate is prescribed. And if the tumor begins to transform, a complete removal of the gland, inguinal lymph nodes is performed.
USE FOR PREVENTION! An innovative biologically active drug that naturally restores the health of the prostate gland. Experts recommend! Read more >>
Hypoplasia of the prostate
Prostate hypoplasia is a disease in which there is an underdevelopment of the organ. Pathology is usually diagnosed in boys during puberty, while the organ ceases to develop normally against the background of hormonal imbalance.
Hypoplasia is a very serious disorder that leads to infertility. The prostate secretes bad prostatic juice, because of which the quality of sperm suffers greatly. In addition, hormonal disorders that accompany this kind of diffuse changes in the prostate often affect the appearance and character of the patient, and also provoke impotence.
Congenital hypoplasia has a significant impact on a man's life. With the timely detection of a problem, hormonal correction helps to alleviate the condition. In the future, patients with hypoplasia often face problems in their sexual life, and changes in the prostate greatly increase the risk of inflammatory processes, the appearance of tumors and atrophy of the gland.
Prostate atrophy
Another type of diffuse changes in the prostate is prostate atrophy. Pathology is a degeneration of an organ as a result of a decrease in the synthesis of sex hormones, and it occurs against the background of age-related changes and a passive lifestyle in men over 50-60 years old.
Atrophy may also develop at a young age, for example, against the background of congenital hypoplasia, as well as as a result of mechanical injuries, benign and malignant tumors and other negative factors.
The treatment of prostate atrophy in older men is aimed at stopping the pathological process and improving the patient's quality of life. Unfortunately, it is completely impossible to reverse age-related changes.
In young men, atrophy requires timely and comprehensive treatment, otherwise the pathology will lead to impotence and urinary incontinence. For sexually active patients, this is a serious problem, in addition, impaired urination greatly impairs the quality of life, preventing a man from working normally and having a personal life.
Atrophy therapy consists of the following activities:
- Surgical treatment is prescribed for stones and tumors;
- anti-inflammatory therapy is prescribed for inflammation;
- Hormone replacement therapy is indicated for hormonal failure.
In case of diffuse changes against the background of age-related changes, symptomatic therapy is prescribed. In case of violation of the outflow of urine, a catheter is installed. With the threat of oncology, the prostate is removed surgically, if the operation is not contraindicated.
Prevention of prostate pathologies
Diffuse changes in the prostate parenchyma in most cases occur as a result of a neglected pathological process in the organ. To prevent the development of the disease, you must:
- At the first signs of prostatitis, you need to go to the doctor, even if the patient is 25-30 years old. The sooner the disease is diagnosed and treatment is started, the more likely it is to avoid diffuse disorders in the future.
- You need to lead a healthy lifestyle. Alcohol abuse, drug addiction, smoking, unhealthy diet are factors that increase the likelihood of developing oncology, including Prostate cancer, at times.
- It is very important to avoid promiscuity from a young age. Infection with an STI greatly increases the risk of developing prostatitis and its complications. When having sex with a stranger, be sure to protect yourself with a condom.
- A man after 40 years of age should be examined annually by an andrologist and a urologist. Boys and young men should be examined at least once every 2 years.
- After 60, you need to lead an active lifestyle, move more. It is also desirable to have a regular sex life if you have an erection. Such prevention will help improve blood circulation in the pelvis and prevent the development of diffuse changes in the organ.
Conclusion
Degenerative disorders in the prostate are serious pathologies that can be avoided by observing preventive measures. The right attitude to your health and life in general will help to avoid not only diffuse changes in the prostate, but also many other serious diseases.



























