Home >
Erectile Dysfunction >
The prostate hurts so that it gives to the legs
The prostate hurts so that it gives to the legs
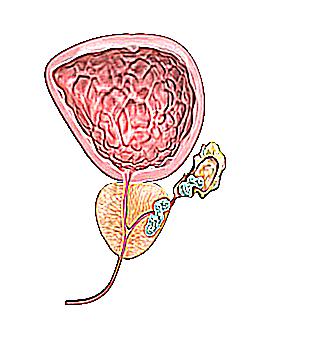
Pain in prostatitis: how and where does it hurt?
Inflammation of the prostate, as has been said more than once, is possible for a number of reasons, and timely diagnosis of the disease is very important for successful treatment.
It is not difficult to recognize the initial stage of prostatitis, but the difficulty lies in the fact that the onset of the disease is no different from a common viral infection. Aches in the joints and muscles, headaches, high body temperature, weakness are symptoms characteristic of a cold, and very rarely men turn to a urologist with this. And in vain.
That's the problem. Behind a seemingly ordinary malaise, a serious and fraught with many problems for men illness can be hidden. And as a rule, people go to the doctor already with a chronic form.
A sensitive attitude towards yourself and your health, a timely visit to the doctor will help to avoid pathology.
Impotence and infertility are common consequences of neglected prostatitis. Better safe than sorry.
Where and how pain manifests itself
Cutting pain in the genital area, aggravated by urination, is one of the first symptoms of prostate inflammation. In acute prostatitis, pain can develop to such an extent that the patient has a psychological barrier to emptying the bladder. In Chronic prostatitis, the pain is much weaker, but the patient constantly pursues and can intensify, for example, at the time of sexual intercourse.
In addition to pain in the genital area, discomfort can spread to the lower back, buttocks, sacrum and legs. Sometimes the pain is also localized in the anus. The prostate itself does not experience pain, because it does not have nerve endings. But nerves do not pass through, like power lines, to the organs of the genitourinary system. That's why they hurt.
The nature of pain in prostatitis, in addition to the stage of the disease, also depends on the presence of other inflammations of the urogenital zone of a man.
Unpleasant sensations can occur both during the day and at night. Last several hours or pass almost instantly.
The following factors may contribute to increased pain:
- lack of sexual intimacy (long time);
- erection;
- sexual intercourse;
- excessive sexual activity;
- bladder emptying;
- ejaculation;
- development of a cold;
- permanent hypothermia;
- consumption of alcoholic beverages in large quantities;
- strong stress;
- nervous tension.
These types of pain are typical for various types of disease, so do not try to diagnose yourself and be sure to seek help from a specialist.
Diagnosis, in addition to a general examination, will include an Ultrasound examination, testing, spermogram and other procedures. Only after that a certain course of treatment will be recommended.
Pain in chronic prostatitis
The phase of the disease, in which pain appears, is divided into infectious and non-infectious. Moreover, young and active men are more susceptible to the first subspecies of chronic prostatitis, and people in years to the second.
Infectious inflammation of the prostate gland occurs as a result of promiscuity and sexually transmitted diseases. Non-infectious - as a result of congestion caused by a sedentary lifestyle, prolonged abstinence and hypothermia.
The nature of pain in infectious prostatitis is expressed in cramping and burning of the urethra during urination, aching pain in the testicles and perineum, extending down the abdomen and into the lower back. Sometimes the joints hurt, but this is not a pronounced, dull pain. During rectal examination, pain is also possible.
For a non-infectious form of prostatitis, pain in the pelvis is characteristic. There are pains in the scrotum, perineum and sacrum. Pain sensations: erased, aching. Occur periodically, and without any concomitant reasons. Pain during ejaculation is also possible.
Pain in testicles
This happens due to the fact that the prostate gland is an organ of the endocrine system responsible for the production of a secret that is part of the sperm. The inflammatory process does not lead to a deterioration in the quality of sperm, to inflammation and blockage of microvessels in the testes.
Pain syndrome in prostatitis is interrelated with exacerbation phases. With the progression of the inflammatory process, the pain becomes sharp and jerking. Due to the sharp cessation of the gland, urination becomes extremely difficult and painful, with pains radiating to the scrotum and lower abdomen. There is pain in the penis. The stool becomes extremely painful, there are shooting pains in the lower back.
Kidney pain
As a result of the narrowing of the urinary canal, the outflow of urine is disturbed.With urinary retention, residual fluid overflows the bladder, which sooner or later leads to inflammation. There is a failure in the waste disposal system. Accumulating, they are converted into poisons that poison the body. Pain in the kidneys with prostatitis indicates a violation of their work, and that the kidneys are under constant toxic effects.
Inflammation of the bladder and obstruction of the outflow of urine can lead to acute kidney failure.
Pain in the legs
Pain in the legs with prostatitis is evidence that the inflammatory process of the gland is so intense that the pain spreads not only to the perineum and scrotum, but also to the lymph nodes and muscle fibers of the lower extremities. With this development, there is swelling and pain in the testicles and penis, giving pain in the leg, or in both legs. These pain sensations are only a component of the general pain syndrome in prostatitis. They spread mainly to the inner thighs in the form of aching and pulling pain.
Chronic prostatitis in its acute form can act as a switch in a chain reaction, in which, due to damage to one organ, another becomes ill. So with a long delay in urination, the bladder and kidneys suffer. As a result of pathology of the kidneys, the heart can hurt. Similarly, pain in the leg, or in the legs with prostatitis, can be an indicator of the development of reactive arthritis. But you should only worry if bacterial prostatitis is diagnosed, and if it is not the muscles of the legs that hurt, but their joints and bones. Reactive arthritis can develop as a complication of prostatitis caused by venereal bacteria.
Abdominal pain
The prostate gland is an organ closely related to the urethra and rectum. It is located just between them, and e inflammation directly affects these organs. Due to the fact that the prostate is located in the lower part of the small pelvis, with inflammation, it becomes a focus of irradiation of pain to all surrounding areas: the lower pubic, lower sacral, lumbar, perineum and external organs. With prostatitis, one specific organ cannot hurt. Painful sensations cover the entire lower part of the pelvis with all associated organs, and pain, for example, in the perineum is only a component of the general pain syndrome. A feature of pain in prostatitis is its persistence. Appearing in the form of aching discomfort and heaviness in the groin, it will not disappear, but will only intensify or return to its original state.
Complete relief from pain will indicate the beginning of recovery.
With prostatitis, pain in the abdomen, in its lower part, is an indicator that the disease is in a chronic form. The intensity of pain directly depends on the degree of exacerbation of the inflammatory process. Pain in the lower abdomen with prostatitis occurs due to inflammation of the seminal vesicles, and is reflected from the focus of inflammation to the external genital organs and anus. The nature of pain is aching, dull, exhausting. Frequent urge to urinate and defecate. Loose stools with mild pain.
Back pain
Back pain is directly related to the disruption of the kidneys, and their pathology. And if your back hurts, then there is a problem with the kidneys. Do not confuse the back with the lower back. Lower back pain in prostatitis is caused by the action of the inflamed prostate on the nerve endings of the sacrum. The sacral region is the lower part of the spine. Simply put, the sacrum is connected to the lower lumbar vertebra.
How to restore well-being
With the development of severe pain that accompanies the process of inflammation of the prostate gland, the doctor usually prescribes painkillers. However, discomfort is only a superficial symptom of the disease, and in order to get rid of it forever, it is necessary to cure the disease itself.
Pain develops after an excessive amount of secretion begins to form in the prostate gland, which does not go out due to blockage of the ducts. As a result, pressure rises inside the organ and causes first slight discomfort, and then (if left untreated) severe pain.
Specific drugs for the treatment of prostatitis and, in particular, for relieving pain, the doctor selects on an individual basis. It depends on the form of the disease, the stage of its development, the age of the patient and various physiological features, such as the presence of concomitant diseases.
One of the main factors contributing to successful treatment is self-discipline.
It is very important not only to follow all the doctor's prescriptions, but also to change your life: get rid of bad habits and an unhealthy lifestyle, go in for sports.
Additional treatment
In addition to the main drug treatment, the doctor often recommends a course of physiotherapy, such as laser therapy, magnetic therapy, leech therapy, prostate massage, acupuncture, etc.
You can also resort to the methods of "folk" medicine, but only after consulting with your doctor. In particular, pumpkin seeds relieve pain well, which must be eaten every day 45 minutes before meals for 7-10 months. Treatment with burdock, bearberry, asparagus seeds, nettle, etc. is common. However, all alternative medicine prescriptions are aimed at relieving superficial inflammation and cannot replace drugs. Therefore, they should be practiced either for prevention purposes, or as an addition to the main therapy.
Remember that untimely treatment of prostatitis leads to the transition of the disease into a chronic form, it becomes much more difficult to get rid of it. Take care of yourself, try to be outdoors more, eat right and lead an active lifestyle.
Lower back pain due to prostatitis
Prostatitis is a chronic disease that provokes pain in various adjacent areas of the body. Prostatitis and back is one of the varieties of pain syndrome from the inflammatory process in the genitourinary system. The disease acquires a chronic and acute form of manifestation, on which the localization of pain depends. More often, pain is given to the buttocks, legs, pubis and lower back / back. Since there are no nerve endings in the prostate gland, it cannot provoke pain, and sensations radiate to other areas.
Back pain with prostatitis
Can the lower back hurt with prostatitis?
Back pain is often noted, and with prostatitis, confusion appears, the cause is in this disease or in other pathological conditions. Does your back hurt with prostatitis? - Yes, it is possible, although it happens infrequently.
The lower back hurts with prostatitis in situations where inflammation flows to external tissues and involves adjacent organs. Pain sensations in patients are of different intensity: from static to short-term pain, from aching to "shooting" character. Mostly the pain syndrome is formed due to the chronic form of prostatitis, which has been in the body for more than a year.
Lower pain due to prostatitis is usually supplemented by other signs of pathology, especially when urinating. In the process of recovery, a burning sensation appears, and the stream becomes weak, often accompanied by a feeling of incomplete bowel movement.
If the inflammatory process has a large affected area, failures may occur in other organs of the genitourinary system, then cramps are formed simultaneously in different areas. If your back hurts, prostatitis is a complication of a disease that needs timely treatment with the help of a urologist.
Can the back hurt with prostatitis?
Pain in the back (not to be confused with the lower back) is a dangerous condition, as this indicates the spread of the pathology to the kidneys or urinary tract. Due to fluid stagnation, the likelihood of pyelonephritis, urolithiasis and cystitis increases.
Back pain as a symptom of acute prostatitis
There are 3 causes of irradiation of pain in the back:
The situation is characterized by the addition of renal pathology, the function of the organs becomes defective, this may be accompanied by:
- the appearance of edema, often of the limbs or face;
- the occurrence of pain in the abdomen / back with a long or short-term character;
- blood clots may appear in the urine, sometimes mucus / pus is released;
- in more advanced forms of kidney disease, heart function may be impaired, this is accompanied by arrhythmia, increased blood pressure and other symptoms of heart problems;
- pain syndrome, reaching an unbearable character, this is how renal colic appears.
Against the background of kidney damage, lumbar pain may occur, often aching, sometimes sharp. The reason is intoxication of the body, the condition is especially dangerous with purulent prostatitis.
Pain in the back may be familiar to men who have been diagnosed with prostate adenoma with stage II-III development. Due to changes in the quality of blood supply, other organs of the small pelvis are exposed to pathology. Significantly less often, symptoms appear in stage I.
Pain in the side during exacerbation of prostatitis
The patient may experience an acute form of urinary retention, this is accompanied by a feeling of fullness, pain in the back, and also in the groin. This condition is severe, as it greatly affects well-being and can provoke a number of pathologies. Be sure to contact a urologist, he will put a catheter to normalize urination.
Pain depending on the form of prostatitis
Back pain with prostatitis rarely appears due to an infectious lesion of the organ, which provokes an acute form of the disease. For the chronic variety, the non-infectious type of provocateur is more characteristic. Mostly chronic prostatitis occurs due to congestion in the pelvis.
In the process of relapse or acute form, the infectious nature of the appearance of the disease in the prostate is distinguished, in which the onset of pain in the lower back is an uncharacteristic phenomenon.
If the back hurts with prostatitis, then the nature of the pain syndrome is predominantly acute, there is a pulsation or as if a cut has appeared, sometimes it has a shooting character. Pain in the lower back with prostatitis intensifies with certain actions, then the sensations become even sharper, the peak of pain falls on a one-time manifestation. Then there is a decrease in sensitivity, often the pain is given to other areas.
In the chronic form, if it is of a non-infectious nature, the nature of the pain is different, more often there is a pulling or aching pain syndrome. Discomfort/feeling of pain accompanies the chronic form almost always and the person rarely experiences relief. The area of occurrence of the pain syndrome does not have a strict and obvious localization.
Lower back pain in chronic prostatitis
When does the pain appear or worsen?
Pain sensations tend to change their intensity with certain actions. Urologists identify a number of main factors that most affect the pain syndrome:
- appearance of an erection;
- in the process of intimacy;
- when ejaculating;
- due to prolonged abstinence;
- due to excessive sexual activity;
- while urinating;
- due to severe and prolonged hypothermia or heating of the body;
- with strong physical exertion, more common in people involved in difficult working conditions, and in athletes;
- prolonged and frequent stress;
- drinking alcohol and smoking
Each of the factors described can provoke an increase in pain or its appearance. Causes often also cause recurrence of prostatitis.
The nature of the pain
Lower back pain in prostatitis varies, but a general pattern has been established based on clinical studies.
Description of pain:
- continuous. Described by a long course, appears in attacks of 12 hours or more;
- whining/groaning. According to the receptors of perception, pain is not acute. The patient feels tired due to the duration of the flow;
- episodic. Pain syndrome occurs only in the case of a number of previously described actions. It is characterized by significant intensity, but has a short-term effect;
- low intensity. Pain appears infrequently, has a mild severity, because of which the patient practically does not pay attention. A similar symptom indicates the appearance of pathology.
Lower pain is not always a consequence of prostatitis, sometimes this phenomenon indicates problems with the kidneys or damage to the nerve endings in the sacrum. The disease is characterized by the presence of other symptoms associated with urination.
How to relieve pain?
Painful sensations are the result of overlapping of the lumen in the ducts, blockage appears due to mucopurulent discharge. It leads to stagnation of the prostatic secret, respectively, it will remain inside the organ and put pressure on it. In the process of expanding the organ, pressure is formed on other areas and tissues, this is the cause of pain.
To eliminate pain, you need to recover from the underlying disease, and until then, symptomatic therapy is used. To prevent the occurrence of a chronic form of prostatitis, it is necessary to take up treatment when an acute course of the disease appears. The most common methods of pain relief: medicines, folk recipes and physiotherapy.
Prostatitis: pain in the lower back and spine
Drug therapy
Doctors prescribe a number of different drugs:
- antibiotics based on a fluoroquinolone ("Levofloxacin", "Norfloxacin", "Ciprofloxacin") or a cephalosporin ("Ceftriaxone"). The dosage is prescribed by the doctor, the course is 1-2 weeks;
- antispasmodics. Means allow you to relieve pain;
- Non-steroidal anti-inflammatory drugs are often supplemented with substances to alleviate unwanted sensations."Nimisulide" is used in 1 package, which is diluted in 100 ml of heated water, applied twice a day;
- muscle relaxants eliminate spasmodic phenomena in the muscles of the perineum, as this condition increases pain
- Bioregulatory peptide compounds are agents synthesized in the bovine prostate that enhance local blood circulation and reduce inflammation
- vitamin therapy to enhance the body's immune function
Physiotherapy
Among the physiotherapeutic methods, the most effective and generally recognized are:
- laser therapy - the course is 2 weeks;
- magnetotherapy - 10-12 procedures;
- leech therapy - 10-12 sessions;
- massage of the gland - 8-12 procedures;
- needle reflexology - course 2 weeks.
Folk methods
Popular recipes:
- a decoction of asparagus. The root is turned into gruel with a blender, 1 tbsp. l. roots pour 200 ml of water and boil the mixture for 10-15 minutes. After straining, the liquid is taken 30 g with a regularity of 4 hours;
- Decoction of burdock. One st. l. root is crushed and poured 1 liter of water. You need to boil the mixture for 15 minutes, then insist for 4-5 hours
- pumpkin seeds. In raw form, they are consumed 1 hour before meals, 1 tbsp. l. The course is 6-9 months.
Prostatitis gives in the leg
Our readers have successfully used M-16 to improve potency. Seeing the popularity of this tool, we decided to bring it to your attention. Read more here-
The formation of stones in the prostate gland is a late complication of prostatitis. According to statistics, it develops in 80% of men after 5-10 years from the onset of the pathological process. The essence of the disease is the development of stones in the tubules of the glandular organ. As a result, the normal outflow of prostate secretion is disturbed. The symptoms of the underlying disease are even more aggravated.
Development factors (pathogenesis)
Calculated prostatitis (another name for the process of formation of calculi (stones) in the prostate gland) is a multifactorial disease.
Main reasons
The pathogenesis is based on the following reasons:
Indirect factors
There are also factors that affect the prostate indirectly, increasing the risk of developing the disease:
- smoking;
- alcohol abuse;
- lack of physical activity;
- frequent urinary tract infections;
- physical inactivity;
- hypothermia.
Clinical picture
All manifestations of the disease can be divided into specific and nonspecific.
Specific symptoms
Specific pathognomonic only for this disease and allow you to make a diagnosis:
Non-specific symptoms
Nonspecific manifestations characterize various diseases of the pelvic organs.
- general weakness;
- feeling unwell;
- appetite reduction;
- hyperthermia at the level of subfebrile marks (37.2-37.5 degrees).
Since we have to talk about the advanced stage of the disease, the clinical picture includes all the manifestations presented above in the complex. The intensity of the signs is high and significantly reduces the quality of life of the stronger sex.
Classification of stones
Gems can be divided for several reasons.
By origin
The origin of the calculus can be taken as a classification criterion.
In this case, highlight:
By mineral composition
Another basis - according to the mineral composition of stones.
Based on the process development mechanism, they distinguish:
Diagnostic measures
Diagnosis and treatment of pathologies of the urinary system is the prerogative of the urologist. Since we are talking about a complex problem that concerns the male genital area, a visit to an andrologist urologist would be the best option. At the initial consultation, the doctor interviews the patient, finds out complaints, collects an anamnesis of life. The presence of chronic prostatitis is of great importance. A number of studies are required to make and verify a diagnosis.
Our readers have successfully used M-16 to improve potency. Seeing the popularity of this tool, we decided to bring it to your attention. Read more here-
- Common urinalysis. Most informative study. It makes it possible to identify salts in urine, as well as their concentration.
- Analysis of capillary blood. Gives a picture of classic inflammation with leukocytosis, high erythrocyte sedimentation rate.
Sperm analysis (spermogram). Chronic prostatitis is a huge danger to sexual health. The number of healthy and mobile cells decreases, oligospermia occurs. In the seminal fluid, blood is determined. Study of prostate juice.Demonstrates a picture of prostatitis with a decrease in the volume of secretion, etc. Ultrasound examination of the prostate and pelvic organs. The most informative study, which makes it possible to identify stones, determine their size and, possibly, nature. Tomography. Urography. Together, these studies allow a diagnosis to be made with great accuracy.
Drug treatment
Predominantly drug treatment is practiced. The basis of therapy is the intake of the following drugs:
- Anti-inflammatory non-steroidal origin. They are used to relieve chronic inflammation in the prostate area.
- Anspasmodics. Help relieve pain.
- Alpha-blockers. They help to relax the smooth muscles of the prostate and bladder, normalizing the evacuation of urine and prostate secretions.
- Antibacterial agents. Necessary in case of infectious origin of calculous prostatitis.
Surgical treatment: types and indications
But it is not always possible to cope with the problem with medication alone. There is a clear list of indications for surgical treatment:
- formation of acute renal failure;
- intense pain syndrome that is not relieved by drugs;
- lack of urination;
- acute urinary retention.
There are only two options for therapy:
Be that as it may, surgery is a last resort.
On the Internet, the so-called. folk recipes for the treatment of stones in the prostate. As practice shows, effective recipes simply do not exist. By resorting to such dubious methods of therapy, the patient only wastes precious time. If there is a desire to normalize sexual health and restore fertility, the only possible way is through traditional treatment by a specialized specialist. Treatment with folk remedies is ineffective.
What causes groin pain in men?
Pain in the groin in men can occur for many reasons, and its symptoms should be taken seriously, as such sensations are a sign of problems with internal organs. Localization of pain in the groin may be due to its transmission from the source of the disease, located elsewhere in the body. Pain in the groin area may be a symptom of a disease of the urogenital area. It is necessary to diagnose and identify possible problems immediately after the appearance of pain of any nature.
What caused the localization of pain on the right and left?
Anatomically, the inguinal region is located on the border of the abdominal region joining the thigh. It has a spermatic cord, large vessels, intestinal loops, various muscle groups. Careful attention should be paid to the pain that radiates to the right side. Pain in the right side can be a symptom of appendicitis, in which case it can increase gradually, starting in the pit of the stomach and going down. When moving, pain in the right groin in the presence of appendicitis may increase.
Renal colic can be the cause of recurrent pain on the right. Usually, in this case, pain in the groin on the right appears suddenly, sharply giving to the side, leg and lower back. The acute pain that appears can be caused by a kidney stone located low in the duct. The duration of the attack can be either minutes or several days. The center of pain, when pulled in the groin, can be located in the lower back and radiate to the hypochondrium, the bladder area.
The appearance of swelling, more pronounced in a standing position and accompanied by the appearance of pain in the groin area, is a sign of a right-sided hernia. In this case, the intestinal loop protrudes through the hernial opening formed in the muscle wall. With a small hole and a large loop, a hernia in the groin area can be strangulated. In this case, the process of blood supply is disturbed and the rapid destruction of the area pinched in the hernial opening of the groin on the right is possible. In such a situation, a man needs urgent surgical intervention.
Pain in the groin on the left can be due to several reasons:
The appearance of such symptoms, accompanied by pain in the left groin, requires an urgent consultation with a surgeon and a urologist. The lack of proper and timely treatment in men can lead to problems such as impotence and infertility.
What happens when the prostate becomes inflamed?
Pain can be signs of advanced prostatitis. Inflammation of the gland is accompanied by a similar pain syndrome in 50% of cases. Early diagnosis is of great importance for the treatment of acute prostate disease. It is possible when contacting a specialist doctor immediately after the onset of pain in the groin in men. The doctor, focusing on the results obtained during the examination, will prescribe treatment, which will help prevent complications and the transition of prostatitis into a chronic process.
The chronic form of the disease can also be manifested by the occurrence of pain in the groin. Such prostatitis is symptomatic less acute, but is very dangerous. Inflammation during a long course can affect other organs (intestines, bladder) of the pelvic area, significantly worsening the condition of a man.
Chronic prostate disease can be indicated by periodic pulling pain, the repetition of which should be the reason for going to the doctor.
The chronic course of prostatitis, if left untreated, can lead to erectile dysfunction and male infertility.
What else causes pain?
Swollen lymph nodes can also cause soreness. Usually, a group of lymph nodes located near the pathological focus is inflamed. If there is a thickening and enlargement of the lymph nodes in the inguinal region, then the phenomenon can be caused by several reasons:
With an increase in lymph nodes, you need to quickly identify the source of infection and carry out the necessary treatment.
If a man’s groin hurts, then you can suspect the presence of a number of other diseases, including acute cystitis (giving pulling pain in the groin), herpes, cysts in the spermatic cord, varicose veins, problems in the intestines (obstruction, dysbacteriosis) and osteochondrosis of the spine. If the pain sensation radiates to the leg, then it may be caused by trauma, neoplasm, urological disease, or hernia. Another reason why it hurts in the groin in men can be an infringement in the lower spine or the presence of problems with the hip joints (coxarthrosis, arthritis).
If it hurts in the groin in men, then the right action would be an urgent visit to the doctor. In this case, you can contact a surgeon, neurologist, urologist or oncologist. The doctor can refer the patient for a consultation with other specialists, since complex diagnostics are needed to find out why it hurts in the groin. The treatment may also require a combination of different methods. The success of treatment, if the groin hurts, largely depends on the timeliness of the provision of medical care to the man.
Prevention of the appearance of pain lies in the organization of a healthy lifestyle, timely detection and treatment of foci of infections in the body. If a problem has arisen, it can be eliminated only after clarifying the question of why a man's groin hurts. It is important to pay close attention to determining the location of the pain - in the right groin or on the left - the degree of its intensity, frequency, nature (acute, aching or pulling). Attentive attitude to the manifestations of the disease will help to quickly determine the causes that caused it and cure the disease.
How to identify prostatitis in time: symptoms of the disease, diagnosis and treatment
Prostatitis is one of the most diagnosed diseases in urological practice. The cause of this disease is the inflammatory process that occurs in the prostate gland. Most often, the development of infection occurs in men during the period of abstinence, when the secretion of the prostate is in a state of stagnation. How to determine prostatitis on your own, preventing the appearance of various complications, can be understood by studying the main symptoms and the form of their development.
Prostatitis - what is it?
There is a stereotype that prostatitis is an age-related disease that affects mainly elderly men. But unfortunately, in recent years, this diagnosis is often made to very young people, whose age does not exceed 30 years. Statistics show that from 30 to 60% of the working-age male population under the age of 40 already suffer from prostatitis.
The prostate gland is a small, walnut-sized process located directly below the bladder.
Our readers have successfully used M-16 to improve potency. Seeing the popularity of this tool, we decided to bring it to your attention. Read more here-
The main role of the prostate in the body of a man is to block the exit of the bladder during erection and produce a small percentage of sperm, called prostate secretion.
The reason for the vulnerability of this organ lies in the peculiarities of its anatomical structure and the process of blood supply.
How to recognize prostatitis at its earliest stage - many men ask this question. The detection of obvious symptoms and their combination will help to understand the development of the disease. The classification of the disease has two main forms: acute and chronic. Studying the symptoms of each form is the easiest way to find out the type of ailment inherent in the patient.
Symptoms of chronic prostatitis
Chronic prostatitis is usually the result of an acute form of the disease and is considered more insidious because it does not have clearly defined signs. In this regard, it is easily confused with many other diseases and is quite difficult to diagnose.The main symptoms of chronic prostatitis:
- pain in the lumbar region, sacrum and pelvic region;
- feeling of discomfort in the lower abdomen and perineum;
- increased pain during urination;
- difficulties with proper urine outflow;
- frequent urination;
- erectile disorders;
- premature ejaculation;
- nervousness, fatigue and irritability;
- Regular pain in the urethra, scrotum and urethra.
Symptoms of prostatitis can be complex or manifest one at a time.
The main signs of a chronic type
The pain syndrome often spreads to the abdomen or falls lower, giving to the legs. Such signs are often mistaken for sciatica or osteochondrosis, which delays the correct diagnosis. Chronic prostatitis is characterized by pulling, regular pains that do not have acute manifestations.
The urge to urinate is frequent and rather rapid. The patient has the impression that a lot of fluid has accumulated in the bladder. The onset of urination is accompanied by pain, and the process itself is quite difficult.
The developing inflammation of the prostate leads to various negative processes in the genital area of men. The negative impact of the infection on the nerve endings provokes the development of premature ejaculation. In the future, the disease leads to problems with potency and the suspension of the production of male sex hormones. Sexual intercourse can also bring significant discomfort and pain.
Such changes in the male genital area, as well as regular pain, have a significant impact on the psychological state of the patient, who has irritability, apathy and increased nervousness.
Consequences of chronic prostatitis
This threatens to develop severe chronic disorders in the process of urination, which in turn has a significant impact on the functioning of the ureter and kidneys, leading to urolithiasis.
In the case of an increase in prostate cells of free radicals that damage DNA molecules, malignancy of healthy cells and the development of cancer are possible. The cause of the oncological disease in the process of chronic prostatitis can also be the synthesis of cytokines and chemokines.
In addition, approximately 35-40% of men who have had a chronic form of prostatitis develop complete infertility or a significant decrease in sperm activity.
Symptoms of acute prostatitis
It is much easier to determine the acute form of the disease yourself, since this stage has more obvious and pronounced signs. The main symptom and reason for a visit to the doctor is general intoxication of the body caused by infectious processes. Signs of acute prostatitis also include:
- increase in body temperature up to 38-39 degrees;
- fever, chills;
- may cause nausea;
- headache;
- increased urge to urinate, accompanied by burning and cutting in the perineum;
- attachment of purulent or bloody discharge from the urethra;
- jet pressure reduction;
- pain during bowel movements;
- severe pain is possible in the lumbar region, lower abdomen or sacrum.
Consequences of a sharp form
The most severe complication of the acute form is the development of an abscess. It is the formation of a cavity filled with purulent secretions, with the further spread of fluid outside the prostate gland. If timely treatment is not provided, the acute form of prostatitis becomes chronic, which is practically not amenable to complete cure.
Most often, young people aged 25 to 50 years are prone to the development of acute prostatitis, while the chronic form is detected, as a rule, in older men, aged 50 years or more. Often, the disease is a consequence of prostate adenoma, the main symptom of which is circulatory disorders and congestion in the pelvic organs.
Disease diagnosis
Before diagnosing prostatitis, a specialist will determine the form of the disease and the degree of its development. Unfortunately, only the acute form of the disease can be completely cured. In the chronic stage, the patient will have to undergo regular examinations by a urologist and repeat the prescribed course of treatment.
There are several basic methods for determining prostatitis even at the very initial stages. The diagnosis and treatment of this disease is carried out by a urologist. The overall picture of the disease is compiled after collecting an anamnesis, as well as confirming the results of tests and diagnostic studies. Despite the similarity of symptoms and the generality of the course of the disease, therapy for each individual patient is selected strictly individually.
Questioning and physical examination
How to determine prostatitis?The very first and most important step is to collect the necessary information and examine the patient. They will help determine further diagnostic appointments and draw up a treatment regimen.
The following factors are taken into account when taking an anamnesis:
- when the first symptoms of the disease appeared;
- sequence of main features;
- whether there are concomitant diseases;
- whether sexually transmitted diseases have been treated before;
- prostatitis duration;
- factors influencing the exacerbation of the disease;
- some data about the patient's genital area;
- information about previous surgeries;
- data on professional and living conditions.
It is the survey that allows the specialist to obtain the necessary information and draw up a presumptive picture of the disease. An important step in how to check the prostate gland is probing the scrotum and palpation of the organ through the rectal opening. If it was not possible to detect violations of the prostate by this method, additional differential diagnosis is prescribed.
Laboratory research
Tests allow you to find out the general health of a man, the nature of the disease and the presence of possible concomitant ailments. Standard list of required tests:
- blood test;
- urinalysis: bacterial, cytological, general;
- urethral swab;
- spermogram;
- polymerase chain reaction test;
- prostate secretion analysis.
Diagnosis using medical equipment
Due to the fact that this testing has a high degree of information content, it allows the urologist to make a more accurate clinical picture and start the necessary treatment sooner.
Another fairly common examination method is uroflowmetry. With the help of this study, a direct graphical determination of the rate of urine outflow is performed. The results show patency of the urinary canal and contractile detrusor ability.
Additional examinations
How to check the prostate in men, if all previous methods could not show the full picture of the disease? In this case, a number of additional measures are assigned, which include:
- cystoscopy examination;
- tomography of the pelvic organs;
- biopsy;
- transurethral ultrasound.
Prostatitis treatment
The most relevant therapy for any form of prostatitis today is still the use of antibacterial drugs. They allow you to eliminate inflammatory processes, so that the main signs of the disease quickly disappear.
Methods of physiotherapeutic treatment have also been widely used. They are also suitable as a prophylaxis, reducing the risk of relapses after treatment, and are also used in the complex therapy of both acute and chronic prostatitis. Physiotherapy methods include thermal procedures, prostate massage, reflexology, ultrasound and much more.
The treatment methods are strictly individual, and the prognosis for a complete cure largely depends on how prostatitis begins, what form the patient has and how long the course of the disease is.
Prevention
To strengthen the body after treatment with medicines, it is recommended to saturate the diet with healthy foods high in vitamins B, A, C, E, minerals: zinc, calcium, iron, and also give up bad habits. In the chronic form of the disease, patients are often advised to take a course of psychotherapeutic measures and reconsider their lifestyle. And remember: any form of illness is not a sentence, and a timely prostate check when you see a doctor will help you start the necessary treatment and forget about unpleasant symptoms for a long time.



























