Home >
Erectile Dysfunction >
What caused the enlarged prostate
What caused the enlarged prostate
What to do and how to treat an enlarged prostate in men?
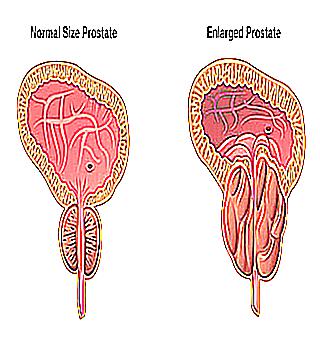
The prostate is located between the urethra and the bladder. This gland plays an important role in the male body, performs various functions.
Under the influence of some factors, it changes its size. Regardless of the reasons, prostate enlargement requires urgent treatment, doctor's supervision.
It must be said that it is problematic to deal with the increase in this organ. However, it is quite possible to slow down, suspend the process.
Why does the prostate gland grow in men?
In the course of the studies, doctors have determined that there are two reasons due to which the prostate gland enlarges. The first is associated with age, the second - with a violation of the functions of the testicles. Next, we will consider the key factors due to which the size of the organ increases.
Hyperplasia or adenoma
Due to the increase in the size of the gland, the urethra begins to gradually shrink. Accordingly, the strength of the flow of urine is weakened. Such an enlargement of the prostate in medicine is called hyperplasia (benign) or prostate adenoma.
Enlarged and normal prostate
In this case, an increase in the organ cannot be called a cancerous tumor. If treatment is not carried out on time, a man may eventually develop Prostate cancer.
Hyperplasia entails such unpleasant complications:
- inflammatory processes;
- chronic stasis of urine;
- renal failure.
Prostate cancer
Another pathology in which the prostate gland enlarges. In such cases, the treatment of the patient is often carried out late.
After all, in the first stages, there are no symptoms that could alert a man. The size of the prostate gland in oncology greatly increases when the tumor grows to a large size.
Bacterial prostatitis
The bacterium is anaerobic, meaning it does not die without the presence of oxygen. During the development of bacterial prostatitis, a pocket is formed in which fluid accumulates. A severe form of bacterial prostatitis entails a significant increase in the prostate.
The organ can grow to large sizes. For this reason, the urethra is blocked completely. Accordingly, urination stops or becomes scarce, drip.
Liquid may begin to stand out completely involuntarily. In such cases, blockage often occurs. Such a phenomenon requires medical intervention.
Characteristic signs of an enlarged prostate
The medical picture of the symptoms of prostate enlargement for various reasons is similar in such a manifestation as difficulty urinating. This happens due to the excess pressure that is exerted on the urinary tract.
If the prostate is enlarged, the following symptoms may appear:
- frequent urination;
- pain during urination;
- persistent feeling of a full bladder;
- Inability to endure, constant urge to urinate.
Severe pains in the lower abdomen, perineum, back are characteristic of the acute form. A man may have a fever, often there is purulent discharge from the urethra.
If the prostate is enlarged, what should I do?
Only specialists can decide what to do with an enlarged prostate. In this case, the patient is sent for a consultation with a urologist, as well as a surgeon, therapist and endocrinologist.
At the same time, doctors prescribe a number of examinations. Thanks to them, it will be possible to identify the cause of an increase in the organ, to assess its condition. Based on the information received, appropriate treatment is prescribed.
The survey process may include the following steps:
- general analysis of blood, urine;
- biochemical blood test;
- performing ultrasound of the pelvic organs;
- blood for sugar, histological analysis.
The main role in the treatment and diagnosis is occupied by the urologist. Other specialists in this process act as consultants. During a manual examination, the specialist makes a preliminary diagnosis, and also sends the patient for tests to confirm it accurately.
What drugs to treat?
In modern medicine, there are many ways to treat an enlarged prostate. Due to the abundance of medicines, it will not be difficult for a specialist to choose the best option for a particular case. The following will describe the most popular remedies for the treatment of an enlarged prostate.
Hormonal drugs
Hormones allow you to regulate the increase in prostate tissue. Androgens, estrogens play an important role in the treatment of hyperplasia.
Thanks to such drugs, the effect of androgen is reduced.The hormones mentioned above block the production of testosterone and also exclude androgenic effects at the prostate level.
Hormones help to reduce the size of the organ, as well as normalize the process of urination. However, in modern medicine, their use is limited due to side effects (impotence, decreased sexual desire).
Antibiotics
Treatment of prostatitis, in which the size of the prostate is enlarged, with antibiotics is the most effective method. The appointment in this case is carried out by the attending physician.
Drugs for the treatment of male disease have certain properties that allow you to respond urgently to the primary manifestations of prostatitis. Antibiotics have the following effect:
The treatment regimen for an enlarged prostate is prescribed by a doctor. In the process of using drugs, it must be followed with maximum accuracy.
For any appointment, the doctor takes into account the stage of the disease, the type of infection and other individual characteristics.
Plant based products
An enlarged prostate can be treated with herbal remedies.
The composition includes extracts that favorably affect the condition and functioning of the prostate gland.
It should be noted that in the case of an acute stage of the disease, phytotherapeutic agents are unable to improve the condition. With an acute manifestation of the disease, it is necessary to use antibiotics and other more effective drugs.
Surgical treatments
Manipulations are carried out through an incision in the perineum or lower abdomen. The advantage of surgical methods is a small percentage of recurrence.
In this case, transurethral penetration is performed. The procedure consists of making incisions on the surface of the enlarged prostate.
Due to this, the pressure of the urethra decreases, and the outflow of urine quickly normalizes.
Related video
About prostate adenoma and methods of its treatment in the video:
When incising the gland, a complication may occur - intense bleeding. If a large amount of blood enters the cavity during the operation, a second surgical intervention may be required.
In the case of prostate tissue incision, another complication after surgery may occur - retrograde ejaculation. In this case, the release of seminal fluid is carried out into the bladder. Therefore, experts do not recommend resorting to this method for those men who plan to have children in the future.
Causes and treatment of prostate enlargement in men
An enlarged prostate is a diagnostic symptom that indicates a serious disease. With age, due to hormonal failure, benign prostatic hypertrophy is observed. With an infectious, congestive lesion, inflammation (prostatitis) develops. The most dangerous pathology, accompanied by a local excess in tissue size, is cancer. All of these diseases require medical or surgical treatment, as they cause complications that threaten the patient's life.
Why does the prostate enlarge and what does it mean
In chronic prostatitis, inflammation occurs - this means the accumulation of macrophages and microphages, which must destroy and absorb the infection or stagnant formations. The enlargement of the gland is focal (local) in nature. With a plurality of foci, their overlap occurs, which makes it seem that the entire prostate is growing.
Adenoma means a uniform increase in the entire area of \u200b\u200bthe gland - it can be 2 times larger in length and width, or even 4 times. The growing tissue is not pathological - the natural glandular epithelium of the prostate is growing.
In cancer, the increase is local in nature - single or multiple tumor foci appear. But if the lymph nodes are affected, then lymphostasis begins and the entire prostate increases.
The causes of prostate enlargement in different diseases are different. Adenoma occurs due to the fact that with age in a man there is a decrease in testosterone levels with a simultaneous increase in dihydrotestosterone. Prostatitis is caused by congestion and/or infection. Malignant neoplasms appear due to hormonal disruptions, hereditary predisposition.
At risk are men with hypodynamia, irregular sex life, hypothermia of the lower body, who have not cured a viral disease, STDs, and bladder stones in time. After 60 years, the risk of prostate pathologies increases 3 times.
Manifestations
Prostatopathic and dysuric symptoms help to suspect an enlarged gland. The clinical picture is as follows:
- Pain in the prostate due to involvement of nerve fibers. Unpleasant sensations are localized in the groin area, in the penis, lower abdomen.
- Disorders of the excretory system.A man is worried about frequent urge to urinate, but complete emptying of the bladder is difficult, the urine stream is weak.
- Deterioration of libido. Erection is weak or absent. Sperm is liquid, it stands out a little.
The listed signs of prostate enlargement are a reason to be examined in the hospital. To make an accurate diagnosis, the doctor performs a physical examination of the prostate. Severe prostate enlargement and large neoplasms are palpated rectally. The next step is laboratory tests of blood, urine and semen to help identify biochemical symptoms:
- For prostatitis: a large number of leukocytes, mucus in the urine.
- With prostate adenoma: an increase in blood urea and creatinine is possible, leukocyturia and hematuria are also detected.
- With prostate cancer: PSA increases (twice or more above the norm), leukocytosis, increased ESR.
In addition, an instrumental examination of the prostate is performed. Ultrasound and CT look for echographic abnormalities. With uroflowmetry, a violation of the urodynamics of the urethra is detected. A biopsy helps to distinguish benign from cancerous formations.
What to do if the prostate is enlarged
Specialists use observation for adenoma with a slight overgrowth of the gland. Passive tactics are also used in cancer - if the tumor is small, and treatment can cause more harm than inaction (for example, in elderly patients with contraindications to chemotherapy and surgery). In this case, a man needs to undergo regular examinations (at least once every six months) and prevent complications.
In the first stages of prostatitis, if the prostate is slightly enlarged, the disease is asymptomatic, so non-drug treatment is used: prostate massage, herbal medicine, exercises to train the muscles of the bladder, perineum. Medication is used for exacerbations and the rapid development of pathology. In the absence of the effectiveness of drugs and the threat to the patient's life, an operation is performed.
Medications: what to take
The choice of a drug for adenoma depends on how much the gland has increased and what symptoms the pathology causes. If the prostate is less than 40 grams, a man should take b1-blockers (Terazosin, Prazosin). When the organ becomes very large, 5-alpha reductase inhibitors (Finasteride, Dutasteride) are used.
The treatment of an enlarged prostate with prostatitis begins with the relief of the cause. In case of an infectious disease, antibiotics are prescribed (drugs are selected according to the type of microbial flora). Inflammation is reduced by taking NSAIDs (Diclofenac, Meloxicam).
Alpha-blockers (Tamsulosin, Silodosin) are taken to improve the patient's condition. By stopping the activity of alpha1-adrenergic receptors, the smooth muscles of the urinary tract relax, which facilitates urination.
Phytomedications
Treatment of an enlarged prostate with herbal preparations is allowed only at the earliest stages of the pathology, as well as as an additional remedy (to enhance the effect of drugs, recover faster after surgery). For inflammation in the gland, pumpkin seed oil, wheat germ extracts are used.
With benign prostatic hyperplasia, remedies like the Powerful, Silver Yantra, Silaprost, Prostarin, Prostacin help. Treatment with them stops the "age menopause" (when after 50-60 years a hormonal imbalance occurs in men). As part of such herbal remedies - calamus root, eleutherococcus, licorice, yarrow, celandine, elamine concentrate, spirulina, sage.
Hormonotherapy
With a strong inflammatory increase, the doctor will prescribe drugs with steroids (Dexon, Medrol, Kenalog, Diprospan). Also, with prostatitis, they drink drugs with testosterone - they do not eliminate inflammation of the prostate, but help to cope with the consequences of prostatitis (impotence, oligospermia).
Hormonal treatment is carried out for cancer. The goal is the blockade of androgens (since oncology is a hormone-dependent formation). Medications are prescribed with:
- LHRH (gonadorelin): Goserelin, Buserelin, etc.
- Estrogens: Hexestrol, Megestrol, etc.
The downside is that hormone therapy in the treatment of cancer is medical castration (the reproductive and reproductive systems are turned off). In addition, there is no complete cure for oncology (injections and pills only slow down cancer).
Folk methods
For adenoma and prostatitis, bathing with infusions of chamomile and coniferous cones can be used. Such treatment with folk remedies can reduce pain, improve the process of urination. With infectious inflammation, onion or garlic baths help (4 handfuls of onion peel / 2 garlic heads pour 2 liters of hot water, leave for 30 minutes and pour into the typed bath).
Decoctions of parsley with lemon and honey (taken orally) help to improve overall well-being.Dandelion tincture is useful for congestive prostatitis (helps improve blood circulation). A decoction of calendula, according to Elena Zaitseva, a popular herbalist on the network, is good to take with a predisposition to prostate cancer (the remedy helps to stop the growth of tumors).
Surgical intervention
The operation is prescribed for the last stages of prostate diseases, when the size of the tissues is increased to such an extent that the urinary ducts are completely squeezed. Also an indication is the rapid development of the disease and the lack of progress with drug therapy. The following types of surgical treatment are used:
- resection - cutting off the affected part of the prostate;
- prostatectomy - complete removal of the gland;
- vaporization - evaporation of pathological zones with a laser.
After the operation, the patient needs rehabilitation, including taking medications (including antibiotics), diet, exercise therapy (special exercises), and physiotherapy. This will avoid postoperative complications.
What is the danger of an enlarged prostate
If the prostate gland is enlarged, then measures must be taken to prevent further growth. Inaction is fraught with dangerous consequences. Tissue hypertrophy leads to blockage of the flow of urine. The result is acute intoxication with uric acid, pyelonephritis, renal failure (failure of the kidneys), rupture of the bladder. These pathologies are deadly.
Prostate cancer should be treated as early as possible due to possible metastasis. If secondary foci of cancerous growths appear outside the gland, the patient's chances of survival are low - in 94% of men with the last stage of the disease live less than 3 years.
Prevention
To prevent prostate hypertrophy, proper nutrition is required (a healthy prostate needs foods with zinc, phosphorus, potassium, selenium, iron). It is important to avoid physical inactivity (sit less than 40 minutes in a row, do gymnastics, walk more). Regular sex life will prevent stagnant formations.
Since the increase in the volume of the gland is asymptomatic at first, a man should undergo a preventive examination by a urologist 1-2 times a year. If the doctor detects pathological changes in the prostate, it is important to start treatment immediately. Any delay threatens the development of complications.
Enlarged prostate: causes and treatment
An enlarged prostate is often detected when examined by a doctor during a medical examination. A change in size most often occurs as a result of an inflammatory process. As a result of this phenomenon, the patient may develop prostatitis. It is impossible to establish the cause of the increase in tissue size on its own. Therefore, you should immediately consult a doctor if symptoms of the disease are detected.
What is the prostate
The prostate is a small gland. It is shaped like a chestnut. The gland is located under the bladder and in front of the rectum: on top of the urethra. The prostate is one of the main components of the male reproductive system. The gland performs many functions, one of which is the creation of sperm.
In some diseases, the prostate can change its size. If you experience such a symptom, you should definitely visit a doctor. An enlarged prostate needs immediate treatment.
For starters, it is recommended to undergo a thorough examination and establish the cause of the development of the disease. Only a qualified specialist is able to correctly diagnose and prescribe adequate therapy.
What you need to know about an enlarged prostate
An enlarged prostate indicates the presence of certain pathologies in the body. When a boy is just born, his prostate gland is tiny. During puberty, testosterone production increases in young people. As a result, the prostate enlarges. Fully iron begins to function at the age of 17.
In the subsequent period of 20 years, the growth of the prostate slows down significantly. Iron does not cause problems. It is worth noting that an enlarged prostate occurs only in 10% of men who are 30 years old.
The growth of the prostate gland does not stop there. The second surge occurs at age 40. More than 50% of men suffer from an enlarged prostate by the age of 60, and 90% by the age of 80.
Code needs treatment
During puberty, the growth of the gland is considered normal and this process proceeds evenly and without symptoms. However, the prostate, enlarged after 40 years, needs therapy. When such a phenomenon occurs, the urethra is the first to suffer. It is strongly compressed, which leads to some difficulty in emptying the bladder. Doctors ascribed the name "benign hyperplasia" to this condition. The second name of such a pathology is prostate adenoma.
In most cases, hyperplasia begins to progress. As a result of this, the man ceases to completely empty his bladder, as the urethra is compressed more strongly. The problems don't end there. It should be noted that the development of this pathology often leads to thickening of the walls of the bladder itself. Timely diagnosis and therapy can get rid of hyperplasia in the early stages.
Symptoms of pathology
The enlarged prostate can be very disturbing for a man. The main symptom of pathology is difficulty in the process of urination. This symptom of disorders occurs in almost all patients who have encountered such a problem.
Symptoms of the disease can be mild. After all, the pressure of the enlarged prostate gland can be compensated to some extent by the muscles of the bladder itself. An enlarged prostate usually presses on the urethra. This may be indicated by an interrupted or compressed urine stream. In addition to these symptoms, the patient may experience:
- discomfort arising from incomplete emptying of the bladder;
- urine in some cases continues to drip even after urination;
- Difficulty urinating.
The severity of these symptoms depends on whether the enlarged prostate bothers you. Treatment also depends on these indicators.
Other features
If the prostate is enlarged by 2 times, then the fluid collected in the bladder can cause irritation. Symptoms of the disease in this case will be different:
- pain during urination;
- incontinence - loss of control over the process of urination;
- frequent urge to urinate, especially at night;
- A sense of urgency that goes along with the urge to urinate.
Enlarged prostate: causes
Treatment of a disease begins with determining the cause of its development. Therefore, it is worth going through a thorough examination. Among the main reasons for the development of pathology are:
- Prostate growth stimulates an increase in estrogen production and a decrease in testosterone production.
- The prostate produces a substance - dihydrotestosterone, which neutralizes testosterone. With age, the synthesis of DHT in the body does not decrease. But the production of testosterone is reduced. As a result, the prostate cells are stimulated.
- Genetic predisposition. The growth of prostate cells can be programmed in adulthood.
- Prostate cancer.
- A variety of infectious diseases accompanied by an inflammatory process.
Basic therapies
What to do if the prostate is enlarged? How to treat such a pathology? And these questions can only be answered by a specialist in a narrow profile. At the moment, there are several main areas: surgical, medical treatment and observational. The choice of the method of therapy depends on which factor influenced the stimulation of the growth of gland cells, as well as on how much the tissues increased in size.
It is simply impossible to choose the right method on your own. Only a doctor can do this. Do not try to independently identify the cause of the development of pathology. Self-medication in this case can cause the development of serious complications.
Observer Method
This type of treatment for an enlarged prostate is chosen if:
- The patient has mild signs of pathology that do not cause severe discomfort.
- If the patient does not want to identify the cause of the disease for a long time and take medications and experience their side effects.
- If the number of symptoms is significantly reduced after lifestyle changes.
What to do while waiting
If the observation method is chosen, then the patient should reduce the amount of fluid consumed during the day. For two hours before going to bed, you can not drink anything.
It is necessary to completely exclude the use of alcoholic beverages. When visiting the toilet, you must completely empty your bladder. Before taking any diuretic drug, you should carefully study its side effects. Do not take medicines without consulting a specialist. Uncontrolled treatment of the symptoms of the disease can aggravate the situation.
Drug treatment
If a man's prostate is enlarged and the method of observation has not brought proper results, then drug therapy is prescribed. This method is justified if:
- observing the patient did not help;
- there is a risk of developing serious complications;
- No changes have occurred since the lifestyle change.
Features of drug therapy
If the method of observation is not suitable and the patient does not improve, then the doctor may prescribe medication. They should only be taken as directed.Do not exceed the dosage allowed by the doctor. The required amount of drugs is determined after establishing the cause of prostate enlargement and examination. When prescribing, the specialist also takes into account the symptoms described by the patient. For therapy can be prescribed:
Hormones; alpha blockers; phytopreparations; antimicrobial agents; homeopathic preparations; polyene antibiotics; anticancer and antiparkinsonian drugs. Treatment with herbal remedies Even in ancient times, various herbs tried to overcome prostate enlargement. At the moment, therapy of this kind offers many collections of medicinal plants, which mainly include extracts.
The effectiveness of such products depends on how much they contain phytosterols. Such drugs can reduce the production of prostaglandin in the prostate, relieve the inflammatory process, completely stop or slow down the active growth of tissue cells. Such drugs are taken only as directed by a doctor.
Hormones
Hormonal drugs allow you to normalize the process of active growth of prostate tissues. With the development of pathology, estrogens and androgens are of particular importance. The latter block the synthesis of testosterone. They can also affect the androgenic effect on the damage to the prostate or hypothalamus-pituitary gland.
Hormonal drugs can not only normalize urination, but also reduce prostate tissue in size. However, the use of such drugs has recently been limited, since such formulations have many side effects. It is especially worth highlighting such disorders as a decrease in impotence and sexual desire. It is not recommended to take any hormones on your own.
Surgical intervention
The doctor may prescribe surgery if the patient has an enlarged prostate. The causes of the development of the disease may be hidden in the formation of tumors. It is worth noting that not so long ago, this method of therapy was considered the most effective. However, more modern drugs have appeared, and surgical interventions for an enlarged prostate are rarely resorted to. Most often, the operation is performed in cases where there are factors that aggravate the patient's condition, or drug therapy has not helped. Surgery is performed if:
Bleeding from the urethra began; there were serious problems with the process of urination; there are stones in the bladder; acute urinary retention appeared; incomplete emptying of the bladder; medical treatment was ineffective; Complications appeared - a violation of the kidneys, an inflammatory process, and so on. Features of surgical intervention The operation, which is performed with an enlarged prostate, is an effective and radical method of therapy, but at the same time quite dangerous. This is the development of undesirable consequences after surgery. The patient may experience problems with potency, as well as uncontrolled leakage of fluid from the bladder and narrowing of the urethra. It is not recommended to perform the operation if the patient has:
- diabetes mellitus;
- severe diseases of the kidneys, lungs, heart;
- mental disorders;
- cirrhosis of the liver.
The most common way to treat an enlarged prostate through surgery is transurethral surgery and prostatectomy. In the first case, the removal of the gland is carried out through the urethra, and in the second - by cutting the abdominal wall.
If left untreated
What if the prostate is enlarged? What to do if such a pathology occurs? If the cause of the development of the disease is not identified in time, complications may appear. First of all, the bladder will not empty completely. It will gradually accumulate fluid, which, ultimately, will lead to the growth of microorganisms and the development of an infectious disease. Often, under such circumstances, stones are formed.
In this case, the vessels located on the inner surface will be subject to regular damage. This can lead to blood in the urine. A similar symptom may occur due to stretching of the tissues of the bladder. If at this stage the man does not consult a doctor, the disease will progress. As a result, urine will begin to flow back to the kidneys, which will further lead to their insufficiency.
It is for this reason that it is worth paying attention to even minor symptoms. If prostate adenoma is enlarged and the disease is not treated, then irreversible consequences may begin.
Final
If the prostate is enlarged, then you should immediately visit a doctor. In the absence of adequate treatment, the pathology will continue to develop, which will eventually lead to irreversible consequences. Do not put off visiting the clinic. Timely treatment will help to avoid the development of prostate cancer.



























