Home >
Erectile Dysfunction >
Three times enlarged prostate
Three times enlarged prostate
Enlarged prostate: causes and treatment
An enlarged prostate is often detected when examined by a doctor during a medical examination. A change in size most often occurs as a result of an inflammatory process. As a result of this phenomenon, the patient may develop prostatitis. It is impossible to establish the cause of the increase in tissue size on its own. Therefore, you should immediately consult a doctor if symptoms of the disease are detected.
What is the prostate
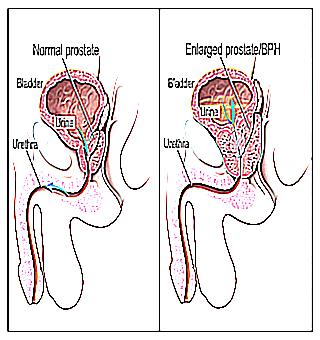
The prostate is a small gland. It is shaped like a chestnut. The gland is located under the bladder and in front of the rectum: on top of the urethra. The prostate is one of the main components of the male reproductive system. The gland performs many functions, one of which is the creation of sperm.
In some diseases, the prostate can change its size. If you experience such a symptom, you should definitely visit a doctor. An enlarged prostate needs immediate treatment.
For starters, it is recommended to undergo a thorough examination and establish the cause of the development of the disease. Only a qualified specialist is able to correctly diagnose and prescribe adequate therapy.
What you need to know about an enlarged prostate
An enlarged prostate indicates the presence of certain pathologies in the body. When a boy is just born, his prostate gland is tiny. During puberty, testosterone production increases in young people. As a result, the prostate enlarges. Fully iron begins to function at the age of 17.
In the subsequent period of 20 years, the growth of the prostate slows down significantly. Iron does not cause problems. It is worth noting that an enlarged prostate occurs only in 10% of men who are 30 years old.
The growth of the prostate gland does not stop there. The second surge occurs at age 40. More than 50% of men suffer from an enlarged prostate by the age of 60, and 90% by the age of 80.
Code needs treatment
During puberty, the growth of the gland is considered normal and this process proceeds evenly and without symptoms. However, the prostate, enlarged after 40 years, needs therapy. When such a phenomenon occurs, the urethra is the first to suffer. It is strongly compressed, which leads to some difficulty in emptying the bladder. Doctors ascribed the name "benign hyperplasia" to this condition. The second name of such a pathology is prostate adenoma.
In most cases, hyperplasia begins to progress. As a result of this, the man ceases to completely empty his bladder, as the urethra is compressed more strongly. The problems don't end there. It should be noted that the development of this pathology often leads to thickening of the walls of the bladder itself. Timely diagnosis and therapy can get rid of hyperplasia in the early stages.
Symptoms of pathology
The enlarged prostate can be very disturbing for a man. The main symptom of pathology is difficulty in the process of urination. This symptom of disorders occurs in almost all patients who have encountered such a problem.
Symptoms of the disease can be mild. After all, the pressure of the enlarged prostate gland can be compensated to some extent by the muscles of the bladder itself. An enlarged prostate usually presses on the urethra. This may be indicated by an interrupted or compressed urine stream. In addition to these symptoms, the patient may experience:
- discomfort arising from incomplete emptying of the bladder;
- urine in some cases continues to drip even after urination;
- Difficulty urinating.
The severity of these symptoms depends on whether the enlarged prostate bothers you. Treatment also depends on these indicators.
Other features
If the prostate is enlarged by 2 times, then the fluid collected in the bladder can cause irritation. Symptoms of the disease in this case will be different:
- pain during urination;
- incontinence - loss of control over the process of urination;
- frequent urge to urinate, especially at night;
- A sense of urgency that goes along with the urge to urinate.
Enlarged prostate: causes
Treatment of a disease begins with determining the cause of its development. Therefore, it is worth going through a thorough examination. Among the main reasons for the development of pathology are:
- Prostate growth stimulates an increase in estrogen production and a decrease in testosterone production.
- The prostate produces a substance - dihydrotestosterone, which neutralizes testosterone.With age, the synthesis of DHT in the body does not decrease. But the production of testosterone is reduced. As a result, the prostate cells are stimulated.
- Genetic predisposition. The growth of prostate cells can be programmed in adulthood.
- Prostate cancer.
- A variety of infectious diseases accompanied by an inflammatory process.
Basic therapies
What to do if the prostate is enlarged? How to treat such a pathology? And these questions can only be answered by a specialist in a narrow profile. At the moment, there are several main areas: surgical, medical treatment and observational. The choice of the method of therapy depends on which factor influenced the stimulation of the growth of gland cells, as well as on how much the tissues increased in size.
It is simply impossible to choose the right method on your own. Only a doctor can do this. Do not try to independently identify the cause of the development of pathology. Self-medication in this case can cause the development of serious complications.
Observer Method
This type of treatment for an enlarged prostate is chosen if:
- The patient has mild signs of pathology that do not cause severe discomfort.
- If the patient does not want to identify the cause of the disease for a long time and take medications and experience their side effects.
- If the number of symptoms is significantly reduced after lifestyle changes.
What to do while waiting
If the observation method is chosen, then the patient should reduce the amount of fluid consumed during the day. For two hours before going to bed, you can not drink anything.
It is necessary to completely exclude the use of alcoholic beverages. When visiting the toilet, you must completely empty your bladder. Before taking any diuretic drug, you should carefully study its side effects. Do not take medicines without consulting a specialist. Uncontrolled treatment of the symptoms of the disease can aggravate the situation.
Drug treatment
If a man's prostate is enlarged and the method of observation has not brought proper results, then drug therapy is prescribed. This method is justified if:
- observing the patient did not help;
- there is a risk of developing serious complications;
- No changes have occurred since the lifestyle change.
Features of drug therapy
If the method of observation is not suitable and the patient does not improve, then the doctor may prescribe medication. They should only be taken as directed. Do not exceed the dosage allowed by the doctor. The required amount of drugs is determined after establishing the cause of prostate enlargement and examination. When prescribing, the specialist also takes into account the symptoms described by the patient. For therapy can be prescribed:
Hormones; alpha blockers; phytopreparations; antimicrobial agents; homeopathic preparations; polyene antibiotics; anticancer and antiparkinsonian drugs. Treatment with herbal remedies Even in ancient times, various herbs tried to overcome prostate enlargement. At the moment, therapy of this kind offers many collections of medicinal plants, which mainly include extracts.
The effectiveness of such products depends on how much they contain phytosterols. Such drugs can reduce the production of prostaglandin in the prostate, relieve the inflammatory process, completely stop or slow down the active growth of tissue cells. Such drugs are taken only as directed by a doctor.
Hormones
Hormonal drugs allow you to normalize the process of active growth of prostate tissues. With the development of pathology, estrogens and androgens are of particular importance. The latter block the synthesis of testosterone. They can also affect the androgenic effect on the damage to the prostate or hypothalamus-pituitary gland.
Hormonal drugs can not only normalize urination, but also reduce prostate tissue in size. However, the use of such drugs has recently been limited, since such formulations have many side effects. It is especially worth highlighting such disorders as a decrease in impotence and sexual desire. It is not recommended to take any hormones on your own.
Surgical intervention
The doctor may prescribe surgery if the patient has an enlarged prostate. The causes of the development of the disease may be hidden in the formation of tumors. It is worth noting that not so long ago, this method of therapy was considered the most effective. However, more modern drugs have appeared, and surgical interventions for an enlarged prostate are rarely resorted to. Most often, the operation is performed in cases where there are factors that aggravate the patient's condition, or drug therapy has not helped.Surgery is performed if:
Bleeding from the urethra began; there were serious problems with the process of urination; there are stones in the bladder; acute urinary retention appeared; incomplete emptying of the bladder; medical treatment was ineffective; Complications appeared - a violation of the kidneys, an inflammatory process, and so on. Features of surgical intervention The operation, which is performed with an enlarged prostate, is an effective and radical method of therapy, but at the same time quite dangerous. This is the development of undesirable consequences after surgery. The patient may experience problems with potency, as well as uncontrolled leakage of fluid from the bladder and narrowing of the urethra. It is not recommended to perform the operation if the patient has:
- diabetes mellitus;
- severe diseases of the kidneys, lungs, heart;
- mental disorders;
- cirrhosis of the liver.
The most common way to treat an enlarged prostate through surgery is transurethral surgery and prostatectomy. In the first case, the removal of the gland is carried out through the urethra, and in the second - by cutting the abdominal wall.
If left untreated
What if the prostate is enlarged? What to do if such a pathology occurs? If the cause of the development of the disease is not identified in time, complications may appear. First of all, the bladder will not empty completely. It will gradually accumulate fluid, which, ultimately, will lead to the growth of microorganisms and the development of an infectious disease. Often, under such circumstances, stones are formed.
In this case, the vessels located on the inner surface will be subject to regular damage. This can lead to blood in the urine. A similar symptom may occur due to stretching of the tissues of the bladder. If at this stage the man does not consult a doctor, the disease will progress. As a result, urine will begin to flow back to the kidneys, which will further lead to their insufficiency.
It is for this reason that it is worth paying attention to even minor symptoms. If prostate adenoma is enlarged and the disease is not treated, then irreversible consequences may begin.
Final
If the prostate is enlarged, then you should immediately visit a doctor. In the absence of adequate treatment, the pathology will continue to develop, which will eventually lead to irreversible consequences. Do not put off visiting the clinic. Timely treatment will help to avoid the development of Prostate cancer.
Prostate enlargement with age and in young men: causes and consequences
What can an enlarged prostate indicate? According to doctors, an increase in the size and volume of the prostate may be the result of a number of dangerous pathologies of the genitourinary system.
The prostate gland can enlarge due to acute or chronic prostatitis, prostate adenoma/cancer/cyst, prostate abscess. Also, an increase in the size of the glandular organ is often observed during the period of male menopause and in people leading an unhealthy lifestyle.
In case of an enlarged prostate, it is recommended to consult a urologist for appropriate treatment. Let us consider in more detail the causes and symptoms of prostate enlargement, and also find out how this phenomenon can be leveled.
Causes of prostate enlargement
The prostate gland is an unpaired glandular organ. It is located under the bladder. The prostate consists of two glands, between which is the so-called groove. Part of the urethra (urethra) also passes through the pancreas.
What are the causes and consequences of prostate enlargement? Let's start with the reasons, of which there are a huge number. Certain diseases, bad habits, hypothermia, etc. can provoke an increase in the size of the prostate gland.
So, the main reasons are:
Predisposing factors include poor ecology, hereditary predisposition, harmful working conditions, the presence of other diseases of the genitourinary system.
How to recognize an enlarged prostate?
When the size of the prostate gland increases, the patient has certain signs. The severity of symptoms directly depends on the root cause of pathological changes and the age of the patient.
The first characteristic symptom is pain in the perineum. The intensity of pain sensations can vary. If the pancreas increases due to congestion, menopause or bad habits, pain may appear periodically and then disappear without a trace.
In more serious pathologies, the patient has pain in the perineum almost constantly. Moreover, pain sensations can irradiate ("give") to the lower back, anus, penis and testicles.
- Erectile dysfunction.Libido may also decrease and premature ejaculation may appear.
- Dysuric disorders. Manifestations of an enlarged prostate can be frequent urge to urinate, a feeling of incomplete emptying of the bladder, intermittent jet syndrome, pain during urination. Also, the patient may complain of itching and burning in the urethra.
- The appearance of blood in the urine / semen.
- Weakness, body aches, fever.
- Urinary incontinence (in rare cases).
- Purulent, mucous, cheesy discharge from the urethra. Occur only with infectious, fungal or bacterial prostatitis.
Differential diagnosis will help to identify the root cause of prostate enlargement.
Diagnostic measures
If you experience dysuric disorders and other symptoms of prostate enlargement, you should immediately seek medical help. A urologist treats diseases of the genitourinary system.
First, the doctor conducts an oral survey, clarifies the patient's complaints, studies the anamnesis data. Then a physical digital examination of the prostate is performed. With palpation, the physician will be able to examine the structure, size and shape of the prostate.
The diagnostics, of course, does not end there. The following examinations are mandatory:
If cancer is suspected, a biopsy and MRI of the prostate may be additionally prescribed.
How to reduce the size of the prostate?
What to do with an enlarged prostate? The principle of treatment is selected by the doctor. The doctor takes into account the root cause of pathological changes. Therapy can be performed conservatively or surgically.
There are a number of general recommendations. Regardless of the underlying cause, patients are encouraged to move more and eat a balanced diet. Also, a prerequisite for recovery is the rejection of bad habits - drug addiction, smoking and alcoholism.
The principles of treatment are as follows:
- Prostatitis. With inflammation of the pancreas, conservative therapy is indicated. The patient will need to take a number of medications - antibiotics, alpha-1-blockers, NSAIDs, herbal remedies, bioregulatory peptides. Prostate massage and physiotherapy are also recommended for prostatitis.
- Male menopause. It is impossible to get rid of it, and there is no need for it. But if a patient has a severe androgen deficiency, testosterone-based hormonal preparations may be prescribed.
- Prostate cyst. If the cystic formation is small, does not fester and does not bring discomfort, the patient is shown dynamic observation by doctors. Remove the cyst only if it increases in size or brings a lot of discomfort.
- Prostate abscess. Treatment is exclusively surgical. After surgery, the patient is prescribed antibiotics.
- Stagnation. The prostate can grow due to the fact that a man has impaired blood circulation in the pelvis. To level this phenomenon is very simple - you need to move more, get rid of excess weight, have sex more often, attend prostate massage sessions.
- Prostate adenoma. BPH is treated conservatively or surgically. If the tumor is small, then the patient will need to take alpha-1-blockers, herbal remedies, and 5-alpha reductase inhibitors. When the tumor is large in size, surgical treatment is prescribed. Adenoma can be removed with a laser, cryosurgery, needle ablation, prostatectomy.
- Prostate cancer. It is treated with an operation during which the neoplasm and the prostate are removed. Additionally, chemotherapy may be prescribed.
As you can see, absolutely any root cause of prostate enlargement can be eliminated. The main thing is not to hesitate and seek medical help in a timely manner.
Complications and prevention
What will happen if you do not get rid of prostate diseases in a timely manner? Negligent attitude to this problem is fraught with many complications. The most dangerous consequences of pancreatic cancer. If the patient does not treat cancer in a timely manner, then metastases may appear. In this case, even death is possible.
Also, the consequences of untimely treatment of prostate diseases are impotence, prostate fibrosis, acute Urinary retention, renal failure, urolithiasis, calculous prostatitis, cystitis, urethritis, pyelonephritis.
As for the prevention of pancreatic diseases, doctors give the following recommendations:
It is also recommended to undergo preventive examinations from doctors from time to time.
Patients over 45 years of age should have a blood test for PSA and ultrasound of the prostate gland at least once every 3-4 months. If diseases are detected in the early stages, they will be much easier to cure.
What does an enlarged prostate mean in men and how to treat it
An enlarged prostate is an overgrowth of the soft tissues of the prostate gland, which is an important part of the male reproductive system.The organ gradually increases under the influence of testosterone during puberty up to 17 years, reaching 25-30 cm. Starting from 30-35 years, in 10% of cases there is a pathological enlargement of the prostate gland: prostate adenoma (BPH), prostatitis or cancer. The second burst of age-related growth falls on the age after 40 years. After 60 years, prostate enlargement is observed in 85-90% of men.
Causes of prostate enlargement:
If the prostate is enlarged, the level of PSA (prostate-specific antigen) may be elevated. Most often this occurs with benign hyperplasia (adenoma) and means that a man has a predisposition to developing prostate cancer. The risk group for malignant transformation includes men aged 80 years and older (develops in 70-80% of cases).
The inflammatory process in the prostate occurs under the influence of the following factors:
- Stagnation processes (low physical activity, prolonged sexual abstinence, coitus interruptus).
- Hypothermia and an unbalanced diet (lack of vegetable fiber, seafood in the menu, the predominance of spicy and fatty dishes).
- Bad habits (alcohol, smoking) and unprotected intercourse with casual partners.
- Injury and dysfunction of the prostate under the influence of constant vibration (for example, drivers).
- Hormonal disorders (relative or absolute androgen deficiency).
- Infectious and bacterial lesions (STIs, kidney pathology, sinusitis, tonsillitis, etc.).
The incidence of prostate adenoma increases with age and under the influence of male hormones. In 60% of cases, the cause is heredity. Among the predisposing factors, obesity should be highlighted, which means that adipose tissue is a substrate for the synthesis of estrogens that provoke BPH. Sexually transmitted diseases (syphilis, gonorrhea, chlamydia, genital herpes, etc.) are of great danger.
Symptoms and signs
Signs of prostate enlargement depend on the cause of growth and the degree of progression of the pathological process. With prostatitis, the symptoms manifest themselves brightly in the case of an acute course of the disease. There is frequent urination, a slight increase in body temperature (up to 37.0-37.5 degrees) and there are problems with potency. There is pain during defecation. In chronic prostatitis, there is a weak erection, discomfort in the perineum and groin, and the excretion of white flakes in the urine.
In benign prostatic hyperplasia, the symptoms depend on the stage of progression of the disease:
At the compensated stage, an increase in the size of the prostate by 2 times is observed, there are frequent urges to urinate, but the urine stream is intermittent. At night, a man can visit the restroom up to 8-10 times. The emptying of the bladder occurs - this requires considerable effort. Libido decreases and sperm quality deteriorates.
The subcompensated stage of BPH occurs after 10 years and even later. It is characterized by the appearance of pain during urination. The urine stream becomes weaker and urine leakage occurs, which is associated with pressure on the urinary tract. Urinary retention is possible after colds, hypothermia and drinking alcohol. There is pain in the groin that radiates to the lower back. Against the background of constant stress, a hernia or hemorrhoids may develop.
After 2-3 years, the third stage of prostate adenoma occurs - decompensated. The health of a man at this stage is deteriorating significantly. The process of urination is carried out only with the help of a urinal, the muscles of the bladder weaken. Additional symptoms are regular thirst, constipation, nausea, drowsiness and weakness.
Prostate cancer is most often discovered by chance during an examination. At the initial stages of development, the symptoms are mild and are manifested by burning and discomfort during urination, frequent urges. With the growth of the tumor, when the prostate begins to compress the urethra, there are difficulties in urination, insufficiency of erection and a decrease in the volume of semen during ejaculation.
How to treat
With the development of pathological changes in the genitourinary system, it is recommended to visit the urologist's office. The doctor will conduct a comprehensive diagnosis, and if the prostate is enlarged, prescribe treatment. The choice of method is influenced by several factors - the causes of the development of the disease, the degree of progression and the general condition of the patient.
In the initial stages of prostate enlargement, the doctor will prescribe medications and prescribe periodic preventive examinations to monitor the effectiveness of treatment. If the drugs do not give the expected result, the patient will be referred for surgery.
Surgical intervention is rarely resorted to, since modern pharmaceutical concerns offer highly effective drugs. They help to cope even with advanced forms of disorders that cause prostate enlargement.
It is permissible to treat an enlarged prostate with pills only after consulting a doctor. Medicines are selected depending on the type and form of the disease.
For an enlarged prostate, the following are prescribed:
- Antibiotics (for prostatitis only)
- Alpha blockers
- Analgesics
- Immunomodulators
Medications help relieve the inflammatory process and improve the patient's condition. Timely measures taken can reduce obstructive urethral changes.
Phytotherapy
Among the effective herbal preparations for a slight enlargement of the prostate, the following should be highlighted:
The treatment of an enlarged prostate with the help of herbal remedies helps to relieve urethral obstruction and reduce the residual amount of urine, normalizing the process of urination. Medicines developed on a plant basis have no contraindications, with the exception of individual intolerance to the components.
Hormonal treatment
Hormonal regulation is necessary when the prostate is enlarged by 3 times and is carried out using the following drugs:
Hormonal treatment contributes to the normalization of testosterone levels and stops the progression of the pathological process. The therapeutic approach is aimed at preventing malignant transformation and reducing the size of the prostate through atrophy and apoptosis of cellular structures.
Alternative medicine
If the prostate gland is doubled, then the following folk remedies can be used:
- Bee subpestilence. Pour raw materials with 500 ml of water and insist for two hours, then carefully strain and drink 1 tbsp. l. 2-3 times a day.
- Aspen and hazel. Grind the bark and brew 20 g of raw materials with 300 ml of boiling water, insist for 30 minutes, strain and take 60 ml 4 times a day.
- Walnut and pumpkin seeds. Clean and grind the raw materials in a coffee grinder, combine with 2 tsp. natural honey, take 1 tbsp. l. 3-5 times a day.
Treatment with folk remedies is used to prevent the progression of prostate diseases or at the initial stages of the development of pathological changes. It is recommended to use folk remedies together with medicines, which helps to increase their effectiveness and bring recovery closer.
Surgical treatment for prostate enlargement is prescribed with a strong increase in the organ of the genitourinary system in size - 4 times, but only if drug therapy does not cope with the problem. Prostatectomy is indicated for prostate cancer, calculous prostatitis and advanced adenoma.
Surgery for an enlarged prostate is performed in several ways, the choice of which depends on the size of the prostate:
- Incision (V - 20-30 cm 3 ) - is prescribed for BPH to normalize the process of urination.
- Transurethral resection (V - 30-80 cm 3 ) - is carried out using a laparoscope and involves curettage of the formation.
- Adenomectomy (V - 80-100 cm 3 ) is an open operation used for benign hyperplasia.
- Laser vaporization - is prescribed for debilitated and elderly patients, performed under local anesthesia.
Before the operation, it is necessary to take a blood test, a biopsy, a PSA test, ultrasound and palpation of the rectal area. After surgical treatment, sexual dysfunction develops in 20% of cases, cancer recurs and retrograde ejaculation occurs.
Consequences
Prostate enlargement has serious consequences, so it is unacceptable to postpone a visit to the urologist. Possible complications include pyelonephritis (inflammation of the kidneys), urethritis (inflammation of the urethra) and the appearance of stones in the bladder. An enlarged prostate leads to impaired reproductive functions (impotence, infertility) and can cause kidney failure.
Among the most serious consequences, one should single out malignant degeneration - the development of adenocarcinoma (prostate cancer). Only timely measures can prevent the development of life-threatening complications.
How to prevent zoom
To exclude the likelihood of developing benign prostatic hyperplasia and prostate adenoma, you should follow the preventive recommendations:
In order to prevent pathological enlargement of the prostate, it is recommended to visit a urologist and take PSA tests at least once a year (if there is a predisposition). Among the effective preventive measures, prostate massage should be highlighted, which is recommended to be carried out in specialized institutions.



























