Home >
Erectile Dysfunction >
How to treat prostate calcification
How to treat prostate calcification
Prostate calcification treatment
Calcification in the prostate
The health of a man is determined by external influencing factors, and the condition directly depends on the lifestyle. Such a common disease as calcifications in the prostate is no exception. To save yourself from serious consequences, you need to consult a doctor in time for the appointment of competent treatment. It will be possible to recognize this diagnosis yourself if you find out what symptoms occur, and then prevent the occurrence of this disease. Every man must comply with preventive measures, then peace of mind for his healthy potency is provided.
What is calcification in the prostate
Calcinosis is the deposition of calcium salts at the site of the collapsed soft tissues of an organ in order to prevent the spread of some kind of infection. This disease affects the kidneys, bladder, prostate gland. Detection of calcifications in the prostate indicates the formation of stones. This diagnosis suggests that the body has a long-term inflammatory process that has been left without proper treatment. Here are some examples:
- stagnation of prostatic secretion;
- changing its composition or consistency;
- Urine from the urogenital canals into the prostate gland;
- chronic/acute prostatitis.
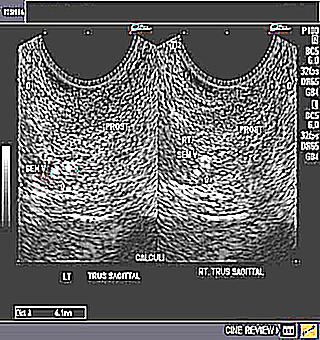
The final diagnosis, its degree can only be made by a urologist. The main diagnostic methods are: ultrasound, radiography, rectal palpation (see photo). When examining fingers through the rectum, only large stones in the prostate can be detected, so the most effective methods are ultrasound (you can see the size, location of calcifications), an x-ray (identifying the cause of salt deposits).
Symptoms of stones in the prostate
If the size of the stones is small (microcalcification), then you will not feel any symptoms of the disease, and their detection may become accidental during a preventive ultrasound examination. With large calcifications in the prostate, there are main symptoms:
- traces of blood are visible when urinating/ejaculating;
- cutting pain (scrotum/perineum), radiating to the back or lower back, aggravated by walking/exercise;
- frequent urge to urinate day and night, pain when urinating;
- pain on ejaculation;
- problems with potency.
In addition to the inflammatory processes mentioned above, calcifications in the prostate can be formed due to the following factors:
- Sedentary. Keep an active lifestyle, avoid prolonged sitting to prevent stagnation of blood in the pelvic organs.
- Sexually transmitted infections of a urogenital nature. Use protective equipment during intercourse.
- Unbalanced (improper) nutrition, addiction to bad habits. Quit smoking, alcohol or limit your intake. Try not to eat fatty, spicy, salty foods.
- Insufficiency of sexual contacts. Irregular sex leads to stagnation of the prostate secretion.
- Tuberculosis. Check the general condition of the body at least once a year.
Prostate stone treatment
Proponents of the traditional treatment of calcifications will prefer drugs with proven effectiveness, while there are a number of traditional medicine recipes that have been tested for centuries. Choosing this or that, it is important not to abandon the treatment halfway, but to reach the finish line and get rid of harmful deposits that can cause more serious diseases and nullify male power.
Folk remedies
In addition to traditional medicine, folk treatment of Prostate stones is practiced. Drinking linseed oil, fir water on an empty stomach, eating fresh onions can remove inflammation and get rid of an imbalance in the secretion of the prostate gland. Rosehip decoction is a diuretic, thanks to which crushed stones are excreted during urination. Prostate massage with calcifications in the prostate gland is contraindicated, because. the formed stones can damage the periphery of the walls of the prostate gland.
By removing prostate calcifications
Crushing stones in the prostate by means of ultrasonic or laser exposure involves crushing stones and then removing them with a secret. However, this method does not always work, since large fragments may not pass through a narrow duct, as a result, they will cause a relapse. Therefore, it is more effective to remove stones from the prostate through surgical intervention: extraction through punctures in the abdomen or abdominal wall. Radical prostatectomy is the removal of the prostate.
Drugs
Drug treatment can slow down or stop the development of calcium salts, prevent the formation of new calcifications. Medications are aimed not only at alleviating symptoms, but also at eliminating the causes of the disease, getting rid of problems with urination, and reducing pain. But only in isolated cases can complete dissolution of stones be achieved.
Video about prostate calcifications
Stones in the prostate require long-term complex treatment. Most of these procedures are very unpleasant, therefore, warning yourself against this ailment, you save your health. To do this, every man should know at what age the disease can occur, what are the first symptoms, how to treat the prostate gland. And you also need to know what methods of prevention exist and, most importantly, how dangerous this diagnosis is. Find out all this from the video below.
Methods of treatment of prostate calcification in a man
Calcifications in the prostate gland are dense formations of an inorganic nature. They are formed under the influence of a number of adverse factors: inflammation, stagnant processes, hormonal disorders, the result of which is the calcification of prostatic secretion clots. At risk are men over the age of 45.
Causes of calcification
The following contribute to the occurrence of prostate calcifications:
- genitourinary system infections;
- an inflammatory process in which the accumulation of salts is formed as a defense mechanism of the body from the source of infection;
- ejection of urine into the prostate;
- thick prostatic secretion of the prostate gland as a result of an irregular sexual life;
- change in the chemical composition of Prostate secretion (lack of citric acid leads to the formation of calcium deposits);
- lack of physical activity, sedentary work;
- neglect of the basic principles of a healthy diet.
Depending on the cause of formation, calcifications in the prostate are distinguished into primary and secondary. Most calcifications are of the first type, while others are formed only as a result of urine reflux into the prostate ducts. This is due to trauma to the genital organs during surgery, inflammatory processes and the presence of stones in the urinary organs.
-The presence of calcifications in the prostate is called prostate calcification. Stones cause tissue inflammation, causing calculous prostatitis, which, acquiring a chronic form, is difficult to treat.
Signs and methods for diagnosing the presence of calcifications
The reason to check for Prostate calcifications is when symptoms occur:
Difficulties in urination, characterized by a high frequency of urge to the toilet, the impossibility of completely emptying the bladder. At an early stage of the development of the disease, there is no pain during urination, however, the appearance of a painful syndrome is possible with the development of inflammation. Pain in the groin area. Discomfort and tension can spread to the back, lower back, scrotum. Visualization of blood impurities during urination, ejection of seminal fluid during intercourse. erectile dysfunction. Timely diagnosis of prostate calcification processes is difficult, since small multiple formations may not give themselves away. Microcalcifications are often found only during a random examination.
For the diagnosis of the disease, the priority methods of examination are ultrasound, CT, MRI, X-ray examination of the prostate, as a result of which the prostate gland is visualized in calcifications. Finger examination by a urologist and indications of analyzes of semen, blood, urine provide only information about the presence of an inflammatory process and the nature of deposits, but do not allow determining the number of inclusions, their size and the mechanism of formation.
Only after a complete comprehensive examination can treatment be prescribed.
Methods of treatment
After making a diagnosis, men ask themselves questions: what are calcifications and how to get rid of the discomfort associated with their presence in the prostate gland.
Traditional medicine and traditional methods of treatment can be used to treat the disease. It is important to understand that it is impossible to completely get rid of calcifications without surgical intervention. In the presence of microcalcifications, the use of agents that prevent the growth of stones is allowed. However, in the presence of large calcifications, strict adherence to the doctor's instructions is required. Ignoring the disease can cause difficult or irreversible consequences: impaired reproductive function, erection; purulent inflammation of the prostate or tissue around it; development of chronic prostatitis.
When deciding how to treat prostatitis, the size of the stones and their location are taken into account.Methods for eliminating prostate calcifications and their symptoms include:
Drug therapy, which includes the use of drugs that relieve spasms (No-shpy, Baralgin), antibiotics (Ciprofloxacin, Augmentin, Norfloxacin), anti-inflammatory drugs (Ibuprofen, Diclofenac). The drug Omnik will help improve the outflow of urine. Crushing of calcifications with a laser. At the same time, a low-frequency laser acts on the stones, which contributes to the separation of the stone into tiny particles that are excreted in the urine. The use of this method is possible only in combination with drug therapy to prevent the risk of complications. Surgical intervention is applicable when treatment with drugs is ineffective for 2 months or with a sudden exacerbation of the disease. The main symptoms of exacerbation are intense pain, signs of renal failure (lack of urine, tachycardia, nausea, diarrhea, diarrhea). Surgical intervention can be carried out by the method of prostatectomy, the use of which involves the complete removal of the prostate. An alternative surgical method is resection of the prostate. During resection, only the part of the prostate containing stones is removed.
After making an accurate diagnosis and eliminating the risk of complications, alternative methods of treatment can be used.
Traditional medicine for prostate calcification
Treatment with folk remedies when calcifications are detected is aimed at preventing or eliminating the inflammatory process, improving urine outflow, and eliminating congestive processes in the prostate. At home, you can use decoctions, infusions, tinctures, but it is strictly forbidden to use prostate massage, since mechanical action on the organ can provoke the movement of calcifications, which will lead to a violation of the integrity of prostate tissues.
To remove microcalcifications from the prostate and relieve the main symptoms of calcification, decoctions and infusions of calamus, heather, chamomile, St. John's wort and juniper are used. Rosehip and chestnut have proven themselves in the treatment of the disease.
Recipes of alternative medicine for the treatment of calcification
- Means prepared on the basis of rose hips contain vitamins of group B and vitamin E, which affect the restoration of reproductive function, the production of spermatozoa; vitamin P, which helps strengthen blood vessels; vitamin K, which affects the normalization of calcium metabolism; vitamin C, which helps to strengthen the immune system and increase the body's resistance to pathogenic microflora. For the treatment of calcification, an infusion of the rosehip root is used, which removes microcalcifications from the organ. To prepare it, you need to mix water with 3 tbsp in a liter container. chopped raw materials, put the mixture on a slow fire for 15 minutes. After 6 hours of infusion, you can use 300 ml of decoction daily before meals, dividing the volume into three doses.
- Means prepared on the basis of horse chestnut can improve blood flow and the release of decay products, strengthen the walls of blood vessels, eliminating the possibility of developing stagnant processes in the prostate area.
To prepare a remedy, it is necessary to carefully grind the shell with a blender and combine with hot water, adhering to a ratio of 1:10. Leave the mixture to cool completely for 12 hours, then strain and put in a water bath until evaporated by 2-2.5 times. The agent is applied 30 drops three times a day until the decoction is completely used. The break between courses of taking funds is 3 months.
Regular consumption of parsley and radish juice, tea with the addition of mint leaves, cinnamon and hawthorn fruit will help prevent the appearance of stones in the prostate and reduce the inflammatory process.
Treatment of calcification, as well as calculous prostatitis, must be carried out under the close supervision of a physician, adhering to the principles of a healthy lifestyle.
Calcifications in the prostate gland: symptoms, treatment
Calcifications are densely structural inorganic formations that are localized in various organs and tissues. Most often, prostate calcification affects middle-aged men (over 45 years). In most cases, the development of pathology is caused by the lack of timely treatment of inflammatory processes in the prostate.
Causes of stones in the prostate gland, symptoms
Among the main causes of calcification are the following:
- urogenital infections;
- inflammatory processes that have not been treated for a long time (the body fights infection by forming a salt shell around the lesion);
- stagnation in the tissues of the prostate gland;
- chronic pathologies of the prostate;
- ejection of urine into the prostate gland from the urethra (reflux);
- Impairment of the balance in the composition of the secretion of the prostate (decrease in the level of citric acid, which prevents the formation of salt crystals).
In addition to health problems, the development of pathology can be triggered by leading an unhealthy lifestyle. which is determined by the following factors:
- alcohol abuse and smoking;
- irregular sexual relations;
- a sedentary lifestyle (lack of movement causes a slowdown in metabolic processes and the appearance of blood stasis);
- an unbalanced diet (insufficient consumption of fresh herbs, fruits, vegetables, as well as an excessive passion for fried, fatty, spicy and salty foods).
Symptoms of the disease
The initial stage of calcification is characterized by the presence of small stones in the prostate gland and is almost asymptomatic. However, most often, the signs of pathology are manifested as follows:
In the seminal fluid and urine of a man, blood impurities are detected. There are intense aching pains in the groin area, which can pass into the lower abdomen and lumbar region. The pain syndrome is aggravated by urination, prolonged walking, during sexual intercourse and physical exertion. There is frequent and difficult urination. The consistency of seminal fluid changes. Ejaculation becomes painful, there is a decrease in potency. If you notice one or more of the above symptoms, you should contact your urologist as soon as possible for a consultation and appropriate therapy.
The appearance of such symptoms may indicate the presence of infected calcifications in the prostate gland. In the absence of infection, stones in the prostate may not bother a man at all. However, the latent course of the disease is fraught with rather serious consequences.
These symptoms may signal the presence of other dangerous diseases of the genitourinary system, so you should not self-diagnose and self-medicate.
Treatment of calcifications in the prostate
There are various ways to treat calcifications in the prostate gland. The choice of a specific method depends on the size of the stones, their location and quantity.
Traditional medicine offers the following options for getting rid of calcifications:
Crushing stones with a laser or ultrasound. This method is the most effective, however, it has one significant drawback: the size of the remaining fragments. Some experts argue that after the procedure, rather large fragments remain that cannot leave the body on their own and become the basis for the formation of fresh calcifications. Laparoscopy. This is an operation to remove stones from the prostate gland, which is performed with minimal trauma and guarantees complete elimination of calcifications. The advanced stage of calcification requires the removal of the prostate gland. The most common treatment for calcification is transurethral resection of the prostate. Surgery is performed through the urethra. Since the procedure is minimally invasive, recovery is quite fast.
This method of treating calcifications has a number of advantages: a short rehabilitation period, a small percentage of complications, and easy tolerability. It is performed by penetrating the urethra, after which the specialist partially removes prostate tissue with a special medical instrument, while cauterizing the vessels to prevent bleeding.
When indications for removal of the prostate, an incision is made in the lower abdomen. Unlike transurethral resection, this is a rather serious operation, which can lead to such unpleasant consequences as the formation of microabscesses up to the disruption of the functioning of the entire genitourinary system as a whole, as well as the appearance of various sexual disorders. In addition, there is a risk of infection from outside.
For men undergoing dispensary observation, a plan of preventive therapy is being developed. This is a drug treatment using non-steroidal anti-inflammatory drugs, antibacterial drugs and physiotherapy. At the same time, a specialist can prescribe drugs that stimulate blood flow in the affected organ.In the presence of calcifications in the prostate gland, massage is strictly contraindicated.
Treatment of calcifications in the prostate with folk remedies
Therapy with infusions and herbs shows very good results in the treatment of calcification, however, when using this method, the patient needs to be patient. It will take quite a long time to get rid of stones in the prostate gland with the help of folk remedies. The course of treatment can last several years.
Before you start treating calcifications with folk remedies, be sure to consult your doctor, since not all natural ingredients can be combined with the medicines prescribed by the doctor.
A decoction of birch bark with the addition of lemon juice has proven itself well in the treatment of calcification.
Crushed birch bark (1 tbsp.) Pour boiling water (1 tbsp), let it brew for 30 minutes, strain. Prepare a solution of decoction, water and lemon juice (all ingredients are taken in 1 tablespoon). Take before meals 3 times / day. Instead of birch bark, birch buds are allowed.
There are legends about the miraculous properties of this plant. Rosehip decoction helps to remove stones not only from the prostate, but also from other organs.
Chop the root of the plant. Raw materials (2 tbsp.) Pour hot water and boil for five minutes (no more), strain. Take 70 ml before meals.
Healing cannot be interrupted. Tangible results will appear in 5-6 months.
Therapeutic collection, consisting of bedstraw, adonis and goutweed, is used not only to treat calcifications, but is also used as a diuretic.
All listed herbs are taken in equal amounts and mixed together. Pour the resulting mixture (8 tsp) with boiling water (0.5 l), insist for four hours, strain. Take 50 ml.
Parsley can be called a universal plant used to treat almost all types of urogenital pathologies. The substances contained in the roots and stems of the plant help to improve metabolic processes and blood flow, and also successfully cope with inflammation and calcification.
For an effective fight against stones in the prostate gland, you can use the following composition: Mix freshly squeezed juice from parsley root with lemon juice (1 tbsp. L) and mdom (1 tbsp. L.). Take before meals.
You can also make a tincture from this plant. It is necessary to chop the stems and roots of parsley. Raw materials (1 tbsp.) Pour into a thermos and pour boiling water (1 tbsp.), Leave for 8 hours or just leave overnight. Take 50 ml. daily.
You can try to dissolve small calcifications with the help of juices prepared on your own. For treatment, the juices of the following plants are used:
Juices are consumed both in pure form and mixed with each other or diluted with water.
The treatment of calcifications involves not only the use of various medications and traditional medicine, but also the use of a special diet.
To prevent the formation of new stones in the prostate gland, it is recommended to completely exclude the following foods from the diet:
Spicy spices; radish; sorrel; spinach; marinades; pickles; fat meat. Preference should be given to sea fish, fruits, vegetables, cereals, poultry, lean meat. In order to improve blood flow and eliminate congestion, moderately active sex life and moderate physical activity are recommended.
Compliance with all the doctor's recommendations and proper treatment of calcifications is the key to successfully getting rid of stones in the prostate and returning to a full-fledged lifestyle as soon as possible.
Prostate calcifications: signs and treatment of the prostate
The prostate is an exocrine organ of the male reproductive system, the main function is the production of secretions, as the main component of the ejaculate. Under the influence of exogenous (external) and endogenous (internal) factors, salts are deposited in the prostate gland, which can be converted into stones. Calcifications in the prostate are localized mainly in the back, in large ducts (macroscopic) and acini (microscopic) of the lateral lobes of the prostate.
The mechanism of prostatolithiasis is intraprostatic reflux of urine, which leads to the deposition of salts. Violation of secretion contributes to the growth of the calculus. Calcification of the prostate often occurs against the background of benign hyperplasia.
There have been studies that have not proven an increase in PSA levels with asymptomatic uninfected stones.
There are a number of pathological conditions that contribute to prostolithiasis:
- excess intake of vitamin D; - alkaptonuria (an autosomal recessive hereditary disease that is caused by a loss of oxidase function, which leads to metabolic disorders and the loss of a large amount of homogentisic acid into the urine); - tuberculosis of the prostate; - systemic diseases; - varicose veins of the small pelvis; - concomitant chronic diseases of the genitourinary system; - metabolic disorder.
Predisposing factors include:
- sedentary lifestyle; - lack of regular ejaculation; - alcoholism and chronic nicotine intoxication; - tendency to constipation; - excessive intake of certain drugs; - malnutrition; - surgical interventions on the prostate, urethra, bladder; - iatrogenic damage during medical research.
In some patients, the deposition of salts in the prostate is diagnosed against the background of prolonged standing of the catheter in the bladder.
What are calcifications
Prostate stones are classified according to their morphological structure and mineral composition. When analyzing the structure of stones in men with benign prostatic hyperplasia using electron microscopy and X-ray microanalyzer, the following elements were revealed:
-zinc; - aluminum; - magnesium; - sulfur; - phosphorus; - calcium.
The size of calcifications correlates with the likelihood of developing prostatitis and the addition of chronic pelvic pain syndrome. Stones in the gland are often uninfected. The main components are calcium salts: calcium phosphate, calcium oxalate in combination with carbonate apatite and hydroxyapatite.
Inflammation of varying severity may accompany calcifications in the prostate, but it is still unknown whether the inflammatory process is the cause or the result of the formation of stones.
Saline formations in the prostate are discovered by chance, during a routine urological examination or during diagnostics for complaints.
Prostate calcifications are common during transurethral resection. In the literature, data on the prevalence of prostatolithiasis are variable, on average - from 41 to 70%, in older men, pathology is recorded more often.
When prostate calcifications accompany complaints
With the addition of pathogenic and opportunistic microflora and the assistance of predisposing factors, inflammation develops - calculous prostatitis.
Symptoms of infection of prostate calcifications
- discomfort with frequent urination; - an admixture of blood in the semen; - heaviness in the perineum; - lower abdominal pain; - erectile dysfunction: sluggish erection, dyspareunia, pain during ejaculation, painful spontaneous erections, decreased libido.
Calcification in the large prostate is one of the causes of chronic pelvic pain.
General complaints characteristic of any inflammatory process include:
- weakness, fatigue; - increase in temperature reaction (the stronger the inflammation, the higher the temperature); - headache; - arthalgia and myalgia.
General symptoms are not pathognomonic for calculous prostatitis and can accompany any infectious and inflammatory process in the body.
Diagnosis of calcifications in the prostate
The urologist, after collecting and evaluating complaints, palpates the prostate through the rectum: areas of density are characteristic of prostate calcifications, sometimes crepitus is possible. Palpation of the prostate gland is not very informative, therefore, a comprehensive clinical and urological examination is carried out to assess the full picture.
Uneven dense areas can be a sign of prostate cancer or urogenital tuberculosis, so specific tests are prescribed to rule out these diseases.
Laboratory diagnostics
In addition to the standard general blood and urine tests, the level of prostate-specific antigen in men over 40 years of age (but not earlier than 10 days after the rectal examination or before it), urine culture for Mycobacterium tuberculosis, Mantoux test and diaskin test are examined. In the general analysis of urine, an increased number of leukocytes, bacteria, erythrocytes and protein may be present, which requires the diagnosis of inflammation of the bladder and kidneys, general uronephrolithiasis.
To identify the provoking factor, tests for sexually transmitted infections are prescribed.
Prostate secretion may contain leukocytes, erythrocytes, macrophages, a decrease in the number of lecithin grains, which is typical for calculous prostatitis.
It may be informative to culture the prostate secretion for flora and sensitivity to antibiotics to determine the need for antibiotic therapy. If the secret of the prostate contains more than 103 CFU / ml of uropathogenic bacteria of one strain or more, antibacterial drugs are prescribed, taking into account sensitivity.
Instrumental diagnostics
The gold standard - transrectal ultrasound - demonstrates hyperechoic inclusions with acoustic shadowing. With a concomitant inflammatory process, an increase in the size of the prostate and diffuse changes in the structure of the tissue are visualized. X-ray examination - excretory urography with voiding cystography - allows you to diagnose the causes of infravesical obstruction, but X-ray negative stones are not visible on urograms.
In case of severe urination disorders against the background of prostate calcifications, it is justified to perform a urodynamic examination - uroflowmetry, and, if necessary, a more complete diagnosis - cystometry.
CT or MRI of the pelvic organs are not mandatory studies, but if a prostate tumor is suspected, their performance is justified.
Treatment of prostate calcifications
The treatment regimen depends on many aspects:
- etiology and pathogenesis; - predisposing factors; - severity of clinical manifestations; - the probability of joining complications; - individual characteristics of the patient; - contraindications to taking drugs.
Asymptomatic uncomplicated prostate calcifications of small size do not require aggressive treatment, it is enough to use preventive measures, correct diet and lifestyle.
Conservative therapy
Prescribe drugs that promote the dissolution of salts, prevent further stone formation, relieve the accompanying inflammatory process:
- antibiotics; - NSAIDs; - uroseptics; - vitamins; - phytopreparations; - enzymes; - preparations with litholytic action; - alpha-blockers; - peptide bioregulators.
Prostate tuberculosis implies specific therapy.
Prostate massage and vibration physiotherapy are not performed for severe calcifications, since the sharp contours of the stone can injure the tissues of the gland, the prostatic part of the urethra, and the stone itself can migrate.
With calculous prostatitis, hyperthermia cannot be used, since the tissues of the gland with prostate stones will heat up unevenly.
Lithotripsy
Lithotripsy for prostate calculus is a non-invasive way to solve the problem. During the procedure, the prostate is remotely affected by ultrasound or a magnetic wave. There is a destruction of the calculus into small fragments (sand) and comes out during the act of urination.
The action of a low-intensity laser is similar. But in order to get rid of prostate calcifications, several sessions may be required. During the laser destruction of the stone, the surrounding tissues do not suffer. Not all experts agree with the effectiveness of low-intensity laser therapy for calculous prostatitis.
A defragmented stone breaks into sharp-edged fragments that can damage the seminiferous tubules and prostate tissue. Stuck fragments provoke the crystallization of new calcifications, which contributes to the growth of the calculus and the addition of new complications.
Surgical method
In case of a pronounced violation of the outflow of urine against the background of calculous prostatitis, sclerosis of the bladder neck or sclerosis of the prostate itself, transurethral incision or economical electroresection of the prostate is performed.
Transurethral electroresection is also used for hard-to-reach calcifications in the central, transient and periurethral zones. If the seed tubercle is involved in the process with the development of blockage of the vas deferens, its resection is performed.
Sclerosis of the prostate, accompanied by persistent symptoms without the effect of conservative therapy, requires the most radical transurethral electroresection of the gland.
Adverse consequences and risks of calcifications in the prostate:
Prostate calcifications: treatment with folk remedies
For a complex effect on the deposition of salts in the prostate, you can use alternative medicine recipes.
Plants that prevent salt deposition:
- half a floor (woolly erva); - field sage; - ostudnik naked; - wild rose (rhizomes).
To dissolve calcifications in the prostate, it is necessary to prepare a decoction. To avoid addiction, it is better to alternate plants.
Take m cups a day, on an empty stomach, 10 days each month. The effectiveness of herbal medicine can be assessed after 6 months when undergoing an ultrasound examination in dynamics.
Honey, lemon juice, chopped parsley (leaves and roots) will be required to prepare a remedy for dissolving prostate stones.
Chop the washed fresh parsley in a blender, squeeze out the juice. Mix with equal amounts of honey and lemon juice. Take l glass 3 times a day for a month.
Important! Before treatment with traditional medicine recipes, you should consult your doctor.The composition of calcifications in the prostate varies, which requires an individual approach even in the use of natural components.
Diet for prostate calcifications
More often, calcifications in the prostate are synthesized in those men who eat a lot of meat and fatty foods, abuse alcohol, and prefer strong tea or coffee instead of pure artesian water. It is necessary to ensure that the diet contains a sufficient amount of vegetables and fruits rich in vitamins and minerals.
Useful fish and seafood, cereals, nuts and seeds, greens.
It is preferable to abandon animal fats in favor of vegetable (olive, sunflower, linseed) oils.
Experts recommend not to get involved in foods with a lot of preservatives, flavors, hidden fats.
It is better to choose lean meat, and cook it in a gentle way by baking or stewing.
Exclude from the diet:
- rich meat broths; - offal and liver; - alcohol; - smoked meats; - strong coffee and tea; - chocolate.
All broths (meat, chicken, fish) are preferable to the second cooking: after boiling, drain the water, rinse the meat and pour new water.
From drinks you can use fresh vegetable and fruit juices, mineral water, unsweetened compotes, herbal decoctions.
Prostate calcifications - how to treat prostate stones
What are prostate stones
Calcifications or calcifications are dense formations that appear in the cavities and channels of the gland. Stones are of different nature, differ in density and chemical composition. A small amount is regarded as the norm for a healthy man. An increase in volume, the appearance of negative symptoms indicates the need for emergency medical care.
The type of calcifications, as well as their size, affects the treatment regimen. Small calculi with a soft and loose structure can be removed from the gland even by folk methods. Calculi with a formed dense structure and a hard calcified surface are removed exclusively by surgery.
Causes of stones in the prostate
What kind of stones are there
Prostate calcification is a serious, constantly progressive disease. The classification of stones divides formations into several groups according to the mechanism of appearance and localization, chemical composition. The type of stones affects the prognosis of therapy. On the basis of diagnostic studies, a treatment regimen is drawn up.
Stones are divided into the following classes:
- According to the mechanism of formation - congestion is responsible for the appearance of endogenous stones. The shape of the stones is oblong, the maximum size is up to 2.5 cm. Malfunctions of urethro-prostatic reflux (reflux of urine into the channels of the gland) lead to the appearance of exogenous formations. A characteristic feature: localization exclusively in the terminal ducts of the prostate and a special pointed shape. Exogenous stones in the prostate are small, only up to 4 mm in diameter.
- By chemical composition - they are classified according to which substances predominate in stones. All formations are divided into several groups: phosphates - salts of phosphoric acid;
- oxalates - consist of oxalic acid;
- urate stones are urea salts.
- Pain in the lower abdomen, radiating to the lumbar region and manifesting itself with a load on the pelvic region;
- Erectile dysfunction;
- Pain during ejaculation;
- Sperm color change, blood in the ejaculate;
- Pain during rectal finger examination;
- Urinary disorders.
When one of the symptoms appears, a thorough medical examination is required in order to establish the causes of malfunctions in the genitourinary and reproductive systems.
What are the dangers of stones in iron
Small formations usually do not cause concern to a man and, subject to the recommendations of the urologist and taking medications, do not cause concern. The consequences of stones of medium and large size, in the prostate gland, are as follows:
In the channels of the gland, seminal fluid is produced, which is responsible for the viability of germ cells. A decrease in the amount of secretion produced impairs sperm reproduction, and the likelihood of successful fertilization decreases.
Stones create the prerequisites for the penetration and reproduction of infections and other pathogens in the cavity. Moreover, such a threat is present, even if microcalcifications are found in the prostate gland. Microorganisms multiply rapidly and become resistant to antibiotics. Infectious chronic inflammation develops.
How to recognize stones and their size (diagnosis)
Suspicion of calcification of the prostate ducts occurs when symptoms of the disease appear, indicating serious pathological changes in the genitourinary system.
During a rectal finger examination, the urologist detects small, painful lumps.After that, an ultrasound or TRUS of the prostate is prescribed. Transrectal examination is preferable, but the method has contraindications: hemorrhoids and acute proctitis.
Ultrasound diagnostics reveals deviations even at the initial stages. The results of the study may be the following:
- Hypoechoic formation in the prostate gland - a diagnosis indicating a number of pathologies: cancer, a benign tumor located in the periphery of the prostate. Additional studies will be required to clarify the disease. Multiple hypoechoic zones indicate stone formation rather than prostate cancer. Additional information is obtained with MRI and PET - CT, as well as puncture. An extensive single hypoechoic nodule often indicates cancer.
- Multiple calcifications of the prostate gland - the prognosis of the disease depends on the effect of stones on the patient's well-being. If the stones are small and do not cause pain, supportive and preventive therapy is prescribed.
- The heterogeneous structure of the prostate gland indicates inflammatory processes. If echo signs of calcifications are found against this background, urgent medical care is needed.
- Prostate petrification - calculi or calcareous deposits formed against the background of prolonged chronic inflammation, trauma. As a rule, formations are accompanied by severe symptoms: pain, dysuric disorders, sexual dysfunction. Periurethral petrificates are located around the urethral canal. The first sign of development will be frequent trips to the toilet and cramps during urination.
- Calcifications in the periurethral zone of the prostate are the same as petrificates. Stones formed in the cavity directly communicating with the urethra. Periurethral calcifications, especially small in size, respond well to drug therapy, dissolve under the influence of drugs.
The urologist is engaged in deciphering the analyzes. Some results are controversial and require further investigation. For clarification, the patient will have to undergo a tomography or pass a puncture. After a differential diagnosis, treatment is prescribed.
How to remove stones from the prostate
The effectiveness of the treatment of calcifications largely depends on the stage at which stone formation is detected and the patient's desire to recover. For healing, you will need to change the diet, give up bad habits. The therapy is long-term.
During the entire course of treatment, it is important to monitor the patient's condition. If the stones increase despite the prescribed therapy, a surgical operation is performed.
Drug treatment of calcifications
Medicines help relieve acute symptoms of the disease and improve urine flow. In some cases, it will be possible to dissolve calcifications and completely restore the functionality of the prostate gland without resorting to surgical intervention.
Phosphates and oxalates respond best to treatment. Stones with a hard calcified shell do not dissolve during medication. Even single formations can cause harm and cause severe pain.
In therapy, antispasmodics, alpha-blockers and NSAIDs are prescribed. To relieve chronic inflammation caused by infection, a course of antibiotics is prescribed. Single calcifications detected at an early stage can be removed or their increase can be stopped by taking medication.
Stone crushing with laser and UVT
Modern methods of stone removal are divided into surgical and those in which surgery is not required. The methods are efficient and invasive.
Non-surgical methods of removal are considered insufficiently effective. 30-40% of all patients undergoing therapy repeatedly seek help. The most common methods are:
- Ultrasound treatment - under the action of narrowly directed and focused beams, tissue is heated and stimulated. There is no vibration during the procedure. Stones are released due to increased muscle contraction.
- Shock wave therapy - in this case, mechanical pressure is applied to the calcifications. The stones are crushed into small fractions, after which they come out naturally through the urethral canal. Not completely crushed calculi remaining in the ducts provoke accelerated re-stone formation.
- Remote lithotripsy is a general term that includes many types and methods of performing the procedure. Apply electrohydraulic, magnetic, piezoelectric crushing of stones. The same term includes laser removal of stones. The equipment is brought through the urethral canal directly to the prostate.
Laser treatment has increased the effectiveness of non-surgical interventions.The recovery of the patient takes 7 days. Efficiency 80-95%. Laser therapy gives results in any type of pathology. Single calcifications and extensive stone formations are removed. The absence of abdominal incisions accelerates the recovery of prostate functions.
Surgery - laparoscopy and TUR of stones
Abdominal surgery continues to be considered the only effective way to remove calcifications from the prostate. Stones are removed completely, without residue, which prevents their re-formation, as is the case with non-invasive methods.
There are two main types of surgical operations:
- Transurethral resection of the prostate - during the intervention, overgrown tissues are excised, after which they are removed through a resectoscope. Stones are removed along with the gland. The advantage of the method is the possibility of layer-by-layer excision of tissues. The resectoscope is brought to the organ through the urethra.
- Laparoscopy of the prostate - for manipulations, several surgical openings are made in the abdominal cavity, no more than 1-1.5 cm long. A laparoscope is inserted through the incisions, through which damaged tissues with accumulations of calcifications are removed.
Surgery is used only in cases where long-term drug therapy has not yielded results, and the patient's condition cannot be stabilized, therefore, there is a constant deterioration in well-being and exacerbation of symptoms. The disadvantage of the surgical method is a long recovery period.
How stones come out of the prostate
With non-invasive and drug therapy, it is important not only to reduce the volume of calculi, but also to remove calcifications from the prostate. For this purpose, the gland is drained. There are several ways to perform the procedure:
- Natural ejaculation is the best method for removing crushed stones. During orgasm, prostate tissues contract intensively, seminal fluid comes out of the channels, washing out calcifications. In the absence of a regular sexual partner, masturbation is recommended as a therapeutic aid for a man.
- Transurethral drainage of the prostate - a catheter electrode is inserted into the urethra. In response to exposure to electromagnetic pulses, contraction and vacuum aspiration of the prostate lobules occur.
The urologist will select the drainage method that is best suited for each individual patient.
Prevention and prevention of stone formation
Regular examination by a doctor, timely treatment of prostatitis, a healthy diet and an active lifestyle - all this will prevent stone formation in the prostate gland.



























