Home >
Erectile Dysfunction >
Rectal discharge in prostate cancer
Rectal discharge in prostate cancer
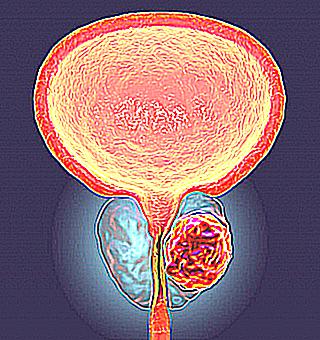
What is the relationship between the intestines and prostatitis
Inflammation of the prostate gland provokes disturbances in the blood supply and motility of the rectum. Conversely, the appearance of hemorrhoids, constipation or diarrhea lasting for several years can cause the development of prostatitis.
How prostatitis affects the intestines
Anatomically, the prostate gland is located in close proximity to the rectum. During defecation, there is some mechanical effect on the prostate, stimulating its work. After a long bowel disorder (lasting about a year or more), stagnation occurs. The lack of stimulation affects the basic functions of the prostate.
Permanent constipation is much more dangerous for the gland. Violation of peristalsis leads to problems in the blood supply to the area of the intestine immediately adjacent to the prostate. Blood stasis eventually affects the gland.
The effect on the rectum due to Chronic prostatitis is associated with a violation of normal blood flow. Only now the initiator of the development of pathology is inflammation of the prostate gland.
Problems with the intestines can lead to the development of prostatitis, but the changes do not occur immediately. If a man has short-term constipation or diarrhea lasting about a week, there is no cause for concern. But permanent disturbances in peristalsis provoke the development of inflammatory processes of the gland, in 15-20% of cases of all patients diagnosed with prostatitis.
Itching and burning in the anus
One of the characteristic signs indicating the development of prostatitis. Burning in the rectum is provoked by pathogenic microorganisms that have got inside damaged soft tissues through cracks and abrasions.
As a rule, the symptom has an undulating appearance. Discomfort in the anus is replaced by a long period of calm.
Doctors distinguish two types of symptoms depending on the etiology:
- Aquagenic or primary - mucosal damage occurs due to the direct entry of microorganisms outside the body into the intestine. The causes of itching in the anus in this case are difficult to differentiate.
- Secondary - the development of unpleasant sensations is associated with the ingress of pathogenic microorganisms into the intestines due to an already existing infectious inflammatory process of the body. If a man itches in the anus, this does not necessarily indicate the presence of prostatitis. Almost any inflammation in the body can act as a catalyst for unpleasant disorders.
Intolerable itching sometimes accompanies sweating of the anus zone - a symptom that clearly indicates an infectious infection of the microflora of the rectum. Before prescribing therapy, it will be necessary to determine the source of the spread of pathogenic microorganisms in the human body.
Constipation and prostatitis
Intestinal obstruction can be a cause or a consequence of prostate inflammation. Violations of peristalsis provoke malfunctions of the prostate:
- During constipation, disease-causing microbes enter the body's bloodstream and spread throughout the body. Infections that enter the tissues of the prostate provoke inflammation in an acute form. Short-term problems with emptying cause discomfort and discomfort to the patient, but are not dangerous. But if constipation continues for a long time or alternates with diarrhea, lead to the appearance of prostatitis. Constant infection causes a decrease in immunity.
- Constipation provokes injury to the intestinal mucosa and the appearance of seals in the hemorrhoidal veins, which leads to a deterioration in blood supply. Congestion also affects nearby prostate tissues. Lack of nutrients, the inability to properly remove toxins and toxins from the body, create prerequisites for the inflammatory process.
- The effect of constipation on the prostate is also associated with excessive mechanical pressure of the rectum on the gland, due to the accumulation of fecal matter.
Now we need to figure out what effect prostatitis has on the colon. Inflammation of the gland extends to adjacent departments and areas. Often, infection due to anatomical proximity passes to the intestines.
With prostatitis, there may be constipation in the following cases:
There are several characteristic signs of constipation caused by inflammation in the prostate gland. During the diagnosis, the doctor will pay attention to the presence of symptoms:
- Constipation lasts at intervals of 3-4 days.
- Clinical tests reveal mucus in the stool.
- The patient complains of a foreign body sensation in the anus. The symptom is associated with an increase in the volume of the gland, which has grown so much that the rectum is squeezed and interferes with peristalsis.
- Feeling of incomplete bowel movement.
Pain in the anus
Prostatitis is not always accompanied by disturbances in the functioning of the intestines.Pain in the anus indicates hemorrhoids or other diseases of the genitourinary system, including inflammation of the gland.
The reasons for discomfort lie in the following:
- Common nerve endings. Pain in prostatitis radiates to adjacent areas and extremities, is given to the anus, spine, scrotum. The reason for this is quite simple. All nerve endings are connected to the lower spine. Pain in the anus does not always indicate hemorrhoids or is accompanied by constipation.
- Unpleasant sensations in the anus do prove intestinal disorders, but do not confirm the presence of inflammation in the prostate gland.
Discharge from the anus
Involuntary leakage of fluids from the anus is far from a harmless symptom. Liquid discharge always indicates the presence of disorders and the presence of an inflammatory process.
There are several reasons for malfunctions in the digestive tract:
- Acute inflammation of the rectum (proctitis).
- Presence of Candida.
- Development of hemorrhoids.
- The appearance of cracks in the anus, etc.
All diseases can develop on their own, or be a secondary symptom of prostate inflammation. In any case, you will need to consult a proctologist and conduct clinical studies of discharges for an infectious factor.
Blood from the anus
Another alarming sign is bleeding from the anus, indicating many disorders, ranging from exacerbation of hemorrhoids to prostatitis and prostate cancer. Even if the symptom was temporary and immediately disappeared, the man still needs to see a doctor to clarify the diagnosis.
Feces with blood in prostatitis is associated with mechanical pressure on the tissues of the rectum from an enlarged prostate, inflammation of the mucosa from infection. Hemorrhoids can exist as a primary or secondary pathology and are also accompanied by black stools.
Dysbacteriosis and prostatitis
In the normal state, beneficial bacteria take part in the digestion of the human body. Any violations lead to a deterioration in peristalsis and changes in the density of feces. Moreover, both thin feces and constipation are observed.
In case of prostatitis, several factors provoke violations:
- Drug therapy - the course of treatment includes the use of antibacterial agents, leading to the destruction of beneficial microorganisms. Intestinal disorders, one of the side effects of taking medications.
- Proctitis and hemorrhoids - inflammation of the tissues caused by prostatitis leads to significant disruption of the intestines and causes diarrhea or constipation, depending on the type of disease.
Violations also work the other way around. Due to poor intestinal microflora, the prostate does not receive useful substances, toxins are not removed from the body in a timely manner, which leads to the appearance of stagnation of the gland.
The negative impact of dysbacteriosis on the prostate is associated with a chronic lack of nutrients necessary for the functioning of the gland, as well as a deterioration in tissue metabolism. Along with antibiotic therapy, a course of maintenance treatment is required to replenish the amount of microorganisms useful for digestion.
Intestinal prophylaxis in the treatment of prostatitis
Regardless of the factors that provoked inflammation of the prostate gland during the treatment of the disease, the state of the gastrointestinal tract is of great importance. The course of therapy includes maintaining the intestines in a normal state.
Cope with prostatitis, if the patient has serious malfunctions in the gastrointestinal tract, it becomes harder and requires more time.
The following measures are taken as preventive and therapeutic measures:
- Gymnastic procedures and exercise therapy. In particular, the use of the Kegel technique gives good results. During the exercises, the muscles of the anus are trained, which helps to improve blood supply and eliminate congestion. Kegel exercises include several types of exercises that are equally useful for prostatitis and gastrointestinal disorders, including: retraction of the anus, walking on the buttocks.
- Microclystering - herbal tinctures are used, as well as medicinal formulations. Complete bowel cleansing is rarely prescribed and has some side effects (promoting dysbacteriosis). Microclysters, on the contrary, gently act on the mucous membrane. Active ingredients quickly enter the gland tissues, which also contributes to recovery.
- Plentiful drink and diet - to effectively deal with constipation, you should drink about 2-3 liters of water per day. It is better to give up foods that are difficult to digest. During dysbacteriosis, the patient is recommended fermented milk products: kefir, yogurt.
Improvement of bowel function, an important condition for preventing or increasing the effectiveness of the prescribed drug treatment for prostatitis.
Symptoms of prostate cancer by stages
The proportion of prostate cancer in the total oncological incidence is growing every year. If a few years ago it ranked 6th in terms of prevalence, then in recent years it has come close to the top three most common cancerous tumors in men in terms of localization.
We will tell you how not to overlook such a formidable disease and with what symptoms you should seek medical help.
Symptoms of the disease
The first two stages of prostate cancer are such a small pathological focus that most often it does not disrupt the normal functioning of the male reproductive system. Such cancers are usually found by chance during surgery or screening.
The tumor grows at a slow pace and the disease progresses unnoticed by the man. In this regard, the first signs of prostate cancer, which clearly attract attention, develop on average 20 years after the onset of the disease.
Stage 1 - a tumor in the submucosal layer, microscopic in size. There are no typical symptoms of grade 1 prostate cancer. From nonspecific symptoms are possible:
- weight loss;
- headache;
- appetite reduction;
- fatigue;
- recurrent thrombophlebitis;
- bleeding.
Most often, prostate cancer at this stage is completely asymptomatic.
In a biochemical blood test, there is a decrease in the level of all proteins, in particular, albumin - hypoalbuminemia.
Stage 2 - the tumor grows through the entire thickness of the organ and the capsule. Depending on whether the tumor interferes with the outflow of urine through the ureter, the symptoms of grade 2 prostate cancer may or may not appear.
If the tumor compresses the ureter, then there are:
- feeling of incomplete emptying;
- frequent urination;
- nocturia - frequent urination at night;
- weakening of the urine stream;
- false urge to urinate;
- imperative urge - the inability to hold urine when you want to urinate.
Sometimes there is Urinary incontinence, which is a consequence of either urinary retention, or a tumor lesion of the sphincter. The germination of the tumor in the sphincter is a symptom of prostate cancer already stage 4.
Stage 3 - the tumor grows outside the capsule. Symptoms of prostate cancer either only occur if there were no manifestations up to grade 3, or progress. Mostly, the tumor is detected at this stage, because the discomfort it causes forces you to see a doctor.
All those signs that were in the previous stages come into full force. Minor pain in the pelvis or back becomes bothersome, it becomes more and more difficult to urinate, weakness increases, and efficiency decreases. Back pain at this stage is due to compression of the overgrown gland of sensitive nerve endings of the small pelvis.
4 stage - invasion of the tumor into neighboring organs, metastases to regional lymph nodes or to distant ones, to bones, to internal organs. The first symptom of the appearance of metastases is moderate pain in the pelvis, lower back.
Signs of prostate cancer spreading into the rectum are symptoms such as:
- constipation;
- tenesmus - painful urge to defecate without bowel movements;
- bleeding from the rectum;
- mucus and anus secretion;
- intestinal obstruction.
If the cancer has grown into the bladder or ureter, there is an admixture of blood in the urine and semen. Urinary incontinence develops when the sphincter of the bladder is damaged.
When metastasizing, the symptoms of grade 4 prostate cancer depend on the location of metastases, the prognosis in their presence worsens significantly.
Most often, the bones of the skeleton are affected, so the main symptom is pain in a place corresponding to the location of the metastatic focus. Germinating, it destroys the bone up to a pathological fracture.
Metastases to the vertebrae can lead to compression of the spinal cord and flaccid limb paralysis.
In addition to the inguinal, para-aortic and supraclavicular lymph nodes are affected.
Rarely, metastasis to organs is observed: lungs, liver, brain and spinal cord. Here, the symptoms of damage to this system will come first:
- cough, shortness of breath with lung injury;
- heaviness or pain in the right hypochondrium, jaundice, indigestion with liver damage;
- Central and peripheral paralysis, loss of sensitivity in CNS lesions.
Cancer can develop from prostate adenoma, the symptoms will remain the same, but the obstructive moment will be more pronounced - impaired urination, development of bilateral hydronephrosis. Chronic prostatitis as a focus of inflammation sometimes degenerates into a malignant tumor.
Diagnosis
Treatment of prostate cancer (prostate) by symptoms and stages
The scheme is drawn up individually, taking into account the stage of the disease and the patient's condition.
Radical prostatectomy is performed at stages 1 and 2. Does not affect potency in half or more patients. In young people, external radiotherapy is used.
Treatment stage 3 - radiation therapy. The pelvic lymph nodes and residual tumors are surgically removed. Radiotherapy plus hormonal therapy may be used. At stages 3 and 4, palliative transurethral resection is performed. Read more about prostate cancer surgery here.
Prevention
Specific prophylaxis has not been developed. Men over the age of forty need to undergo an annual examination by a urologist to detect a tumor in the first stages.
This test includes a digital examination of the prostate and a PSA test. To reduce the risk of prostate cancer, you need to:
- limiting the amount of animal fats in the food consumed, dieting;
- exclusion of toxic effects on the body of alcohol, nicotine;
- regular sex life;
- high physical activity and light sports (with the approval of a doctor!);
- rational mode of work and rest.
Attentive and careful attitude to your own health will allow you to notice the signs and symptoms of incipient prostate cancer in time. Diagnosed in the first stages and treated with cancer is a guarantee that many more years of a full life lie ahead.
Learn about early symptoms of lung cancer in case you suspect metastasis.
What is the prognosis for lung cancer at different stages? In this material, you can find out what to hope for.
Rectal cancer
Rectal cancer equally often affects men and women, has a high mortality rate in many countries of the world. Every year the incidence of colorectal cancer is increasing. Urban residents are more likely to get sick, the disease is observed in all age groups, most often rectal cancer is found in people over 60 years old.
You can get rectal cancer diagnosed at the Yusupov hospital. With the development of any intestinal discomfort, you should be examined and tested for tumor markers. At a consultation at the oncology clinic of the Yusupov Hospital, you will be told about modern methods and will select an individual treatment based on your particular disease.
Classification: rectal cancer
The rectum is the final segment of the large intestine that starts from the sigmoid colon and ends in front of the anus. In the rectum, feces accumulate. In men, this part of the intestine is adjacent to the prostate gland, seminal vesicles and bladder, in women it is adjacent to the back wall of the vagina and uterus.
According to the type of tumor growth, they are distinguished:
- endophytic form of the tumor. The neoplasm grows in the thickness of the wall of the rectum;
- exophytic tumor. Grows in the intestinal lumen, eventually causes obstruction;
- saucer shape. Combines both types of tumor growth, occurs as a tumor-ulcer.
Rectal cancer classification by histological parameters:
- adenocarcinoma;
- mucosal adenocarcinoma;
- glandular cell carcinoma;
- basal cell carcinoma;
- mucocellular carcinoma;
- squamous cell carcinoma;
- undifferentiated cancer;
- Unclassified cancer.
The most common is adenocarcinoma of the rectum.
Symptoms of early rectal cancer
Signs of rectal cancer, the first symptoms do not appear immediately. The initial stage of tumor development is characterized by certain discomfort, symptoms similar to those of various intestinal diseases. The first manifestations of a tumor are the appearance of streaks of blood in the feces, which appear due to injury to the tumor by passing feces, pain, diarrhea or constipation.
Rectal cancer, first symptoms: photo
Rectal cancer, first symptoms: tumor markers for diagnosis
Tumor markers are special substances that are released as a result of the vital activity of a malignant tumor or are produced as a response of healthy tissues and organs to the invasion of cancer cells. They are found in the urine and blood of sick people. Conducting an analysis for oncomarkers of rectal cancer can detect cancer at an early stage, save the health and life of the patient. Early diagnosis of cancer, carried out at the initial symptoms of the disease, allows you to remove the tumor before the first metastases appear. With the help of an analysis for oncomarkers, the patient's health status is monitored after cancer treatment for a certain time - this allows timely detection of the development of tumor recurrence.The level of tumor markers may be increased due to non-oncological diseases.
How quickly rectal cancer develops
The initial symptoms of rectal cancer often go unnoticed. It takes several years from the onset of tumor development to the onset of severe symptoms. The tumor slowly captures the organ, then grows into its wall and affects the surrounding tissues and organs - about two years pass from the beginning of growth to its metastasis.
Intestinal cancer and rectal cancer: symptoms
Intestinal cancer and rectal cancer have the same risk factors and causes of development. Of all bowel cancers, colon cancer accounts for two-thirds of cases, and one-third is rectal cancer. The main symptoms of bowel cancer are the appearance of streaks of blood and mucus in the feces, pain of varying intensity. With the growth of the tumor, the symptoms become more pronounced - persistent constipation or diarrhea develops, the temperature rises, the skin turns pale, jaundice develops, nausea, vomiting, pain during bowel movements, the patient loses appetite, body weight, and intestinal obstruction occurs as a complication.
Causes of colorectal cancer
Oncologists at the Yusupov hospital are often asked the question - "What causes rectal cancer?" The reasons for the development of cancer in humans have not been studied so far. According to research results, the causes of the development of a malignant tumor are:
- malicious smoking and alcoholism;
- living in an area with a difficult environment;
- harmful working conditions;
- drinking a lot of beer, meat, fats;
- eating food with dyes, carcinogens;
- poor water quality;
- chronic inflammatory processes in the intestines;
- intestinal polyposis;
- hemorrhoids;
- sedentary lifestyle;
- anal sex.
Chemotherapy for colorectal cancer
Chemotherapy is most often prescribed in the postoperative period as an adjunct treatment. Chemotherapy is used with caution, often as a palliative treatment when the tumor cannot be removed. Chemotherapy in most cases is carried out by drip infusion. Along with chemotherapy, antiemetic drugs that reduce nausea are used.
Symptoms of rectal cancer in women
Signs of rectal cancer in women often appear at a late stage of cancer development, when the vaginal wall and bladder are damaged. A fistula appears in the vagina, through which feces and gases exit. Cancer of the rectum is manifested by symptoms similar to those of diseases of the stomach, intestines, and genitourinary system. Signs of rectal cancer at an early stage have no special manifestations, often similar to manifestations of hemorrhoids, intestinal disorders.
Diagnosis of rectal cancer in women
Diagnosis of rectal cancer in women is carried out in the Yusupov hospital by several methods of endoscopic examination, using X-ray, ultrasound, computed tomography, fibrocolonoscopy, radioisotope scanning of the liver to detect metastases, internal urography to assess the spread of metastases. A woman is being examined by a gynecologist to exclude the germination of the tumor in the uterus and vagina. If polyps or tumors of the rectum are found, a biopsy is performed with a histological examination of a tissue sample. An analysis is prescribed for oncomarkers CA 19-9, cancer embryonic antigen. Such studies are carried out in conjunction with other studies.
Symptoms of rectal cancer in men
The first signs of rectal cancer in men are intestinal discomfort, nausea, abdominal pain and the appearance of streaks of blood in the stool. As the tumor grows, the following symptoms appear:
- blood discharge increases, pus appears in the feces;
- the patient is tormented by persistent constipation that is not amenable to treatment;
- fecal and gas incontinence;
- pain of varying intensity;
- painful urge to defecate;
- abdominal rumbling and bloating;
- when the tumor affects the lower rectum and sphincter muscles, the symptoms of cancer appear at an early stage;
- pain causes the patient to sit strictly on one buttock;
- when a tumor of the upper part of the rectum grows into other organs and tissues, the pain increases;
- anemia develops;
- exhaustion;
- fatigue, pale skin;
- Rectal cancer often affects the prostate gland and seminal vesicles, manifests itself with symptoms of dysfunction of the prostate gland, an increase in its size.
Rectal cancer, symptoms: photo
Causes of rectal cancer in men
The most common causes of rectal cancer in men are the love of beer, alcoholism and heavy smoking.Negative factors affecting the development of the disease: work in hazardous conditions, living in environmentally hazardous areas, obesity, malnutrition and heredity, sedentary lifestyle. It is believed that a large consumption of meat and animal fats also negatively affects the condition of the intestine, increases the risk of developing cancer due to the characteristics of the microflora.
Heavy smoking is characterized by the negative effect of nicotine on blood vessels. Epidemiological studies have shown that with an increase in the amount of beer consumed, the risk of developing rectal cancer increases. Alcohol irritates and damages the intestinal walls, is one of the factors influencing the development and growth of malignant tumors. Regular consumption of beer increases the risk of bowel cancer. Beer contains the toxic product of ethanol oxidation, acetaldehyde. Ethyl alcohol causes damage to the mucous membrane, which contributes to the development of the inflammatory process, and exposure to a toxic product leads to cell mutation. In men, regular alcohol consumption increases the risk of oral, liver, throat, colon, and prostate cancers.
Rectal cancer: age category
Rectal cancer is rarely found in people under the age of 40, the risk of developing rectal cancer increases after age 40 and rises sharply after age 60. Intestinal polyposis increases the risk of cancer in people over 50 if they do not get regular screening and treatment for bowel disease.
Pain in rectal cancer
Pain in bowel cancer occurs in 80% of patients. In some cases, the symptoms are similar:
- with acute appendicitis;
- stomach or duodenal ulcer;
- colic in urolithiasis, cholelithiasis.
Pain can be combined with tension in the muscles of the anterior abdominal wall, fever, vomiting and nausea. An increase in the pain syndrome occurs with an increase in the size of the tumor, germination of the tumor in neighboring organs and tissues, with the development of intestinal obstruction, the development of an inflammatory process in the tumor, an abscess.
Diagnosis: types of rectal cancer
The appearance and severity of symptoms are influenced by: the type of tumor, the stage of development, the nature of the spread in the body. Exophytic tumors germinate inside the rectum, eventually creating obstruction of the affected part of the intestine. Squamous cell carcinoma of the rectum mainly begins to develop in the mucous membrane of the anal canal, then spreads further.
Poorly differentiated squamous cell carcinoma of the rectum
The tumor consists of mutated squamous epithelial cells, they can be keratinized and not keratinized. The appearance of the tumor resembles an ulcer, in some cases cauliflower. Ulceration of the neoplasm indicates a high malignancy of the tumor of the rectum. Squamous cell carcinoma has symptoms similar to those of hemorrhoids and anal fissures. A poorly differentiated form of squamous cell carcinoma is a highly malignant cancer that tends to rapidly metastasize, affecting nearby organs and tissues, as well as distant ones. A poorly differentiated form of squamous cell carcinoma is prone to relapses, which very often occur in the first two years after treatment.
How to tell hemorrhoids from rectal cancer
Since the symptoms of rectal cancer are very similar to the symptoms of hemorrhoids, you should learn to distinguish between them:
- With hemorrhoids, blood appears at the end of a bowel movement and is located on the surface of the feces. In rectal cancer, blood is mixed with feces, often very dark in color, unlike blood in hemorrhoids;
- in rectal cancer, mucus may come out of the intestine before and after the appearance of feces, often with an unpleasant odor;
- the nature of the stool changes - the narrowing of the intestinal lumen causes a change in the shape of the feces;
- Constipation becomes persistent. Treatment fails in rectal cancer;
- with the development of an intestinal tumor, pain is always present - in the abdomen, during defecation and at rest;
- the patient begins to lose weight, appetite decreases;
- In the advanced stages of cancer, fistulas form, through which urine exits the anus or feces exits the vagina.
Metastases in rectal cancer: symptoms
Metastasis of a tumor of the rectum occurs through two systems - lymphatic and circulatory. In the lymphatic system, metastases spread up the rectal vessels and behind along the rectal vessels, to the side walls of the pelvis through the lymphatic vessels to the iliac and hypogastric lymph nodes. Through the lower rectal lymphatic vessels to the inguinal lymph nodes. Retrograde spread of the tumor to the underlying lymphatic apparatus is also possible.
Through the blood vessels, metastases very quickly enter the liver, disperse through the visceral peritoneum, and are detected in other distant systems and organs. Metastasis is accompanied by the appearance of symptoms of tumor development in other organs. With liver damage, patients develop jaundice, pain in the right side, nausea, vomiting.
Where does rectal cancer metastasize?
The first metastases are detected in nearby lymph nodes. Then metastases spread to distant organs and systems: lungs, liver, skeletal system, ovaries, brain, serous membrane of the peritoneum, heart. The liver and lungs are most often affected.
Methods of treatment
The methods of treatment for rectal cancer are traditional - the main method of treatment is the surgical method. The radical method is the most effective method of removing a malignant formation of the intestine. Chemotherapy and radiotherapy serve as complementary treatments.
Surgery for rectal cancer
Radical removal of a tumor of the rectum is a resection of the affected segment of the intestine. Open sections of the intestine after resection of the affected segment are sutured, intestinal patency is restored. In some cases, a stoma is applied to quickly heal the rectum. Metastases in the lymph nodes are removed along with the lymphatic apparatus, damaged vessels are removed.
Surgery for rectal cancer, depending on the type of tumor, the stage of development of the neoplasm, the patient's condition, is carried out by several methods:
- laparoscopic (through punctures in the anterior abdominal wall);
- by laparotomy (open method, through an incision in the abdominal wall).
Immunotherapy for rectal cancer
Immunotherapy in the first stages of cancer is prescribed as an additional treatment. In the third stage of rectal cancer and the fourth stage, it becomes necessary. To defeat cancer, all the forces of the body are required, a good response to the ongoing treatment. Immunotherapy is the treatment of cancer with the help of antitumor biological agents (cytokines and monoclonal antibodies). Such treatment is carried out for a long time, the patient is under the supervision of doctors for the entire period. The purpose of such treatment is to make our body recognize cancer cells and destroy them.
Survival rate: colorectal cancer
An optimistic prognosis for the survival of patients with rectal cancer is noted in countries with a highly developed level of medicine. In such countries, more than five years after the detection of cancer, about 60% of patients survive. In countries with a lower level of medicine, this figure does not exceed 40%.
The first symptoms of rectal cancer do not differ from the manifestations of gastrointestinal diseases, therefore, with the development of any intestinal discomfort, you should undergo an examination at the Yusupov hospital and be tested for tumor markers. How to diagnose rectal cancer, what tests are given for tumor markers - they will tell you at a consultation at the oncology clinic of the Yusupov hospital. If you are over 40 years old, it is necessary to diagnose bowel cancer using a colonoscopy every five years



























