Home >
Erectile Dysfunction >
Treatment of acute inflammation of the prostate
Treatment of acute inflammation of the prostate
Acute prostatitis in men: symptoms and treatment
Acute and chronic prostatitis are the most common male diseases. In clinical urology, these diseases are diagnosed in 30-60% of men of reproductive and working age (30-50 years).
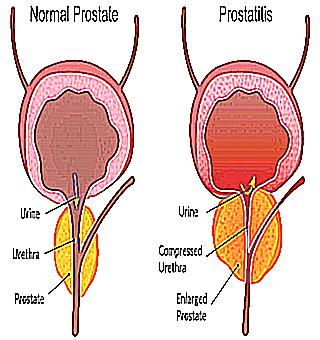
Acute prostatitis is an inflammatory lesion of the prostate gland, accompanied by edema and the formation of purulent foci in the tissues of the prostate. The disease is caused by exposure to various pathogenic microorganisms.
The disease does not require emergency treatment. However, ignoring Acute inflammation can lead to the fact that it becomes chronic. Therefore, when the first symptoms occur, you should consult a doctor and get an appointment for treatment.
Causes of disease
Most often, the disease affects men over the age of 30 years. The causes of its occurrence are usually associated with the negative impact of various pathogenic microflora. Among the microorganisms that can lead to the appearance of symptoms of acute prostatitis, there are:
- Escherichia coli and Pseudomonas aeruginosa;
- Staphylococcus aureus;
- enterococcus;
- Klebsiella;
- Proteus
Many of the bacteria are in the body all the time. But in the normal state, they do not lead to the appearance of an inflammatory process. When they penetrate the mucous membrane of the prostate gland through the urethra, they begin to actively multiply and cause a strong inflammatory process.
Some bacteria enter the body through unprotected intercourse. Therefore, men who do not use contraceptives and constantly change partners suffer from the disease especially often.
There are also non-infectious causes of the inflammatory process. Among them are:
- inactive (sedentary) lifestyle;
- overweight;
- unhealthy composition and diet;
- severe hypothermia;
- insufficient sexual activity;
- coitus interruptus;
- smoking;
- excessive drinking.
All these factors (individually or in combination) lead to stagnation of secretion in the prostate gland and blood in the vessels located next to the organ.
The accumulation of secretion creates favorable conditions for the reproduction of pathogenic microorganisms, which causes an inflammatory process. And in turn, the latter can cause a variety of complications from abscess and prostate adenoma to prostate cancer. Often men have problems with potency and conceiving children.
Symptoms and forms of the disease
When Acute prostatitis occurs in men, the symptoms may vary. The severity of the manifestations of the disease depends on the stage and form of the inflammatory process in the prostate gland.
At the initial stage of the onset of the disease, a subacute form of the disease may be noted. Its symptoms are very weak. This is due to the low activity of pathogens or a good level of body resistance. The disease is very difficult to diagnose. Therefore, treatment may not be timely. And then the disease goes through several stages: catarrhal, follicular, parenchymal.
The clinical manifestations and symptoms of acute prostatitis correspond to the stages of the process. Common manifestations are pain, urination disorders and intoxication.
Catarrhal form
When the infection enters the excretory ducts, a catarrhal form of acute prostatitis is observed. In this case, the pathogenic microflora affects the mucous membrane without penetrating into the deep layers of the organ. Inflammatory foci appear in the prostate, it swells and increases in size. There is also squeezing of the urethra. Often, such signs appear under the influence of the influenza virus.
Mild symptoms still appear as:
- minor urinary problems;
- more frequent urination, especially at night;
- heaviness in the perineum in a sitting position;
- increase in body temperature to 37-38C.
At the same time, hyperthermia and subfebrile condition are sometimes completely absent.
Symptoms of acute inflammation of the catarrhal form may disappear on their own after 14 days. However, treatment is not always required. However, in this case, there is a high probability that the disease will become chronic.
Treatment started in the catarrhal stage of acute prostatitis leads to recovery in 7-10 days.
Follicular form
In the absence of treatment of the catarrhal type of the disease, the appearance of a follicular form is observed. During this period, there is a spread of infection, damage to individual lobes of the prostate.Symptoms become pronounced and manifest as:
- acute pain when urinating;
- dull aching pain in the perineum radiating to the penis, anus or sacrum;
- difficulty in debugging due to severe pain;
- increase in body temperature up to 38C;
- complications of urination.
At this stage, a purulent lesion of the prostate is observed, as evidenced by the threads of pus in the urine.
With vigorous therapy of follicular prostatitis, after 12 days, complete elimination of the signs of the disease can be noted. Otherwise, it goes into the next more difficult stage.
Parenchymal form
The diffuse or parenchymal form is the final stage of acute prostatitis. The inflammatory process extends to the parenchyma of the organ, where purulent foci are formed. Sometimes there is a complete lesion. The gland increases significantly in size.
The symptoms of this form are very pronounced:
If the treatment of acute prostatitis in the parenchymal stage is started on time, then the prognosis for a complete cure is favorable. Otherwise, the disease will become chronic or a prostate abscess will form.
Disease diagnosis
Diagnosis and staging of acute inflammation of the prostate is carried out by a urologist and is based on a comprehensive physical, laboratory and instrumental examination of the patient.
Examination of the prostate through the rectum allows you to determine the size, consistency, homogeneity, symmetry of the gland, pain reaction, foci of destruction, signs of purulent fusion of tissues.
In the obtained secret of the prostate, an increase in the number of leukocytes and amyloid bodies, a decrease in the number of lecithin grains are found.
There is also increased leukocyturia in the third portion of urine.
To isolate the causative agent of acute prostatitis and find out its cause, it is necessary to carry out:
- urine culture and urethral discharge with antibiogram;
- PCR studies of scrapings;
- blood culture for blood culture.
The nature and severity of dysuric disorders in the acute course of the disease is assessed using uroflowmetry.
Ultrasound of the prostate gland with moderate pain syndrome can be performed transrectally, and in case of severe pain reaction - transabdominally. The shape, size of the gland, the presence of focal or diffuse changes are evaluated echoscopically, the stage of an acute inflammatory process is established.
When planning a surgical operation for destructive forms of acute prostatitis, it is advisable to conduct an MRI of the pelvic area.
Treatment of disease
The leading role in the treatment of acute prostatitis belongs to etiotropic therapy. It is necessary to prescribe antimicrobial (antibacterial, antiviral, antitrichomonas, antimycotic) drugs as early as possible to suppress the reproduction of microorganisms in the gland and tissues of the urethra.
In order to reduce spasms and painful urination, analgesics, antispasmodics, rectal suppositories with anesthesin or belladonna, thermal microclysters are prescribed. In the complex therapy of acute prostatitis, NSAIDs, enzymes, immunomodulators, vitamins, infusions of solutions are used.
Physiotherapy for acute prostatitis is carried out after the acute symptoms subside.
Diet plays an important role in therapy. Also, during the treatment period, it is worth drinking plenty of fluids. This helps to ease the process of urination and relieve pain.
Folk recipes can also help speed up the healing process.
Medicines
The treatment of acute prostatitis is aimed at eliminating the infection that caused inflammation, as well as normalizing blood circulation and eliminating congestion. It is usually done on an outpatient basis. Hospitalization may be required for patients with parenchymal disease.
In acute infectious prostatitis, therapy necessarily includes taking antibiotics. The duration of therapy and the drugs used in this case should be prescribed exclusively by a specialist.
Different antibiotics are effective against different microorganisms. Therefore, the doctor must evaluate the result of sowing and choose a remedy that will help to cope with the infection that provoked the disease. Usually treatment is carried out with:
Fluoroquinolones are recognized as the most effective in inflammation of the prostate. Therefore, they are often prescribed in the acute course of the disease.
In addition to antibacterial drugs, antihistamines (Zirtek, Zodak, Suprastin) and intestinal bacteria (Lactobacterin, Bifidumbacterin, Linex) are prescribed.
During the treatment period, it is necessary to maintain immune protection at the proper level.For this purpose, the following drugs are prescribed:
Timalin (promotes the restoration of gland tissues); Taktivin (indispensable in the presence of purulent foci); SIAM (good for bacterial damage).
You may also need to take interferons. They are used in the form of rectal suppositories and intramuscular injections. Among them, high efficiency is noted:
Physiotherapy
After the signs of the acute stage of the disease subside, you can undergo physiotherapy. It is necessary to eliminate the inflammatory process, relieve swelling of the gland tissues, eliminate pain, improve microcirculation and increase local immunity.
Common methods of influence are:
- rectal electrophoresis;
- UHF therapy;
- UHF therapy.
Prostate massage is also effective.
The diet for prostate inflammation is based on the principles of a healthy diet and limiting the intake of junk food. The diet is selected taking into account the severity of the manifestation of the disease and the characteristics of the organism.
During the treatment period, you should stop using:
- fatty meat and fish;
- salty and spicy food;
- preservation products;
- smoked meats;
- cabbage;
- legumes;
- strong tea and coffee;
- alcohol.
It is worth enriching the diet with fermented milk products, cereals and juices.
An element such as zinc plays an important role in the treatment of inflammation of the prostate. It is contained in:
- chicken meat;
- eggs;
- pumpkin seeds;
- walnuts.
During the treatment period, it is imperative to consume a large amount of liquid. In this case, you must completely abandon the intake of alcoholic beverages. They slow down the healing process, provoking various complications.
Folk recipes
Doctors believe that it is impossible to cure the disease with the help of folk remedies. But to alleviate the patient's condition in the acute course of the disease with their help is completely realistic. After all, even many medications are made on the basis of medicinal plants, which are widely used in traditional medicine recipes.
A specialist can advise the use of decoctions and infusions of medicinal herbs and plants. They are taken orally or added to water during sitz baths. Among the useful plants are:
- aspen bark;
- chestnuts;
- horsetail;
- chamomile;
- coltsfoot;
- oak bark.
It is worth remembering that some herbs can cause allergic reactions. Therefore, you should not prescribe them on your own. Otherwise, you can provoke the appearance of various complications.
The acute form of prostatitis is quite amenable to therapy. It is important to start it in a timely manner when the first symptoms occur. If delayed with therapy, the disease can become chronic. In this case, it will be much more difficult to cure it.
Useful video
Acute prostatitis
Acute prostatitis is an infectious and inflammatory lesion of the prostate gland, accompanied by edema and the formation of purulent foci in the tissues of the prostate. Manifestations of acute prostatitis depend on the stage (catarrhal, follicular, parenchymal, abscessing) and may include dysuric disorders, pain in the perineum, fever, intoxication. Diagnosis is based on palpation of the prostate, ultrasound and dopplerometry of the prostate gland, examination of the discharge of the urethra and secretion of the prostate. Treatment of acute prostatitis includes the appointment of antimicrobial therapy, NSAIDs, antispasmodics, analgesics, immunomodulators, physiotherapy.
Acute prostatitis
Acute and chronic prostatitis are the most common and socially significant male diseases. In clinical urology, prostatitis is diagnosed in 30-58% of men of reproductive and working age (30-50 years). The course of acute prostatitis is accompanied by disorders of sexual function and fertility, disorders of the psycho-emotional state and social maladaptation.
Causes of acute prostatitis
The causative agents of acute prostatitis are predominantly non-specific infectious agents that penetrate into the tissues of the prostate - gram-negative (E. coli, Klebsiella, Proteus) or gram-positive (staphylococci, enterococci, streptococci). Often, acute prostatitis can be caused by pathogens of urogenital infections - chlamydia, trichomoniasis, ureaplasmosis, gonorrhea, mycoplasmosis, candidiasis, etc.
Most often, the penetration of microbial agents into the tissues of the prostate occurs in a transcanalicular way - through the excretory ducts of the gland, which open in the wall of the posterior urethra. Therefore, urethritis of any origin is very often complicated by acute prostatitis. Less commonly, microbial flora enters the prostate from the bladder in acute cystitis.The introduction of pathogens into the gland is greatly facilitated with increased intraurethral pressure (strictures, urethral stones), endourethral manipulations (urethral bougienage, bladder catheterization, ureteroscopy, cystoscopy, etc.).
In addition, acute prostatitis may be the result of hematogenous penetration of infection, which is facilitated by the conditions of blood supply to the prostate with a well-developed system of arterial and venous anastomoses. With hematogenous drift, microbes can enter the tissues of the prostate from distant purulent foci with tonsillitis, sinusitis, caries, cholecystitis, bronchitis, pyoderma, etc. Lymphogenous infection of the prostate gland from the intestine is possible with anal fissures, proctitis, colitis.
Non-infectious factors contributing to the development of acute prostatitis include persistent congestive (stagnant) phenomena in the pelvic veins and impaired drainage of the prostate acini. Congestion can be caused by dysrhythmia of sexual life and sexual disorders - the practice of coitus interruptus, the absence or irregularity of sexual activity, excessive sexual activity, etc. mainly alcohol) intoxication, varicose veins of the pelvis.
Forms of acute prostatitis
In the development of acute prostatitis, 3 forms are distinguished, which are at the same time its stages - catarrhal, follicular, parenchymal, abscessing.
Acute prostatitis begins with catarrhal inflammation - changes in the mucous and submucosal layer of the excretory ducts of individual lobules of the gland. In the future, swelling of the walls of the ducts contributes to the stagnation of the mucopurulent secretion in the prostate follicles and the progression of inflammation, in connection with which focal suppuration of the lobules can develop - acute follicular prostatitis. With multiple lesions of the lobules and diffuse involvement of the parenchymal and interstitial tissue of the prostate in the purulent-inflammatory process, acute prostatitis passes into its next stage - parenchymal. In the case of the fusion of small abscesses into a large focus, an abscess of the prostate gland is formed, which can open into the urethra, perineum, rectum or bladder.
Symptoms of acute prostatitis
Clinical manifestations in acute prostatitis correspond to the stages of the process. Common manifestations are pain, urination disorders and intoxication.
In the acute catarrhal stage of prostatitis, there is heaviness and pain in the perineum. Dysuric disorders are characterized by a painful increase in urination, especially at night. Body temperature remains within the normal range, may be slightly elevated; there is no intoxication. On palpation examination, the prostate is not changed or slightly enlarged, somewhat painful. Examination of the secret of the prostate reveals an increase in leukocytes, an accumulation of mucopurulent filaments. White blood cells appear in the urine when emptying the excretory ducts of the acini. prostate massage is usually not possible due to pain. Treatment started in the catarrhal stage of acute prostatitis leads to recovery in 7-10 days.
The follicular form of acute prostatitis is more pronounced, accompanied by dull aching pains in the perineum, radiating to the penis, anus or sacrum. Against this background, urination is painful and difficult, up to the development of acute urinary retention. The act of defecation in acute follicular prostatitis is also difficult due to severe pain. In view of the increase in body temperature to 38C, the general condition is disturbed. Palpation per rectum is determined by an enlarged, dense, tense, asymmetric prostate, sharply painful in some areas during digital examination. Urine collected after palpation of the gland contains a large amount of leukocytes and purulent filaments that form a cloudy sediment. Carrying out massage to obtain a secret of the prostate in the follicular stage of acute prostatitis is contraindicated. With vigorous treatment, acute follicular prostatitis may resolve favorably; otherwise, it proceeds to the next, parenchymal stage.
The clinic of acute parenchymal prostatitis is developing rapidly. Characterized by severe hyperthermia (up to 39-39.5 C and above) with chills, general weakness, appetite suppression, thirst. At first, urination is sharply accelerated and difficult, then it may stop altogether. Attempts to empty the bladder or intestines are accompanied by intense pain. Excruciating tenesmus, constipation, flatulence develop. The pain spreads to the rectum, is pulsating in nature, makes the patient take a forced position - lying with his legs tucked in. With the development of reactive inflammation of the rectum, mucus is released from the anus.
On palpation, a diffusely enlarged, with indistinct contours of the gland is determined, extremely painful at the slightest touch.Prostate massage in the parenchymal stage of acute prostatitis is contraindicated categorically. Sometimes, due to a sharp swelling of the pararectal tissue and pain, a rectal examination cannot be performed. In the urine - a pronounced leukocytria, pyuria. The outcome of acute parenchymal prostatitis can be the resolution of the disease, the formation of a prostate abscess or chronic prostatitis.
Diagnosis of acute prostatitis
Recognition and staging of acute prostatitis is carried out by a urologist (andrologist) and is based on a comprehensive physical, laboratory and instrumental examination. The study of the prostate through the rectum allows you to determine the size, consistency, homogeneity, symmetry of the gland; pain reaction, foci of destruction, signs of purulent fusion of tissues. In the resulting secret of the prostate, an increase in the number of leukocytes and amyloid bodies, a decrease in the number of lecithin grains are found.
In acute prostatitis, there is increased leukocyturia in the third portion of urine and in the urine collected after palpation of the prostate. To isolate the causative agent of acute prostatitis, it is necessary to carry out bakposev of urine and urethral discharge with an antibiogram, PCR studies of scrapings, and blood cultures for blood culture. The nature and severity of dysuric disorders in acute prostatitis is assessed using uroflowmetry.
Ultrasound of the prostate gland with moderate pain syndrome can be performed transrectally; in the case of a pronounced pain reaction - transabdominally. Echoscopically assesses the shape, size of the gland, the presence of focal or diffuse changes, the stage of acute prostatitis is established. The use of dopplerometry allows a detailed and differentiated assessment of the vascularization of the prostate.
When planning surgical tactics for destructive forms of acute prostatitis, it is advisable to perform CT or MRI of the pelvis.
Treatment of acute prostatitis
The leading role in the treatment of acute prostatitis belongs to etiotropic therapy. It is necessary to prescribe antimicrobial (antibacterial, antiviral, antitrichomonas, antimycotic) drugs as early as possible to suppress the reproduction of microorganisms in the gland and tissues of the urethra. In order to reduce spasms and painful urination, analgesics, antispasmodics, rectal suppositories with anesthesin or belladonna, and thermal microclysters are prescribed. In the complex therapy of acute prostatitis, NSAIDs, enzymes, immunomodulators, vitamins, infusions of solutions are used.
Physiotherapy for acute prostatitis is carried out after the acute symptoms subside. For the purpose of anti-inflammatory, anti-edema, analgesic action, improvement of microcirculation and local immunity, rectal electrophoresis, UHF therapy, microwave therapy, prostate massage are used. In acute prostatitis, bed rest, a sparing diet, and sexual rest are shown.
With urinary retention against the background of acute prostatitis, bladder catheterization is avoided, preferring trocar cystostomy. When abscessing the prostate gland, there is a need for a surgical aid for opening and draining the abscess cavity.
The cure of acute prostatitis is judged by the restoration of the structure of gland tissues and its functions, the normalization of the composition of prostate juice, the elimination of pathogens that caused inflammation from biological fluids.
Forecast and prevention
As a rule, timely and reasonable etiotropic therapy leads to relief of signs of acute prostatitis. Abscessing of the prostate or chronic inflammation occurs in advanced cases.
Prevention of acute prostatitis should include sanitation of infectious foci in the body, endovesical and endourethral manipulations in accordance with asepsis standards, timely treatment of STDs and urethritis, normalization of sexual life and physical activity.
Basic principles of diagnosis and treatment of acute prostatitis
Among all men's diseases, according to statistics, prostatitis is considered the most common. Among men 30-50 years old, the incidence is 30-60%. This percentage increases with age. In acute prostatitis, the prostate gland develops, the excretory ducts of the gland are clogged, and then pus begins to form. Acute inflammation of the prostate causes symptoms associated with impaired urinary and sexual function, accompanied by a psycho-emotional disorder. The treatment of this pathology is complex.
Forms of acute prostatitis
Be careful!
Before reading any further, I'll ask you one question. Are you still looking for a working method to improve potency?
I hasten to warn you, most drugs for potency are a complete scam of marketers who wind up hundreds of percent on drugs whose cost is approaching zero. Everything would be fine, and it seems that Viagra-type drugs work. BUT.
Almost all potency pills are instantly addictive.
It's very simple, after drinking just a few times the remedy for potency, you will not be able to do absolutely NOTHING in bed without the help of this remedy. This is no coincidence, because the pharmacy mafia earns a lot of money on repeat sales. They just put you on a needle.
But what if one's strength is no longer enough? We have studied a huge amount of materials and, most importantly, tested most of the means for potency in practice. So, it turned out that the only drug that is not addictive and does not cause any side effects is Prodstanol. This drug is not sold in pharmacies and is not advertised on the Internet, it consists of natural ingredients, and completely excludes chemistry. Here is the link to the official website.
According to clinical signs, there are three stages of acute prostatitis, they are also forms of the disease:
The excretory ducts leading to the posterior urethra are most involved in the process of inflammation. In the future, there is a risk of developing posterior urethritis. The process of inflammation captures only the mucous layer and does not penetrate deeper.
In the follicular form of acute prostatitis, the formation of purulent foci, as well as the ingress of pus into the urethra, is not excluded.
- as a result of the development of prostatitis following the follicular stage;
- regardless of the disease, through blood or contact after instrumental interventions (punctures, operations).
What causes inflammation?
The main cause of the disease is an infection that most often enters from the back of the urethra into the excretory ducts of the prostate gland. Also, the infection can penetrate through the lymph (due to acute urethritis or complications of bladder catheterization) and through the blood (with bacteremia, when bacteria are found in the systemic circulation).
The development of inflammation in the prostate gland is facilitated by such conditions as:
- stagnation of venous blood in the pelvis due to obesity, sedentary lifestyle, hemorrhoids, paraproctitis;
- decreased immunity;
- presence of certain diseases (HIV, alcohol dependence, diabetes).
There are also a number of factors that can trigger infection in men, for example:
- presence of stones in the prostate gland;
- phimosis - narrowness of the opening of the foreskin;
- urethral catheterization;
- instrumental interventions in the urethra;
- dysfunction of the urethral sphincter resulting in intraprostatic reflux of urine;
- the presence of acute or chronic infectious diseases in the sexual partner.
How is acute prostatitis manifested?
Identify the main symptoms of prostatitis, regardless of stage:
- pelvic pain;
- problems with urination (frequent urge, painful and difficult urination);
- symptoms of intoxication (headache, weakness, nausea);
- lack of libido;
- Anorgasmia and pain during sex.
The catarrhal stage is characterized by frequent painful urination, significant pain in the perineal area. Symptoms of intoxication at this stage may be, but many do not have them.
More pronounced symptoms are noted at the time of follicular acute prostatitis. The pain is felt not only in the perineum, but also in the penis, sacrum. The process of emptying the bladder is difficult and becomes unbearably painful, this often leads to urinary retention. Sometimes there is constipation. At this stage, symptoms of intoxication are always expressed, characterized by poor health and fever.
With parenchymal prostatitis, urinary and fecal retention often occurs. When a man tries to empty his bladder, intense pain appears. Symptoms of intoxication are very pronounced: weakness, chills, fever, thirst, loss of appetite. The pain radiates to the rectum, acquires a pulsating character.
In the second and third stages, the patient may notice purulent discharge from the urethra. It is extremely important not to massage the prostate during these stages, so as not to spread the pus to other tissues. Treatment is carried out only as directed by a doctor.
Possible complications
Often, acute prostatitis provokes acute urinary retention, for all men this is a very unpleasant condition. In this case, immediate hospitalization, urinary excretion by instrumental methods and inpatient treatment are required.
Prostate abscess is a serious and often occurring complication of acute prostatitis. This is the parenchymal stage of acute prostatitis. It is impossible to recover without surgical intervention. It happens that the abscess spontaneously opens into the bladder or urethra, most men at this time feel relieved.But, subsequently, fistulas and phlegmons begin to form in the area where the abscess broke through. These conditions also require urgent surgery.
When the process passes to the tissues surrounding the prostate, paraprostatitis is formed. The parenchymal form of prostatitis can lead to such complications as phlebitis of the paraprostatic venous plexus. Subsequently, this condition can develop into sepsis.
The most common complication of prostatitis is the transition to a chronic form. Chronic prostatitis is not as life-threatening as previous conditions, but its treatment takes a very long time, the disease returns again and again.
Diagnostic methods
Methods for diagnosing the disease are based on the results of an examination by a urologist, laboratory tests, and ultrasound. If you are indicated for surgical treatment, you need to undergo an MRI or CT scan of the pelvic organs. Palpation of the prostate through the rectum allows the doctor to find out the symmetry, size and consistency of the tissues of the organ, the severity of pain in the patient.
Examination by a urologist is carried out very carefully, without strong pressure. In ultrasound diagnostics, a transrectal method is used, but only if the pain syndrome in men is insignificant. This method is more effective than transabdominal. However, in case of severe pain, ultrasound is performed through the abdominal cavity.
During the catarrhal stage of the disease, an increased number of leukocytes is found in the prostatic secretion of men, the doctor notes a slight increase in the prostate by palpation.
Acute prostatitis during the follicular stage is characterized by a large number of leukocytes and pus in the urine. To the touch, the prostate gland is larger than normal size, it is characterized by asymmetry, tension. When probing some parts of the prostate, the patient may feel a sharp pain.
In the parenchymal stage of prostatitis, the prostate gland is diffusely enlarged to the touch, has no clear boundaries. The patient experiences severe pain on examination. Rectal examination cannot be performed due to pain and pronounced recoil of the perirectal tissue. According to the results of the tests, as well as in the follicular stage, pus and a high level of leukocytes are found in the urine.
Basic methods of dealing with prostatitis
The main task in the fight against acute prostatitis is the suppression of the pathogen in the prostate gland and tissues of the urethra. For this, treatment with antimicrobial drugs (antibiotics, antifungal, antiviral, etc.) is used.
To get rid of severe pain, antispasmodics and analgesics are prescribed. Candles for rectal use with belladonna or anesthesin do their job well. Relieve pain and warm microclysters.
In combination with the main drugs, acute prostatitis is treated with auxiliary drugs:
- non-steroidal anti-inflammatory drugs;
- vitamins;
- immunomodulators;
- enzymes.
If urinary retention occurs, doctors resort to trocar cystostomy (i.e., puncture of the bladder followed by placement of a catheter). Catheterization through the urethra will not be possible due to severe recoil. If an abscess of prostate tissue has occurred, surgeons open it surgically, then drain the cavity.
After the acute symptoms subside, the patient is prescribed physiotherapy methods: UHF, microwave, rectal electrophoresis. These methods improve blood circulation in the prostate, reduce edema and tissue inflammation, and locally increase immunity.
Should I have sex with acute prostatitis?
When the disease is in an acute stage, and the symptoms are pronounced, intimate life should be postponed a little. Even the body of a man at this time will give signals that now is not the time: sexual desire fades away, there is no erection, there are problems with achieving orgasm, pain does not give rest. The danger of having sex during prostatitis is also the presence of an infection that can be transmitted to a sexual partner.
All these are temporary problems. The main thing is to kill the infection that has settled in your body. While the treatment is being carried out, the symptoms will subside, and then the intimate life will definitely need to be resumed. Regular sex has a great effect on the health of men and helps to ensure that further treatment is more successful. The only caveat is that while the pathogens are still in the body (this can be seen from laboratory parameters), they come out with the sperm. Therefore, it is recommended to have sex during this period with a condom.
Proper diet
If you take the pills prescribed by your doctor, this is good, but not enough for the treatment to be complete. Be sure to check your diet. Eliminate fatty, floury, spicy, smoked and canned foods from your diet. Tea, coffee and alcoholic beverages are contraindicated for prostatitis.Until the disease is eliminated, do not eat legumes (peas, beans), mushrooms (any kind) and offal.
The daily diet should consist of fermented milk products, boiled vegetables and herbs. It is advisable to eat fruits not only raw, but also baked, especially apples. Nuts also have a good effect on male strength, do not forget to use them several times a day.
Instead of tea and coffee, drink more plain clean water (at least 1.5 liters per day). From drinks, you can afford a compote of dried fruits or fresh fruits, freshly squeezed juices, herbal teas with mdom.
This type of diet helps to restore the body's strength, increase immunity. Following a balanced diet, you will feel a surge of strength and energy.
It is not difficult to cure acute prostatitis, you just have to want it and stop being ashamed of your problem. If you turn to a specialist in time, you will be able to avoid complications and, possibly, never again encounter this disease. Do not forget about the preventive visit to the urologist. Take care of personal hygiene, have regular sex with a regular sexual partner, take time for physical activity.
Conclusions
Did you have a misfire? Judging by the fact that you are reading this article, victory is not on your side.
And of course, you know firsthand what a violation of potency is:
- Low self-esteem
- Women remember your every failure, tell their girlfriends and your friends
- Prostate disease
- Developing depression that negatively affects your health
Now answer the question: DOES THIS SUIT YOU? Can this be tolerated? Do you remember that feeling when you look at a naked woman and can't do anything? Enough time to get rid of problems with potency, once and for all! Do you agree?
We have studied a huge amount of materials and, most importantly, tested most of the means for potency in practice. So, it turned out that Predstanol is a 100% working drug without any side effects. This drug consists of natural ingredients that completely exclude chemistry.
WARNING! PROMOTION! You can try the drug for free, place an order via the link or by filling out the form below:



























