Home >
Erectile Dysfunction >
How does prostate cancer begin
How does prostate cancer begin
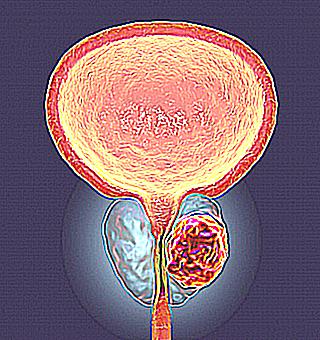
Prostate cancer: symptoms and signs of development
What is the prostate, its functions. Causes of Prostate cancer and predisposition factors.
Methods of prevention and early diagnosis. Signs and symptoms of prostate cancer in men. Techniques and methods of examination. Prognosis of the development of the disease.
The prostate gland, or prostate, is an internal glandular organ located under the bladder and covering the urinary tract.
About the disease
The gland, being part of the reproductive system, produces a secret that ensures the viability of spermatozoa. In the total volume of seminal fluid, such a secret can be about 30 percent. The importance of the prostate also lies in its ability to retain urine inside the bladder.
What is prostate cancer: symptoms, prognosis? Prostate cancer is considered a common disease, it is a malignant tumor that has developed inside the glandular tissues. Prostate cancer can metastasize, like any malignant neoplasm.
Prostate cancer - symptoms, prognosis for life: according to medical statistics, the disease affects over 12% of men over fifty. Death from prostate cancer in the world in frequency is in third place after cardiovascular diseases and lung cancer in older men.
Every year, more than 400 thousand cases of prostate cancer are recorded in the world. In the statistics of localization, Signs of prostate cancer in European countries take 2nd place after lung cancer
It is known that residents of Asia, South America, Africa are less likely to get this type of cancer than residents of North America and Europe.
Reason for development
Medicine does not have accurate data on the factors that cause the disease. It has been established that the culprit for the occurrence of a malignant tumor is DNA changes in gland cells, the cause of which has not been established.
It is known that the older the man, the higher the likelihood of the disease.
According to the findings of medical statistics, the hereditary factor plays a significant role.
The presence of prostate cancer among direct relatives increases the risk of the disease by 2 times or more
Research has established that the disease is associated with an excess of testosterone, the male sex hormone.
The likelihood of the disease and the aggressiveness of the neoplasm directly depend on the level of testosterone in the blood of a man.
Official medicine assumes such risk factors in the occurrence of the disease:
- excessive consumption of animal fats, lack of fiber in the diet;
- age over 50;
- prostate cancer among direct relatives;
- prostate adenoma;
- poor environmental situation;
- harmful production factors (work in a printing house, welding work).
The risk of disease increases for lovers of fatty foods, "red" meat - beef, pork, lamb against the background of reduced fiber intake.
You can reduce the risk of illness with the help of several rules:
How to recognize a disease?
The first signs of prostate cancer are not felt, there is no discomfort until the malignant tumor begins to grow. For this reason, men over the age of 40 are recommended to undergo regular preventive examinations to detect prostate pathology.
Prostate cancer: symptoms, signs
How does prostate cancer manifest in men?
The first symptoms of prostate cancer in men:
Burning sensation when urinating; urge to urinate again within 30 - 60 minutes after the previous one; feeling of incomplete emptying after urination; decrease in pressure and intermittency of the jet during urination; reduction of time intervals between visits to the toilet, mainly at night. The presence of several or one of the listed symptoms is enough to visit a specialist - a urologist or an oncologist.
The first symptoms of prostate cancer in men:
Such symptoms of prostate cancer are often found in men over 50 years of age. The symptoms of prostate adenoma, which is a benign tumor, are the same as in cancer. Therefore, you should urgently undergo an examination in a medical institution to make an accurate diagnosis.
In later stages of prostate cancer, you may experience:
- blood in semen or urine;
- with prostate cancer, pain in the perineum.
In advanced cases with metastasis, the first symptoms, Signs of prostate cancer in men:
- pain in the spine, hips, or chest;
- Urine retention due to tumor growth may develop.
Later stages are characterized by cancer intoxication, which manifests itself in:
- a sharp decrease in body weight;
- weaknesses;
- quick fatigue.
At the same time, the patient's skin acquires a characteristic pale earthy hue.
Read more about the stages of prostate cancer development here.
Prostate cancer symptoms - photo:
Diagnosis
Until the disease has a limited localization and the period of metastasis has not set in, there may be no symptoms, so it is important, as a diagnosis, to periodically undergo a test for the presence of PSA, or prostate specific antigen, which is produced by a healthy gland and is found in the blood.
An increase in this factor in the blood serum, as well as a change in the ratio of the free and bound forms of the antigen, is a probabilistic factor indicating the presence of a malignant neoplasm. The higher the PSA, the higher the chance of cancer.
When examining a patient for prostate cancer, a number of tests and studies are performed:
Chances of healing and methods of therapy
According to medical statistics, more than 80 percent of patients successfully overcome the disease after diagnosis. Often, the obvious symptoms of the disease appear in the later stages, when the disease is advanced, and the chances of a quick cure are rapidly falling.
The main favorable factor is the timely diagnosis, as well as the use of advanced treatment methods.
If the diagnosis is confirmed, treatment should be started immediately. If the tumor has a clear localization, endoscopic or surgical removal of the prostate is indicated. An effective method is radiation therapy using advanced medical equipment.
Patients after surgery or radiation therapy are prescribed long-term antitumor therapy aimed at blocking testosterone. Chemotherapy is also used.
Prostate cancer. Causes, symptoms, stages, treatment of the disease. Surgery for prostate cancer.
The site provides background information. Adequate diagnosis and treatment of the disease is possible under the supervision of a conscientious physician. All drugs have contraindications. Expert advice needed
Prostate cancer (prostate carcinoma) is a malignant tumor that develops from prostate cells. This internal genital organ is only in the representatives of the stronger sex. He is deservedly called the second male heart for playing a big role in the sexual sphere. A malignant tumor of the prostate grows relatively slowly. It can remain small for years, but, like other types of cancer, it is dangerous and forms metastases.
Prostate cancer is the most common malignant tumor in men and has become more common in recent decades. But our compatriots are relatively lucky, because this disease often affects representatives of the Negroid race. But the Japanese and South Asians get sick several times less often than Europeans.
A neoplasm can occur after 35 years in 1 in 10,000, but with age, the risk of getting sick increases hundreds of times. Among men over 60 years old, one in a hundred is sick. And in old age, after 75 years, prostate cancer is found in one in eight men. Therefore, after 50 years, you need to be especially attentive to your health and take special blood tests that will indicate that there are problems with the prostate.
Anatomy of the prostate
The prostate or prostate gland is the internal gonad in men. In shape, it resembles a chestnut, 4 by 3 cm in size. It consists of lobes of different sizes: right, left and middle.
The prostate gland is located in the small pelvis. It is located below the bladder, between the rectum and the pubis. The prostate surrounds the urethra (urethra) with a wide open ring. Therefore, its increase causes problems with urine excretion.
The prostate performs many functions that provide "male power":
Prostate structure
- Prostatic glands, there can be from 30 to 50 of them - this is the main part of the prostate. Their task is to produce prostatic juice, which makes up a third of the sperm.
- Smooth muscles contract and remove prostatic juice from the gland. Its congestion in the prostate can cause inflammation.
- A connective tissue capsule covers the outside of the gland. Inside, elastic partitions depart from it, between which the glands are located. The prostate can be felt through the rectum. It is located at a depth of 5 cm from the anus.Normally, the gland is resilient and elastic to the touch, without compacted areas and nodules.
Causes of prostate cancer
Scientists are still looking for an answer to the question of what causes prostate cancer. Some doctors argue that a malignant tumor develops only on the affected gland. Chronic diseases and other changes undermine the functioning of the body and cause disturbances in the structure of cells.
Most often, the appearance of a tumor is preceded by:
- Hormonal failure. The cause of the appearance of a cancerous tumor may be an increase in the concentration of male sex hormones: testosterone, dihydrotestosterone and androstenedione. They cause the growth of the gland and the multiplication of tumor cells. In connection with this feature, prostate cancer is called a hormone-dependent tumor.
- Prostate adenoma and other benign changes cause the growth of cells that should not be in the gland. They mutate more often than healthy cells of the glandular epithelium.
- Prostatitis. Chronic inflammation in the prostate causes poor circulation and lack of oxygen.
In addition, prostate cells attack bacteria and immune bodies. Under their onslaught, the genetic apparatus in the nucleus, which is responsible for cell reproduction, changes. Such conditions contribute to the appearance of a tumor.
Precancerous conditions
There are also precancerous conditions. They are more likely than others to lead to the appearance of a cancerous tumor. These changes may be congenital or develop in adulthood. These include:
- Atypical adenosis (atypical prostatic hyperplasia). Nodules appear in the central part of the gland, in which cells grow and multiply more actively than the surrounding ones. In addition, they change their structure. Their large nuclei indicate that the cells are in a borderline state between the norm and the tumor. It is considered an optional precancerous condition - this means that cancer can occur in its place if mutagenic factors act on the body.
- Hyperplasia with malignancy (intraepithelial neoplasia of the prostate gland). Cells in individual foci of the prostate begin to multiply actively. Gradually, they become less like typical cells of the prostate gland, and acquire the properties and signs of a malignant tumor. It is considered an obligate precancer - this means that the likelihood of a malignant tumor is very high.
But still, not every man has changes in the prostate that turn into cancer. This happens if the body is affected by factors that increase the risk of developing a malignant tumor.
Signs of prostate cancer
In the early stages, signs of prostate cancer will not be noticed. The tumor behaves secretly and does not cause any symptoms. Only an increase in the level of specific prostate antigen (PSA) in the blood can give it away.
So doctors discover prostate cancer by accident when a man is being examined for another disease. Symptoms of the disease appear when the tumor has affected neighboring organs: the bladder and intestines.
- I have to get up 2-3 times at night to empty my bladder (normally 1 time)
- urination during the day becomes more frequent up to 15-20 times
- there is a strong urge to urinate that is difficult to endure
- severe pain and burning during urination
- urinary incontinence
- pain in the perineum and pubis
- difficulty initiating urination
- Intermittent urine stream
- at the end of urination, urine does not flow, but is excreted in drops
- after going to the toilet, there is a feeling that the bladder is still full
All these symptoms do not appear at once, but gradually, and grow over several years. But none of these signs clearly indicates prostate cancer, and may be a manifestation of other diseases. But in any case, this is a reason to consult a urologist.
Degrees and stages of prostate cancer
The grade or stage of prostate cancer is determined based on the size of the tumor and its spread to neighboring organs. Another important factor is the presence of metastases. This is the name of secondary tumors that appeared due to the fact that blood and lymph carried malignant cells to distant organs.
In order to establish the stage of prostate cancer, you need to conduct an examination. To do this, use different diagnostic methods.
Staging of prostate cancerAfter the examination, the doctor makes a diagnosis and determines the stage of prostate cancer.
I stage - the tumor has a microscopic size. It cannot be felt or seen on ultrasound. It is indicated only by an elevated level of prostate specific antigen (PSA). At this stage, the patient does not notice any signs of the disease.
Stage II - the tumor grows, but does not go beyond the boundaries of the organ. It is limited to the prostate capsule.Cancer of the second degree can be felt with a digital examination in the form of dense nodes and detected by ultrasound. With second-degree prostate cancer, urination disorders may appear, which are associated with the fact that the prostate squeezes the urethra. At the same time, the urine stream becomes sluggish, cramps and pains appear in the perineum. The need to go to the toilet makes a man wake up 3-4 times at night.
Stage III - a cancerous tumor extends beyond the prostate and grows into neighboring organs. The seminal vesicles, bladder and rectum are the first to be affected. Tumor metastases do not penetrate into distant organs. Prostate cancer of the third degree is manifested by a violation of potency, pain in the pubis and lower back. There is blood in the urine and a strong burning sensation when emptying the bladder.
IV stage - a malignant tumor increases in size. Metastases form in distant organs: bones, liver, lungs and lymph nodes.
With cancer of the fourth degree, severe intoxication, weakness, loss of strength appear. When emptying the bladder and intestines, there are difficulties and severe pain. Often a man cannot urinate on his own and has to put a catheter.
Prostate cancer treatment
The doctor selects the treatment of prostate cancer individually for each man. An oncologist-urologist must take into account the age, stage of the tumor, concomitant diseases and the wishes of the patient.
Waiting tactics. The advanced age of a man (over 70 years), severe chronic diseases of the heart, blood vessels and lungs can become contraindications to the treatment of prostate cancer. It can be more life-threatening than the disease itself. If the tumor is small, does not go beyond the boundaries of the gland and has stopped its development, then the doctor will suggest postponing the treatment. In this case, you will have to do an ultrasound of the prostate every 6-12 months and take a PSA test.
Surgery to remove the prostate gland (radical prostatectomy) is one of the main methods of treating a tumor. This is the most common method of fighting cancer in men under 65.
The surgeon makes a small incision in the lower abdomen or perineum. Through it, the gland is completely removed. The doctor also dissects the surrounding tissue and, if necessary, the lymph nodes. The operation lasts 2-4 hours. The man is currently under general anesthesia. Sometimes they do regional anesthesia (epidural anesthesia) when there is no sensitivity below the belt.
If the tumor has not gone beyond the connective capsule, then it is possible to defeat the disease in 100% of cases. But if the tumor has grown into neighboring organs, then it can also be removed, but the prognosis for recovery worsens. Additional chemotherapy or radiotherapy may be required.
Modern clinics offer treatment with the help of a special Da Vinci robotic surgeon. The doctor controls all the actions of the robotic system, which rids the body of the tumor with high accuracy. The operation is performed through small punctures, which then heal quickly. New technologies can reduce the risk of complications to a minimum. It is possible to avoid side effects such as urinary incontinence and impotence.
Chemotherapy
Chemotherapy for prostate cancer is the destruction of tumor cells with drugs that contain special toxins. These substances destroy cells that are rapidly dividing. It is this feature that distinguishes cancer cells from the rest. Chemotherapy destroys the nuclei and membranes of tumor cells, causing their death.
Chemotherapy is used instead of surgery for stages III and IV, when the tumor has grown and metastases have appeared. Toxins are carried by the blood throughout the body, find cancer cells and destroy them. The drugs are administered intravenously in courses (Paclitaxel), sometimes they are taken in the form of tablets. In total, the treatment lasts six months.
Prostate cancer is sensitive to chemotherapy, but it is rarely prescribed in the early stages. The reason is that chemotherapy drugs also affect healthy cells and cause many side effects (baldness, weakness, nausea).
Radiotherapy
Radiotherapy is the treatment of prostate cancer using x-rays, neural, gamma, beta or other radiation. Radiation damages the DNA of tumor cells. This leads to the fact that they cannot divide, grow old and die.
In the treatment of prostate cancer, irradiation is carried out using special equipment - a linear accelerator. This method is called external beam radiation therapy.
The doctor will advise remote irradiation if the neoplasm is large and metastases have appeared in other organs. In this case, it is necessary to irradiate not only the tumor itself, but also the lymph nodes. The course of treatment lasts about 2 months, 5 days a week. Irradiation lasts 15 minutes and is absolutely painless. After the procedure, you need to rest for 1-2 hours and you can return home the same day.
But it will be more effective to inject radioactive particles directly into the prostate. The method is called brachytherapy.For this purpose, iridium or radioactive iodine is used. As a result of such exposure, the cancerous tumor dies off, and healthy tissues are irradiated minimally. This avoids serious side effects.
The procedure is performed under anesthesia. There are methods when radioactive granules remain in the gland. There are also those when needles with irradiating material are inserted for a while and removed on the same day.
Radiation therapy is used to treat cancer in the early stages, and in advanced cases, when surgery is no longer possible.
Fewer complications occur if prostate cancer is cauterized with a thin beam of high frequency ultrasound (HIFU therapy). Under its influence, the protein in cancer cells is destroyed, and they die
Medicine treatment
Treatment with hormones
For older men who cannot have surgery for health reasons and for those with stage 4 cancer, hormone therapy is the only treatment available.
To treat prostate cancer without surgery, use:
- Antagonists of gonadotropin-releasing hormone: Firmagon, Fosfestrol, Diethylstilbestrol. Drugs lower testosterone levels. They inhibit tumor growth, help its cells become more differentiated (similar to other prostate cells).
- Analogues of the pituitary hormone: Diphereline, Lucrin, Decapeptyl. Injections of these hormones provide "medicated castration". The level of male hormones after 2-3 weeks drops as much as if a man had his testicles removed. But this phenomenon is temporary, and gradually the concentration of testosterone in the blood rises again.
- Antiandrogens: Casodex, Flucinom, Anandron. These drugs prevent tumor cells from interacting with hormones that are secreted by the adrenal glands. They are used in conjunction with analogues of the pituitary hormone. This combination is called "maximum androgen blockade" and allows you to achieve the best result in the treatment of cancer.
In some cases, the doctor prescribes only one drug from the group of antiandrogens - Casodex. If this treatment is suitable for a man, then it is possible not only to stop the growth of the tumor, but also to maintain sexual desire and erection.
In men under 60, hormone treatment is combined with cryotherapy - freezing the tumor with low temperatures. Ice crystals that form in cancer cells destroy their membranes. The combined use of hormones and radiation therapy has a good effect.
If hormonal treatment does not work, the doctor will advise you to have an operation to remove the testicles. After it, testosterone levels fall and tumor growth stops. But men have a hard time undergoing surgical castration psychologically.
Monoclonal antibodies
Virotherapy
Among the new methods of treatment, virotherapy is considered the most promising. Viruses are specially developed that find and dissolve (lyse) cancer cells. ECHO 7 Rigvir proved to be the best. The drug reduces the tumor and stimulates the immune system so that it fights mutant cells on its own. It is prescribed in the early stages of the disease before and after surgery.
In the event that cancer is detected at stage 4, the doctor prescribes treatment that is aimed at relieving pain and improving the condition. In this case, the tumor is not removed, but they try to stop the spread of metastases.
An operation or the right treatment can help a man live 15 years or more. Research is ongoing in this area and new drugs are being tested. This gives hope that in a few years doctors will be able to cope with the disease in the later stages.
Prognosis for prostate cancer
The prognosis for prostate cancer is favorable if the man consulted a doctor on time and the disease was detected at stage I. Treatment allows you to completely get rid of the tumor, as well as maintain male strength and avoid problems with urinary incontinence. The man can continue to work. Life expectancy with successful treatment is unlimited.
At the diagnosis of "prostate cancer" stage II or III, more complex and lengthy treatment will be required. Its success depends not only on the skill of the doctor, but also on the age of the man and his state of health. Life expectancy in most patients with stage II is more than 15-20 years. Patients with stage III who have successfully completed a course of treatment can live 5-10 years.
It is believed that with stage IV prostate cancer, the prognosis for recovery is unfavorable. The average life expectancy is 3 years. But a combination of treatment and the will to live can work wonders. And some men manage to live longer than 5-7 years.
Doctors have a 5-year survival rate. He talks about what percentage of patients after treatment live five or more years. This allows you to judge what are the chances of a successful cure in patients with different stages of cancer.
Prostate cancer
Prostate cancer is a malignant neoplasm in the prostate gland and develops from the epithelium of the alveolar cell gland.
What is prostate cancer?
Prostate cancer is a common insidious disease among middle-aged and older men. It ranks second in terms of male mortality in all countries, since prostate cancer occurs in every eighth person. According to recent studies, it is known that over the course of 30 years, oncology of the genitourinary organs has increased even more, and prostate carcinoma has taken the third position among oncological diseases.
Prostate cancer in men symptoms, treatment
The prostate gland is located inside the genitourinary system. It is a muscular-glandular organ, similar in size to a walnut. Under the bladder (up to the anus and at the base of the penis), it, like a bracelet, covers the urinary system in the initial zone: the initial part of the urethra or the urethra, through which the body removes urine and sperm.
The prostate is responsible for producing seminal fluid and keeping it alive. Reproductive function depends on ejaculation, in which The prostate gland is directly involved. The prostate secretes a substance that is part of the sperm to keep the sperm active.
The internal pathological process in prostate cancer in the early stages goes unnoticed. Therefore, complaints in patients appear when a malignant tumor of the prostate gland grows to a large size and begins to metastasize. Patients cannot recognize the primary symptoms from the fact that a malignant tumor of the prostate grows in its capsule, and it is distant from the urethra.
In addition, prostate adenocarcinoma can hide behind manifestations of benign hyperplasia - an enlarged prostate that is adjacent to the urethra. Hyperplasia also affects urination, like cancer, by blocking the flow of urine, making it weak and provoking frequent urges.
Oncological disease goes beyond the capsule of the prostate and along the fibers of the nerves reaches the lymphatic channel, affecting the bones and metastasizing to the lymph nodes and distant organs.
Causes of prostate cancer
Science is not yet able to name the specific causes of prostate cancer in men. Doctors can only warn about cancer risk factors so far: age, heredity, smoking and unbalanced and poor-quality nutrition, poor ecology and living conditions. Cadmium affects the body when working on welding machines, with rubber and in a printing house.
If prostate cancer is suspected, the causes should be sought in concomitant diseases of the genitourinary system (prostate adenoma), in the appearance of secondary cancer due to metastasis, for example, to the liver. It is known that prostate cancer and alcohol are interrelated. Drinking men develop cirrhosis and liver cancer, which increases the risk of cancer of the pelvic organs.
Swedish research has now shown that dutasteride causes prostate cancer, just like finasteride, as published by the FDA (Federal Food and Drug Administration).
Important! These drugs are used to treat benign hyperplasia and alopecia. But, on the other hand, they increase the risk of developing an aggressive prostate tumor. A dosage of 1-5 mg is considered dangerous with long-term daily use of drugs. Men over the age of 50 may develop a particularly aggressive cancer.
Information! The American National Cancer Institute conducted clinical studies and found that the drug Avodart (Dutasteride) inhibits the development of pancreatic cancer in the early stages. Due to this, the aggressive therapy used is reduced, but side effects appear: the mammary glands increase and the sexual dysfunction of men increases.
It can be seen that the research information of Swedish and American scientists is somewhat different. The FDA recently announced that 5-alpha reductase inhibitors in the treatment of prostate cancer may be more likely to lead to high-grade prostate cancer. Urology scientists from North Carolina suggest that treatments will most likely be non-medical and non-invasive. The future lies with high-temperature therapy that eliminates the symptoms of prostate cancer.
Symptoms of prostate cancer in men
Signs of prostate cancer in men begin with uncomfortable urination: frequent urination, burning with incomplete emptying of the bladder. Signs of prostate cancer in men are similar to those in benign prostate enlargement (with adenoma). You should not count on this, but undergo a thorough examination so as not to miss the time for early treatment.
Symptoms of prostate cancer in men can be indicated by:
- difficulty starting to urinate;
- weak, pressureless jet, interrupted by urination;
- going to the toilet every half an hour, especially at night, which negatively affects the psyche;
- high temperature in prostate cancer;
- Sensation of pain in the genitals when urinating.
In the later stages, symptoms and signs indicate prostate cancer: urinary incontinence, erectile dysfunction, pain around the pubis, blood in the urine and semen (geospermia).
When the tumor grows and metastasizes, the symptoms of prostate cancer are indicated by:
- pain in the lumbar region and in the bones;
- lymphostasis - swelling of the legs;
- Lack of appetite, nausea and vomiting leading to weight loss.
Late symptoms include conditions associated with blood poisoning and vascular rupture.
Pathological changes in prostate cancer last slowly - 15-20 years. Cancer is prone to metastasis to the lymph nodes, pelvis, thighs, liver, spine, adrenal glands and other organs. If treatment is carried out before the appearance of metastases, it can be cured without causing serious consequences to the male body.
Diagnosis of prostate cancer
Diagnosis of prostate cancer in men is carried out depending on the symptoms and stages. Conduct rectal digital diagnosis of prostate cancer and examine the blood test for prostate-specific antigen or PSA. In the blood, a special substance is detected that is produced by the cells of the prostate gland. In other words, the PSA test for Prostate cancer is a cancer marker.
Finger method
Method of medical diagnostics
Diagnosis of prostate cancer using palpation is carried out as follows: through the rectum, the doctor probes the prostate tissue with a finger. At the same time, painful and uncomfortable sensations, deviations in the consistency of the secretions are revealed.
If there is a small tumor, it may not be palpable or be in a place inaccessible to the finger. Then a prostate specific antigen (PSA) is performed for prostate cancer. The PSA test is almost the only way to detect prostate cancer in the absence of symptoms, so PSA is of great importance in prostate cancer.
When PSA is done
Indications for PSA:
- presence of suspicion of a tumor after examination with a finger or ultrasound;
- active monitoring of the patient's condition after treatment in prostate cancer;
- Identification of the effectiveness of treatment.
PSA for prostate cancer is carried out every 3-4 months after radical antitumor treatment. Conduct preventive examinations for men after 40 years and reveal the dynamics of PSA levels after removal of prostate cancer.
General PSA values for all ages should normally be -0-4.0 ng / ml. If in men over 40 years of age PSA levels exceed 2.5 ng / ml, from 50 years old - 3.5 ng / ml, then this may be due to diseases such as prostatitis or benign prostatic hyperplasia (adenoma).
PSA temporarily increases during mechanical action on the prostate: prostate massage, biopsy, cystoscopy, as well as urinary retention, bladder catheterization.
Indicators of the tumor marker PSA in prostate cancer can increase up to 10 ng / ml. The growth rate of PSA in prostate cancer confirms the possible development of a tumor - 0.75 ng / ml or more per year.
The size of the prostate gland is taken into account before determining prostate cancer by PSA levels. It was previously thought that a larger gland had a higher PSA value. But this turned out to be a misconception. In practice, with a low PSA level, an oncological tumor can develop.
In the blood, the content of PSA is observed in bound and free form
Here is how prostate cancer manifests itself in men as a percentage of free PSA and serum levels:
According to research in Rotterdam (ERISRP, ERSPC) screening for prostate cancer stage and PSA level is as follows:
If the level of the dog in prostate cancer grade 3 is high and is more than 8.0 ng / ml, then the % chance of developing cancer is quite low - more than 30%. This discrepancy once again indicates a long process of pathomorphological changes and cancer cure before the appearance of metastases.
The norm of PSA after removal of prostate cancer should be in men:
- up to 40 years - 1.4-2.5 ng / ml;
- up to 50 years - 2.0-2.5 ng/ml;
- up to 60 years - 3.1-3.5 ng / ml;
- up to 70 years - 4.1-4.5 ng/ml;
- after 70 - 4.4 - 6.5 g/ml.
If the PSA values after prostate cancer surgery are below 2.5 + the norm of the finger test results, then the patient is considered healthy and the test is repeated in a year.If the PSA values are above 2.5 ng / ml + normal / pathological indicators of the prostate examination with a finger, a biopsy study is prescribed. If PSA values are 4-10 ng / ml, this is a sign of a disease or a physiological norm. For a year, the indicator should not exceed 0.75 ng / ml.
If the ratio decreases, prostate carcinoma is suspected. If the PSA reaches a value above 20 ng / ml, then a scintigraphy of the pelvic bones is performed if metastasis is suspected.
Also performed for suspected prostate cancer diagnostics:
- prostate ultrasound;
- CT at an early stage of cancer;
- research: X-ray and isotope;
- transrectal ultrasound: a special sensor is inserted into the rectum and the prostate tissue is examined on the screen, where it is easy to determine the oncocenter and diagnose cancer;
- According to biopsy results: the presence of pathology in the tissues indicates cancer.
Informative video
Prostate cancer stages. Classification of the disease according to the international TNM system
Staging of prostate cancer (Jew-Whitemore system):
- before the first - no symptoms, the cell develops in the prostate gland, the growth of the prostate begins;
- A - no symptoms, cells grow within the prostate;
- B - tumor in the prostate can be palpated during examination;
- C - the tumor invades the prostate gland, growing on the prostate membrane, the PSA level is increased;
- D - metastasis reaches regional lymph nodes and distant organs.
Prevalence of prostate cancer
According to the TNM classification system:
- T 0-4 - indicates the primary tumor, its condition and location;
- N X, 0, 1 - indicates regional lymph nodes;
- M X, 0, 1 - distant metastases.
Life expectancy in prostate cancer
When diagnosed with prostate cancer, the prognosis for survival depends on the stage of the disease:
Prostate cancer treatment
Prostate cancer treatment is standard:
- drug therapy;
- irradiation;
- methods of surgical intervention.
The prostate organ is removed as a treatment for prostate cancer, in exceptional cases, if there are no metastases in distant organs and lymph nodes. If the surgical methods of treating prostate cancer are carried out correctly, there are positive forecasts that there will be no detrimental consequences for the male body and there will be no recurrence.
The treatment of prostate cancer with medications includes hormonal drugs that reduce or completely block the level of testosterone in the blood in the early stages of the disease. But with complete blocking of testosterone levels, hormone therapy for prostate cancer does not completely cancel the pathological development of prostate tissues.
With radiation therapy - irradiation of the tumor, the pathological process in the tissues of the prostate is reduced and metastasis to other organs in the early stages is minimized.
If radiation therapy is given for prostate cancer, the consequences may be as follows:
- fatigue increases;
- there is a rare or frequent urge to urinate, accompanied by burning and tingling;
- may develop hemorrhoids, rectal irritation and bleeding;
- body temperature rises;
- impotence develops after 2 years of training;
- Loose stools, diarrhea, and bowel problems may occur.
To reduce the effects of irradiation and enhance the therapeutic effect, medication is added to it. Brachytherapy for prostate cancer is an alternative to radiation. At the same time, radioactive iodine granules are injected into the prostate, which do not adversely affect the tissues surrounding the tumor.
Prostate cancer symptoms and treatment
Chemotherapy for prostate cancer is used in advanced stages along with hormonal therapy. In the early stages, chemotherapy will not give a positive effect, since toxic and systemic treatment destroys cancer cells along with healthy cells. Chemistry acts on cells with an increased metabolism. It is known that a cancerous tumor grows slowly, and the rate of division of its cells is the same as in healthy ones. This means that there is no increased metabolism, which could be affected by cytostatics.
Chemotherapy is used if there are metastases in prostate cancer, also as an adjunct to hormone therapy.
An operation to remove prostate cancer is performed using different methods:
- transurethal resection (TUR);
- transurethral radiofrequency thermodestruction (TURT);
- laser operation;
- Laparoscopic surgery, including DaVinci mini-invasive robotics;
- radical retroglobulinal prostatectomy with lymphodenectomy;
- perineal prostatectomy.
Folk remedies for prostate cancer
It's important to know! Shiitake mushrooms, Maitake, reishi, cordyceps and birch chaga have anti-cancer properties. They renew the immune system and slow down tumor growth.
Shiitake with the help of lentinan polysaccharide Cordyceps tones up, prolongs life, like ginseng, and exhibits anti-cancer activity. Reishi activates the immune system and increases its antibacterial, antiviral and antifungal properties.
Meitake mushrooms are able to suppress the growth of oncocells, stimulate apoptosis (programmed death) of cells. Mushroom extract (D-fraction) with anticancer activity prevents the development of metastases. Maitake inhibits angiogenesis (vascular growth) by reducing the level of growth factor VEGF.
Prevention of prostate cancer
Prevention of prostate cancer lies in the timely conduct of urological screening:
- checking a blood test for prostate-specific antigen (PSA);
- perform a prostate examination with a finger method;
- examine the prostate transrectally on ultrasound.
If necessary, perform a multifocal prostate biopsy.
Nutrition changes with prostate cancer: fatty, spicy, fried foods are excluded, foods with carotenoids - fresh fruits and vegetables - increase in the diet. And also with phytoestrogens, similar in composition to natural female sex hormones to reduce the level of testosterone in the blood without losing the sexual power of men. This reduces the risk of developing prostate cancer.
The lifestyle is also changing: smoking, alcohol and drugs are excluded. Physical activity and tempering reduces the risk of prostate cancer.
Informative video
How useful was the article for you?
If you find a bug just highlight it and press Shift + Enter or click here. Thank you very much!
Thank you for your message. We will fix the bug soon



























