Home >
Erectile Dysfunction >
Prostate cancer survival
Prostate cancer survival
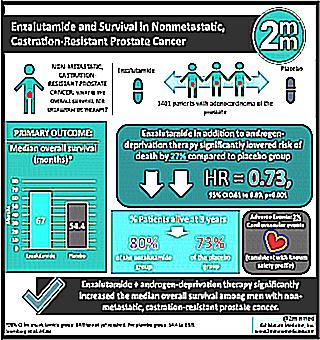
Prostate cancer: life expectancy at different stages of the disease
The prostate is a small gland in the male body, located between the bladder and the urethra. Rather small in size and having limited functions (mainly the production of a special secret for the formation of high-quality sperm), it causes great trouble to a huge number of men. Problems can start at an early age (25 years or even earlier), when young men discover that they have a disease such as prostatitis. This is inflammation of the prostate gland, which makes itself felt with frequent urination, heaviness in the lower abdomen, erection problems, insomnia, etc. Experts say that prostatitis has rejuvenated these days, i.e. it is increasingly being diagnosed in young men (before it was a disease rather 30-40-year-olds).
Causes of disease
There are several reasons: promiscuous sex life (infections), poor hygiene (also infections), a sedentary lifestyle (a typical office clerk who spends most of his working time in front of a computer), irregular sex life (lack of sperm output), etc. They treat prostatitis with antibacterial agents, prescribe prostate massage, and also recommend lifestyle changes (do more sports, do not catch colds, etc.).
The most serious disease of the prostate: cancer
Prostatitis, if left untreated, becomes chronic. But even more unpleasant and serious diseases that can develop in this part of the body are prostate adenoma (benign tumor) and Prostate cancer. prostate cancer is already ranked 3rd in some countries (after lung and stomach cancer), but in terms of mortality, it ranks 2nd (after lung cancer). The symptoms of this disease are similar to those of prostatitis: frequent urge to urinate, weak urine stream, erection problems, heaviness in the lower abdomen. However, in the stage of cancer, drops of blood appear in the urine, there are pains in the perineum, chronic impotence, pain in the bones, swelling of the lower extremities. There are 4 stages of a disease such as prostate cancer. Life expectancy in stage I cancer is more than 10 years for 90% of all patients. 100% of patients live with the disease for 5 years. But at this stage, the disease stops only in case of successful treatment. If the treatment is prescribed incorrectly, or the patient does not fulfill all the requirements of the doctor, progressive prostate cancer is observed. The life expectancy of a patient in case the cancer progresses to stage II will be more than 10 years for only 60-70% of patients. The remaining 30-40% of patients who receive this difficult diagnosis live less than 10 years. According to other data, 100% of patients live for at least another 5 years. Again, with unsuccessful treatment (or in its absence, if the patient did not turn to the doctor on time), or depending on other factors (for example, the individual characteristics of the body), the patient continues to develop prostate cancer. Life expectancy of 10 years or more remains only in 30-40% of all patients with stage III prostate cancer. Other sources speak of a 5-year survival rate of 50%. At this stage (and even at earlier ones), metastases are observed (the spread of cancer cells to other parts of the body). Prostate cancer is dangerous because metastases with it can develop almost asymptomatically, imperceptibly. In general, the earlier treatment is started, the more effective it will be, and the slower the cancer will develop.
Prostate cancer: stage 4 (last)
Unfortunately, despite all the efforts of doctors, the patient himself and his relatives, some patients are diagnosed with stage IV of this disease. This is the last, most dangerous and severe stage of the disease of a patient with prostate cancer. Life expectancy at this stage does not exceed 10 years in 85-90% of all patients. Of course, it all depends on the methods of treatment, on the mood of the patient himself, on following all the doctor's prescriptions, etc. However, it gives hope that medicine does not stand still, and more and more often you can hear the expression cancer is not a sentence, including and for prostate cancer. New treatments are being developed, and the life expectancy of patients with this type of cancer is increasing.
Methods of treatment
Therapy for prostate cancer includes hormone therapy, medical therapy, Surgical treatment, as well as chemotherapy (in the early stages of metastasis). Nowadays, cryotherapy is also used (treatment of affected areas by freezing). In 2009 Altai Regional Oncology Center examined data on treatment methods for 200 patients (middle-aged men) with prostate cancer. As a result of the study, conclusions were drawn that with localized forms of cancer, surgery increased life expectancy.In stages III-IV, the use of hormone therapy in combination with radiation therapy was more effective in increasing life expectancy.
How many people live with prostate cancer
Currently, the prognosis of survival for prostate cancer directly depends on how timely therapeutic measures are taken, how much the body fights the tumor process, and also on what stage the malignant tumor is at and how it can be treated.
Our readers recommend
Our regular reader got rid of PROSTATITIS by an effective method. He tested it on himself the result of 100% complete elimination of prostatitis. This is a natural remedy based on honey. We tested the method and decided to recommend it to you. The result is fast. EFFECTIVE METHOD.
Survival forecast
Depending on the stage of prostate cancer, you can predict life expectancy. It is important to carry out timely treatment that will help eliminate a dangerous complication.
At Stage 1
This stage in the development of the disease is usually very difficult to detect. This is due to the fact that the tumor usually does not spread beyond the prostate gland, at the reception the urologist cannot probe it. Ultrasound diagnostics also cannot determine the presence of neoplasms.
It is possible to detect a disease at this stage only with the help of regular preventive testing of blood fluid for antigens or tumor markers. If the concentration of the antigen in the blood fluid is exceeded, we can talk about a predisposition to oncological processes or that the first stage of the disease develops in the body.
With timely diagnosis of pathology at this stage of development, it is possible to increase life expectancy by more than 17 years. Usually death at this stage is not predicted. In the absence of metastases, the pathology is easily therapeutic.
Determining the percentage of survival from a malignant neoplasm at this stage is not easy, since it is problematic to make a correct diagnosis. This stage is characterized by the isolation of the pathological process and the location of pathogenic agents in different planes of the penis. Usually, the focus of localization is the surface of the gland; the pathological process has not yet penetrated into the organ itself. Survival at this stage is high. More than 95% of patients can live for 10 years after they are diagnosed.
At Stage 2
This degree of development of the disease is characterized by rapid progression in the body. Prostatic disease can already be diagnosed with the help of an ultrasound examination of the organ. With a timely examination and timely treatment, the oncologist predicts the exclusion of a lethal outcome over the next five years.
At this stage, the neoplasm increases in size so much that the doctor can already feel it, but at this stage there are still no metastases, the tumor is located within the tissues of the prostate gland. Usually during this period it occupies about 50% of the tissues of the organ. Surgery and treatment should be carried out as quickly as possible. Removal of the neoplasm and subsequent therapy will prevent the development of metastases, or another consequence of the disease.
In some cases, oncology involves expectant management for a patient who has any contraindication to radical or conservative treatment.
At this stage, the following options for eliminating the main ailment are offered:
- radical prostatectomy with excision of lymph nodes;
- irradiation;
- brachytherapy;
- complex irradiation;
- cryolysis.
A person should not die at this stage, despite his age. With prostatectomy, the survival rate is 99% for five years, 90% for 10 years, and 85% for 15 years. The brachytherapy procedure is an effective option for dealing with pathology. If the disease progresses slowly, the prognosis is 95% 10-year survival. If cancer cells spread quickly, these figures decrease to 80-85%.
In order to reduce the risk of a return of the disease with a radical removal of the organ, complex radiation therapy is prescribed in parallel by oncologists. The reliability of predictions of survival during cryodestruction has not yet been indicated. It is known that the absence of recurrence is observed in 80% of patients within 5 years.
At Stage 3
At this stage, in many cases, the prognosis is negative. The tumor spreads beyond the boundaries of the prostate capsule, passes to the seminiferous tubules. But metastases are still absent. The method of therapeutic action is directly determined by the results of diagnostic measures. During this period, treatment involves:
There is no expectant tactic. In the third stage, the five-year survival prognosis is about 50%.The main task of specialists is to slow down the spread of malignant processes in the body and alleviate pronounced symptoms. When choosing the tactics of therapy, doctors take into account all the indicators and individual characteristics of the patient's body.
In the final stages
4 and 5 degrees of development of the disease are characterized by an unfavorable outcome. During this period, growths quickly spread to other organs. In some cases, they can form in one day. Cancer agents are carried with the blood and lymph fluid. This causes damage to regional and central lymph nodes. Since in the pre-mortem period there is an intensive growth of metastases, the patient suffers from severe swelling. When metastases penetrate into bone tissues, this is manifested by severe painful sensations, cranial, femoral, vertebral, costal bones are affected.
What will be the life expectancy is directly affected by the selected treatment and the individual characteristics of the organism of each patient. If there are metastases in nearby or distant organs, the fight against the disease becomes much more difficult. When prostate cancer is diagnosed at stages 4 and 5, the prognosis is usually poor. And no matter which treatment option is chosen by the oncologist, it is impossible to completely get rid of the disease. And if the treatment is chosen incorrectly, the overall survival rate is no more than 30% within 5 years. There is no possibility of cure through any of the therapy options.
At these stages of the development of the disease, it is impossible to control the spread of metastases and cancer cells in the body. There is the formation of multiple new foci of pathological processes. The tissues of those organs that are located in close proximity to the prostate gland are affected - the bladder, rectum, urethral sphincter. The general condition of the patient deteriorates sharply. The task of doctors at these stages is to prolong the life of the patient. Therapy options are radiation and drug therapy, which are aimed at alleviating the patient's condition and maximizing life extension.
Prognosis depends on symptoms
The first two stages of development are characterized by tumor growth, there are no metastases. Growths appear already at the third stage. The person feels severe pain.
The fourth and fifth stages are characterized by the spread of metastases to other organs. With cancer with metastases, the duration and quality of life are reduced. If the pathological process quickly spreads through organs and systems, the patient's life expectancy can be no more than two years.
Risk factors affecting prognosis
The following factors can affect life expectancy:
- timeliness of therapy;
- age category of the sick person;
- presence or absence of growths;
- leading a right or wrong way of life;
- nutrition of the sick person;
- option of the selected therapeutic effect;
- individual characteristics of the organism;
- speed of spread of pathological processes;
- correct diagnosis.
How to improve your chances of survival
The prognosis of survival is determined by the stage of development of the pathology and the type of tumor detected. Of course, it is not possible to prevent the development of the pathological process. But it is important to undergo preventive examinations by a urologist after the age of 45 once a year. This way you can identify the pathology in the early stages of development and deal with it effectively.
With timely ultrasound examination and prostate screening, the slightest changes in the tissues of the organ can be determined. And the right treatment will help increase the chances of survival. It is also necessary to treat inflammation of the organs of the reproductive system in time, regardless of the nature. A man should not ignore the symptom of diseases, contact a urologist, andrologist, oncologist in time.
When prostate cancer is diagnosed, in order to reduce the proliferation and aggressiveness of cancer cells, doctors recommend eliminating foods that contain carcinogens and animal fats from the diet:
- fried foods;
- food cooked on an open fire;
- fast food;
- fatty foods;
- smoked meats;
- margarine.
To prevent the development of pathology in the future, doctors recommend systematically consuming foods that contain lycopene: tomatoes, grapefruits, apricots, papaya.
Who said that it is impossible to cure prostatitis?
Do you have PROSTATITIS? Have you already tried many remedies and nothing helped? These symptoms are familiar to you firsthand:
- constant pain in the lower abdomen, scrotum;
- difficulty urinating;
- sexual dysfunction.
The only way to operate?Wait, and don't act radically. Prostatitis is POSSIBLE to cure! Follow the link and find out how the Specialist recommends treating prostatitis.
Prostate cancer in men: prognosis
When a prostate tumor is diagnosed in men, the prognosis for survival depends on the type of cancer, the stage of tumor development, the state of health and the age of the patient. The survival rate for prostate cancer is higher if the tumor is detected at an early stage of development. The early stages of the development of a malignant neoplasm are local types of cancer - the tumor does not extend beyond the organ, there are no metastases. The disease responds well to treatment. When metastatic prostate cancer is diagnosed, the consequences are severe - the disease is less treatable, tumor metastases are found in the bones, liver, lungs, lymph nodes, the patient is weakened, often depressed.
The Yusupov hospital treats prostate cancer at all stages of development. The patient is examined by a urologist, an oncologist, and receives the help of a psychologist. In the hospital, a patient with malignant diseases of the prostate can be diagnosed using innovative medical equipment, receive all types of medical care, depending on the type of tumor, the stage of development of the neoplasm. In the rehabilitation center, patients undergo recovery under a special program for cancer patients.
Prostate cancer: symptoms and treatment, prognosis
The prostate gland is an organ consisting of several parts. The gland is in a capsule, parts of the gland are separated by elastic partitions. The prostate gland is involved in the production of seminal fluid, which serves as a nutrient medium for spermatozoa, is involved in the production of spermatozoa, is responsible for the quality of spermatic fluid, for the function of removing sperm to the outside, for erectile function, for urinary retention. Prostate cancer is a common disease that occupies one of the first places among malignant diseases. Due to the asymptomatic in the initial stages of development and the similarity of symptoms with the symptoms of prostate adenoma, prostate cancer is more often diagnosed at stages 3-4 of development, when pronounced symptoms of the disease appear, urination is disturbed, defecation is disturbed, erection, pain appears in the lumbar region, lower abdomen , bones.
Symptoms of local prostate cancer in the first stage are a slight enlargement of the prostate gland, occasionally there is discomfort during urination. At stage T1a and 1b, local tumors of the prostate are not palpable due to the small volume of the neoplasm, most often they are highly differentiated tumors. In some cases, well-differentiated cancer is determined (cancer cells are found in less than 5% of the tissues examined). If the PSA is within the normal range, dynamic observation of the patient is established. Local prostate cancer can be a latent form of cancer that never develops into clinical forms of the disease.
Prostate cancer is rarely detected at an early stage, the PSA test is considered the main method that helps to detect a malignant disease of the prostate at an early stage. Characteristics of a malignant tumor of the prostate by stages:
- Stage T1 - tumor can be felt on digital examination, often not detected on transrectal ultrasound.
- Stage T1a - in most cases, cancer is detected by histological examination after removal of prostate adenoma tissue. The study shows a small content of cancer cells - no more than 5%.
- Stage T1b - Cancer cells detected by histological examination after treatment of prostate adenoma. In contrast to stage T1a, there are more than 50% of cancer cells in the tissues of the prostate.
- Stage T1c - PSA test showed an elevated level, histological examination showed the presence of prostate cancer.
- Stage T2 - the tumor is felt during rectal examination, it is diagnosed using ultrasound, CT and other research methods. The tumor does not extend beyond the prostate.
- Stage T2a - at this stage, the cancer affects half or slightly less than half of the lobe of the prostate.
- Stage T2b - cancer affects more than half of the organ lobe.
- Stage T2c - cancer affects both lobes of the prostate.
- Stage T3 - the tumor extends beyond the organ, often affecting the seminal vesicles.
- Stage T3a - cancer extends beyond the organ, but does not affect the seminal vesicles.
- Stage T3b - malignant tumor affects the seminal vesicles.
- Stage T4 - the tumor extends beyond the prostate, affecting the muscles of the bladder, rectum, pelvic wall and other organs and tissues.
Treatment of cancer at stages T1c-T2c is carried out depending on the age of the patient. Surgical treatment is not indicated for men over 70 and older.Surgical treatment is not prescribed for elderly men with severe diseases associated with prostate cancer, in the presence of a highly differentiated tumor. In most cases, radical prostatectomy is prescribed for young men. At an older age, support for the patient is carried out with the help of radiation therapy and chemotherapy. With an increase in PSA levels after radical prostatectomy, adjuvant therapy is prescribed. An increase in PSA levels indicates the development of tumor recurrence or metastasis.
The third stage of prostate cancer is characterized by the appearance of a persistent violation of urination due to an enlargement of the prostate, located around the urethra. After radical surgery, adjuvant radiation therapy is prescribed for T3 with Gleason scores greater than 7 points, PSA levels greater than 10, if local tumor recurrence is proven. Radiation therapy is indicated for patients with local forms of prostate cancer at the first and second stages of the disease, in case of impossibility or unwillingness to perform surgical treatment, as well as for patients with stage T3 and the absence of tumor metastasis to regional and distant lymph nodes. For radiation therapy, the patient must have a long life expectancy. To increase efficiency, combined treatment is used: radiation therapy + hormonal therapy.
The use of adjuvant hormonal therapy is justified in patients with diploid tumors. For the treatment of T1-T2, brachytherapy is also used - irradiation of the prostate by introducing radioactive granules. For patients with stage T3, brachytherapy is performed in combination with external irradiation. If a prostate tumor is found in an aged man, in the presence of concomitant serious diseases, highly differentiated prostate cancer in the stage T1a, T1c, dynamic observation is justified. In the case of tumor progression, a decision is made on the methods of treatment, taking into account the age and health of the patient.
Prostate cancer grade 3: life expectancy
When Stage 3 prostate cancer is detected, the prognosis depends on the presence or absence of tumor metastasis, the prevalence of the process, and the aggressiveness of prostate cancer. The prognosis for the moderate severity of the disease is more difficult to set than for the early stages of cancer. The prognosis in the later stages is unfavorable, the fourth stage of the disease refers to the incurable stage of cancer. Stage 3 prostate cancer has a 40% survival rate five years after treatment.
Prostate cancer grade 1: life expectancy
Prostate cancer grade 1 life expectancy (within five years) after cancer treatment is 90%. Stage 1 prostate cancer responds well to treatment, but tumor detection rarely occurs in the first stage of development. In most cases, cancer is diagnosed during a histological examination of tissues after resection of prostate adenoma, as well as using a PSA test.
Prostate cancer: prognosis of survival
Prostate cancer is a serious disease that is asymptomatic in the early stages of development, aggressive prostate tumors develop rapidly, quickly leading to the death of the patient. The prognosis of survival in cancer is calculated on the basis of a five-year period, depending on the stage and aggressiveness of the tumor, the prognosis of a five-year survival of the patient is determined. The prognosis is based on the survival of a certain percentage of patients after the initial diagnosis. The survival prognosis did not include patients who had cancer recurrence within a five-year period.
Prognosis of survival has a measure of relative survival. The calculation of relative survival was carried out for patients who suffered from cancer of a certain localization, and death occurred from cancer-related diseases. Criteria such as cancer stage, tumor localization, age, gender, drug sensitivity, presence of concomitant diseases are important for predicting survival.
Prostate cancer grade 2: life expectancy
Prostate cancer grade 2 life expectancy within five years is 80%. The survival rate for stage 2 prostate cancer is high, the tumor responds well to treatment at this stage, the success of cancer treatment depends on the experience of the oncologist, the effectiveness of the prescribed treatment.
Prostate cancer prognosis: how many people live with prostate cancer
The life expectancy of patients with prostate cancer depends on many factors: the state of health of the patient, the stage of cancer, the psychological state of the patient, the effectiveness of treatment and many other components of the prognosis of survival. Some patients are cured completely in the early stages of cancer development, some patients experience relapses, cancer metastasizes - the survival prognosis worsens. With timely access to a doctor, life expectancy is 15 years or more.Unfavorable prognosis for grade 4 prostate cancer: life expectancy with constant palliative treatment is no more than 7 years. Prostate cancer of the 4th degree life expectancy for five years was observed in 15% of patients.
Hormone-dependent malignant tumor of the prostate: how long do they live
An increase in testosterone levels in a man's body can lead to the development of hormone-dependent prostate cancer. The survival prognosis for this form of cancer is poor. The tumor is characterized by rapid progress, with the appearance of metastases, the life expectancy for prostate cancer of this type is no more than 3-4 years. If prostate cancer is detected, the survival prognosis is made after a complete examination of the patient, diagnosis.
In the Yusupov hospital, a comprehensive diagnosis of prostate cancer is carried out. The type of malignant disease and the stage of tumor development are determined. Diagnosis of the disease is carried out using various research methods:
- PSA test. A blood test is performed for a tumor marker for prostate cancer. This analysis allows you to identify a malignant tumor at the first stage of development. An analysis is prescribed annually for men who have a hereditary predisposition to prostate cancer.
- The patient is examined by a urologist or oncologist. The doctor performs rectal palpation, determining the presence of education, its location, size.
- Transrectal ultrasound of the prostate is ordered.
- To determine the degree of tumor growth into neighboring tissues, the presence of metastases in regional or distant lymph nodes and organs, the doctor refers the patient to an MRI, CT or PET-CT examination.
- After the studies, a biopsy of the prostate tissue affected by the tumor is prescribed.
Depending on the indicators of research, age, health status of the patient, the oncologist prescribes treatment. The oncology department of the hospital uses innovative methods for the treatment of prostate cancer



























